Cellular Respiration Part III: Krebs Cycle
advertisement

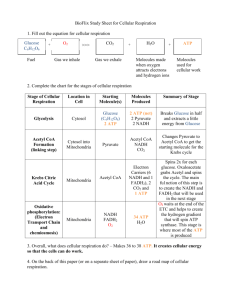
Cellular Respiration Part III: Krebs Cycle Figure 9.6-3 Electrons carried via NADH Glycolysis Glucose Pyruvate Electrons carried via NADH and FADH2 Citric acid cycle Pyruvate oxidation Acetyl CoA CYTOSOL Oxidative phosphorylation: electron transport and chemiosmosis MITOCHONDRION ATP ATP ATP Substrate-level phosphorylation Substrate-level phosphorylation Oxidative phosphorylation Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs Cycle) Curriculum Framework 3. In the Krebs cycle, carbon dioxide is released from organic intermediates, ATP is synthesized from ADP and inorganic phosphate via substrate level phosphorylation, and electrons are captured by coenzymes. 4. Electrons that are extracted in the series of Krebs cycle reactions are carried by NADH and FADH2 to the electron transport chain. 4 Figure 9.11 Pyruvate CO2 NAD CoA NADH + H Acetyl CoA CoA CoA Citric acid cycle 2 CO2 3 NAD FADH2 3 NADH FAD + 3 H ADP + P i ATP 6 Krebs Cycle • Occurs in the mitochondrial matrix • Releases the remaining carbons from the remnant glucose • Transfers the energy to NAD, FAD, and ADP 7 Coenzyme A Carbon dioxide Electron carrier (NADH) Carbon dioxide ATP Electron carrier (FADH2) Coenzyme A Electron carrier (NADH) Figure 9.12-1 Acetyl CoA CoA-SH 1 Oxaloacetate Citrate Citric acid cycle Figure 9.12-2 Acetyl CoA CoA-SH H2O 1 Oxaloacetate 2 Citrate Isocitrate Citric acid cycle Figure 9.12-3 Acetyl CoA CoA-SH H2O 1 Oxaloacetate 2 Citrate Isocitrate NAD Citric acid cycle 3 NADH + H CO2 -Ketoglutarate Figure 9.12-4 Acetyl CoA CoA-SH H2O 1 Oxaloacetate 2 Citrate Isocitrate NAD Citric acid cycle NADH 3 + H CO2 CoA-SH -Ketoglutarate 4 NAD NADH Succinyl CoA + H CO2 Figure 9.12-5 Acetyl CoA CoA-SH H2O 1 Oxaloacetate 2 Citrate Isocitrate NAD Citric acid cycle NADH 3 + H CO2 CoA-SH -Ketoglutarate 4 CoA-SH 5 NAD Succinate GTP GDP ADP ATP Pi Succinyl CoA NADH + H CO2 Figure 9.12-6 Acetyl CoA CoA-SH H2O 1 Oxaloacetate 2 Citrate Isocitrate NAD Citric acid cycle Fumarate NADH 3 + H CO2 CoA-SH -Ketoglutarate 4 6 CoA-SH 5 FADH2 NAD FAD Succinate GTP GDP ADP ATP Pi Succinyl CoA NADH + H CO2 Figure 9.12-7 Acetyl CoA CoA-SH H2O 1 Oxaloacetate 2 Malate Citrate Isocitrate NAD Citric acid cycle 7 H2O Fumarate NADH 3 + H CO2 CoA-SH -Ketoglutarate 4 6 CoA-SH 5 FADH2 NAD FAD Succinate GTP GDP ADP ATP Pi Succinyl CoA NADH + H CO2 Figure 9.12-8 Acetyl CoA CoA-SH NADH + H H2O 1 NAD 8 Oxaloacetate 2 Malate Citrate Isocitrate NAD Citric acid cycle 7 H2O Fumarate NADH 3 + H CO2 CoA-SH -Ketoglutarate 4 6 CoA-SH 5 FADH2 NAD FAD Succinate GTP GDP ADP ATP Pi Succinyl CoA NADH + H CO2 Figure 9.12a Acetyl CoA CoA-SH H 2O 1 Oxaloacetate 2 Citrate Isocitrate Figure 9.12b Isocitrate NAD NADH 3 + H CO2 CoA-SH -Ketoglutarate 4 NAD NADH Succinyl CoA + H CO2 Figure 9.12c Fumarate 6 CoA-SH 5 FADH2 FAD Succinate GTP GDP ADP ATP Pi Succinyl CoA Figure 9.12d NADH + H NAD 8 Oxaloacetate Malate H 2O 7 Fumarate Where does each atom end up? C6H12O6 27 So what did we get from Krebs? • Name the energy related end products of Krebs. • By what process is ATP formed? • Name the waste products. • Where do the events of Krebs occur? • Do cells in all kingdoms go through the Krebs cycle? • Where are the electrons headed? 28 So, What Did We Get From Krebs? 29 Figure 9.6-3 Electrons carried via NADH Glycolysis Glucose Pyruvate Electrons carried via NADH and FADH2 Citric acid cycle Pyruvate oxidation Acetyl CoA CYTOSOL Oxidative phosphorylation: electron transport and chemiosmosis MITOCHONDRION ATP ATP ATP Substrate-level phosphorylation Substrate-level phosphorylation Oxidative phosphorylation Curriculum Framework • f. Cellular respiration in eukaryotes involves a series of coordinated enzymecatalyzed reactions that harvest free energy from simple carbohydrates. 31