BUS312A/612A Financial Reporting I
advertisement

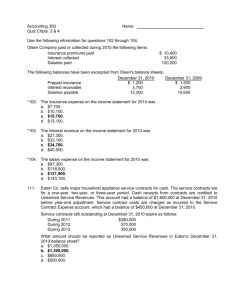
BUS312A/612A Financial Reporting I Homework 9.17.2014 & 9.22.2014 Statements of Income and Retained Earnings Chapter 4 E4-2 (Income Statement Items) Presented below are certain account balances of Viel Co. at December 31, 2014, the end of its first year of operations. Sales revenue Cost of goods sold Selling & Admin. Expenses Gain on sale of plant assets Unrealized gain on available-for-sale investments $310,000 140,000 50,000 30,000 Interest expense $ 6,000 Loss on discontinued operations 12,000 Allocation to noncontrolling interest 40,000 Dividends declared and paid 5,000 10,000 Compute the following: (a) income from operations, (b) net income, (c) net income attributable to Viel Company’s controlling shareholders, (d) comprehensive income, and (e) retained earnings balance at December 31, 2014. Alt. E4-3 (Income Statement Items) Presented below are certain account balances of Paczki Products Co. Rental revenue $ 6,500 Interest expense 12,700 Beginning retained earning 114,400 Ending retained earnings 134,000 Dividend revenue 71,000 Sales returns 12,400 Allocation to noncontrolling interest 17,000 Sales discounts Selling expenses Sales revenue Income tax expense Cost of goods sold Administrative expenses $ 7,800 99,400 390,000 31,000 184,400 82,500 From the foregoing, compute the following: (a) total net revenue, (b) net income, (c) dividends declared during the current year, and income attributable to controlling stockholders. E4-4 Single step Income Statement Fire destroyed L Jones Inc. financial records. Prepare an income statement for 2014 in singlestep form using the data the controller kept. 1. The beginning merchandise inventory was $92,000 and decreased 20% during the current year. 2. Sales discounts amount to $17,000. 3. 20,000 shares of common stock were outstanding the entire year. 4. Interest expense was $20,000 for the year. 5. The income tax rate is 30%. 6. Cost of goods sold amounts to $500,000. 7. Administrative expenses are 20% of cost of goods sold but only 8% of gross sales. 8. Four-fifths of the operating expenses relate to sales activities. P3-6 Adjusting Entries and Financial Statements Cash Accounts Receivable 49,600 Allowance for Bad Debts $ Inventory 1,960 Prepaid Insurance 1,100 Equipment 1. $29,500 750 3. 4. 25,000 Accumulated DepreciationEquipment 6,250 Notes Payable 7,200 Owner’s Capital 35,010 Service Revenue 100,000 Rent Expense Salaries and Wages Expense Utilities Expense Office Expense 2. 5. 6. 7. 9,750 30,500 1,080 8. 720 $149,210 $149,210 Fees received in advance from clients $6,000. Services performed for clients that were not recorded by December 31, $4,900. Bad debt expense for the year $1,430. Insurance expired during the year $480. Equipment is being depreciated at 10% per year. Perez gave bank a 90 day, 10% note for $7,200 on December 1, 2014. Rent of the building is $750 per month. The rent for 2014 has been paid, as has that for January 2015. Office salaries and wages earned but unpaid at December 31 , $2,510. 1. Fees received in advance from clients $6,000. 2. Services performed for clients that were not recorded by December 31, $4,900. 3. Bad debt expense for the year $1,430. 4. Insurance expired during the year $480. 5. Equipment is being depreciated at 10% per year. 6. Perez gave bank a 90 day, 10% note for $7,200 on December 1, 2014. 7. Rent of the building is $750 per month. The rent for 2014 has been paid, as has that for January 2015. 8. Office salaries and wages earned but unpaid at December 31 , $2,510. E4-5 (Multiple-step and Single-step) 2014 information for P. Bride Co. ($000 omitted). Administrative expense Officers’ salaries Depreciation of furniture and equipment Cost of goods sold Rental revenue Selling expense Delivery expense Sales commissions Depreciation of sales equipment Sales revenue Income tax expense Interest expense $ 4,900 3,960 60,570 17,230 2,690 7,980 6,480 96,500 9,070 1,860 a) b) Multiple-step income statement for 2014. Shares outstanding = 40,550 ($000 omitted). Single-step income statement for 2014. c) Which one is best? Discuss. Alt. E4-6 (Multiple-step and Extraordinary Items) The following balances were taken from the books of MCA Corp. on December 31, 2014. Interest revenue Cash Sales Accounts receivable Prepaid Insurance Sales returns and allowances Allowance for doubtful accounts Sales discounts Land Equipment Building Cost of goods sold $ 86,000 51,000 1,380,000 150,000 20,000 150,000 7,000 45,000 100,000 200,000 140,000 621,000 Accumulated depreciation-equipment Accumulated depreciation-building Notes receivable Selling expenses Accounts payable Bonds payable Administrative and general expenses Accrued liabilities Interest expense Notes payable Loss from earthquake damage (extraordinary item) Common stock Retained earnings $ 40,000 28,000 155,000 194,000 170,000 100,000 97,000 32,000 60,000 100,000 150,000 500,000 21,000 Assume the total effective tax rate on all items is 34%. Prepare a multiple-step income statement; 100,000 shares of common stock outstanding during the year. E4-14 (Change in Accounting Principle) Tim Mattke Company began operations in 2012 and for simplicity reasons, adopted weighted-average pricing for inventory. In 2014, in accordance with other companies in its industry, Mattke changed its inventory pricing to FIFO. The pretax income data is reported below. Year EBIT Weighted-Average EBIT FIFO 2012 $370,000 $395,000 2013 390,000 430,000 2014 410,000 450,000 Instructions (a) What is Mattke’s net income for 2014? Assume a 35% tax rate in all years. (b) Compute the cumulative effect of the change in accounting principle. (c) Show the comparative income statements for the company, beginning with income before income tax, as presented on the 2014 income statement. E4-15 (Comprehensive Income) Carter Corporation reported the following for 2014: net sales $1,200,000; cost of goods sold $750,000; selling and administrative expenses $320,000; unrealized holding gain on available-for sale securities $18,000. Prepare a statement of comprehensive income, using (a) the one statement format, and (b) the two statement format. Ignore income taxes and earnings per share). Alt. E4-16 (Comprehensive Income) Reither Co. reports the following for 2014: sales revenue $700,000; COGS $500,000; operating expenses $80,000; and an unrealized holding loss on available-for-sale securities of $60,000. It declared and paid a cash dividend of $10,000 in 2014. January 1, 2014 balances in common stock $350,000; accumulated other comprehensive income $80,000; retained earnings $90,000. No stock issued in 2014. Alt. CA4-6 (Classification of Income Statement Items) What section of the income statement or retained earnings statement should these items be classified? Explain. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. A merchandising company incorrectly overstated its ending inventory two years ago. Inventory for all other periods is correctly computed. An automobile dealer sells for $137,000 a rare 1930 S type Invicta which it purchased for $21,000 10 years ago. The Invicta is the only such display item the dealer owns. A drilling company extended the estimated useful life of drilling equipment from 9 to 15 years. As a result, depreciation for the current year was materially lowered. A retail outlet changed its computation for bad debt expense from 1% to .5% of sales because of changes in its customer clientele. A mining concern sells a foreign subsidiary engaged in uranium mining, although it (the seller) continues to engage in uranium mining in other countries. A steel company changes from the average-cost to FIFO inventory costing. A company, at great expense, prepared a major proposal for a government loan, which is not approved. A water pump manufacturer has had large losses resulting from a strike by its employees early in the year. Depreciation for a prior period was incorrectly understated by $950,000. The error was discovered in the current year. A sheep rancher suffered a major loss because the state required that all sheep be killed to halt the spread of a rare disease. Such a situation has not occurred in the state for 20 years. A food distributor that sells to supermarket chains and fast-food restaurants (two distinguishable classes of customers) decides to discontinue the division that sells to supermarkets. CA4-3 (Earnings Management) The controller for Kelly Corporation is preparing the company’s income statement at year-end. He notes that the company has lost a considerable sum on the sale of some equipment it had decided to replace. Since the company has sold equipment routinely in the past, he knows the losses cannot be reported as extraordinary. He does not want to highlight it as a material loss since he feels that will reflect poorly on him and the company. He reasons that if the company had recorded more depreciation during the assets’ lives, the losses would not be so great. Since depreciation is included among the company’s operating expenses, he wants to report the losses along with the company expenses, where he hopes it will not be noticed. Instructions (a) What are the ethical issues involved? (b) What should the controller do? Classification in the Balance Sheet Question The correct order to present current assets is a. Cash, accounts receivable, prepaid items, inventories. b. Cash, accounts receivable, inventories, prepaid items. c. Cash, inventories, accounts receivable, prepaid items. d. Cash, inventories, prepaid items, accounts receivable. Order of Liquidity Statement of Cash Flows Question In preparing a statement of cash flows, which of the following transactions would be considered an investing activity? a. Sale of equipment at book value b. Sale of merchandise on credit c. Declaration of a cash dividend d. Issuance of bonds payable at a discount receivable. IFRS SELF-TEST QUESTION Current assets under IFRS are listed generally: a. by importance. b. in the reverse order of their expected conversion to cash. c. by longevity. d. alphabetically. IFRS SELF-TEST QUESTION Companies that use IFRS: a. may report all their assets on the statement of financial position at fair value. b. are not allowed to net assets (assets 2 liabilities) on their statement of financial positions. c. may report noncurrent assets before current assets on the statement of financial position. d. do not have any guidelines as to what should be reported on the statement of financial position. IFRS SELF-TEST QUESTION A company has purchased a tract of land and expects to build a production plant on the land in approximately 5 years. During the 5 years before construction, the land will be idle. Under IFRS, the land should be reported as: a. land expense. b. property, plant, and equipment. c. an intangible asset. d. a long-term investment.