Cells, Tissues, Organs and Systems
advertisement

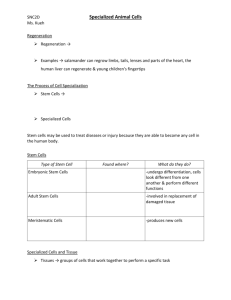
Cells, Tissues, Organs and Systems Homework Page 90 #1,3 Page 92 #2, 5,6,8 What Factors Influence Cell Specialization in Animals? Cell Specialization is the process by which cells develop from similar cells into cells that have specific functions within a multicellular organism Scientist estimate that there are between 75 and 100 trillion cells in the body of an adult Most of those cells are specialized to do certain tasks 3 main factors that influence cell differentiation in animal cells are; The contents of the cells cytoplasm 2. Environmental conditions, such as temperature 3. The influence of neighbouring cells 1. What Factors Influence Cell Specialization in Animals? The Effects of Cytoplasm on Cell Specialization Mitosis ensures that daughter cells receive identical sets of chromosomes, however the contents of the cytoplasm (number and type of organelles present) may differ in each daughter cell The Effects of Environmental Conditions on Cell Specialization Environmental conditions such as temperature or the presence or absence of nutrients can effect cell specialization Environmental factors also play a significant role when things go wrong in cell development (e.g. 90% of problems in developing embryos can be traced back to environmental factors such as a mother’s exposure to heavy metals The Effects of Neighbouring Cells on Cell Specialization When cells are close to one another, the substances produced by one cell can sometimes diffuse through a neighbouring cells membrane These substances can change how the information in the other cell is expressed (what genes are turned on and therefore what proteins are produced) Similar Cells for Similar Conditions As cell matures, more of its genes get turned on or off by the effects of the organelles present, the environment or neighbouring cells One combination of active and inactive genes will produce muscle cells while a different combination will produce nerve cells The genes that are active and inactive in the cell will determine what type of specialized cell will be formed At some point in a cells life, the cell will stop dividing (no longer undergo mitosis and cytokinesis) and live out their lives as a mature specialized cell Cells that experience similar conditions (e.g. Develop at the same temperature) will typically become specialized into the same type of cells and perform similar jobs in the body Groups of similarly specialized cells are referred to as tissues Types of Tissue Although their are millions of different organisms on earth, there are only a few different types of tissue Animals have 4 different types of tissue 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial tissue Muscle tissue Nervous tissue Connective tissue Recall that an organ is a combination of several types of tissue working together to perform a specific function (e.g. The heart is an organ that consists of several types of tissues working together to pump blood throughout our bodies) As part of an organ system, the activities of different organs are co- ordinated to work together to perform a specific function The Body’s Organization: A Hierarchy We can see that the body is organized into a hierarchal arrangement Organ systems are made up of various organs Organs are made up of different tissues Tissues are made up of similar types of specialized cells The human body contains 11 organ systems that keep you alive and healthy Circulatory System Digestive System Respiratory System Skeletal System Immune (Lymphatic) System Muscular System Endocrine System Nervous System Integumentary System Reproductive System Excretory (Urinary) System We will focus on 3 of these systems; the digestive system, the respiratory system and the circulatory system focusing on how they interact and why they are critical for survival Stem Cells Recall that plants have meristimatic cells that remain unspecialized and continue dividing throughout their life Animals have similar cells known as stem cells an unspecialized animal cell that can produce many different types of specialized cells As an animal grows to adulthood, stem cells continue to divide and produce more cells so the animal grows larger Mammals only have the ability to replace a small amount of tissue (e.g. Tissue needed for bone or skin repair) organs are formed in the embryo cannot produce new ones if they become damaged Stem Cells Early in development, human embryos (the product of a fertilized egg) contain Totipotent stem cells these stem cells can become any kind of cell in the body As the embryo develops, its stem cells become pluripotent stem cells these stem cells are less versatile as they care capable of producing many, but not all types of cells Late in development (after birth) humans contain only adult stem cells these stem cells can produce only specific kinds of cells (e.g. Only skin stem cells can produce cells to repair the skin) Fertilized egg Totipotent Stem Cells Pluripotent Stem Cells Adult Stem Cells Medical Potential and Ethics of Stem Cells Embryonic stem cells an unspecialized cell found in the embryo that can become any one of an organisms body cells Embryonic stem cells are totipotent cells that are able to keep dividing for up to a year without ever differentiating These cells are referred to as “start” or “source” cells because they can become any of the 300 different types of human tissues which makes them extremely valuable for research and medical treatments Scientists obtain stem cells from eggs fertilized in vitro (outside of the womb) the sources of stem cells are usually unused embryos from fertility clinics Controversy! Obtaining stem cells from these embryos will destroy the embryo so some people view the use of stem cells to be taking a human life Medical Imaging Technology Today physicians can use a variety of medical imaging technology (techniques used to form an image of a body’s internal cells, tissues and organs) to look inside the body There are 4 main types of medical imaging technologies used today 1. 2. 3. 4. X-ray CT or CAT scan (computerized axial tomography) Ultrasound (medical sonography) MRI scan (magnetic resonance imaging) A physicians decision on which technology to use is not always straightforward it depends on the balance between wanting an accurate diagnosis for reasonable cost with minimal pain and anxiety for the patient