DFC Webinar Handout - The Center for Health & Safety Culture
advertisement
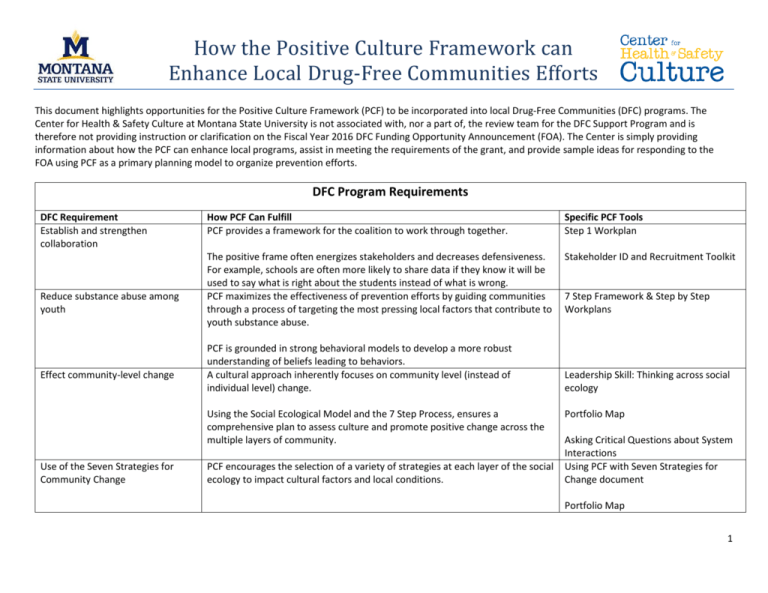
How the Positive Culture Framework can Enhance Local Drug-Free Communities Efforts This document highlights opportunities for the Positive Culture Framework (PCF) to be incorporated into local Drug-Free Communities (DFC) programs. The Center for Health & Safety Culture at Montana State University is not associated with, nor a part of, the review team for the DFC Support Program and is therefore not providing instruction or clarification on the Fiscal Year 2016 DFC Funding Opportunity Announcement (FOA). The Center is simply providing information about how the PCF can enhance local programs, assist in meeting the requirements of the grant, and provide sample ideas for responding to the FOA using PCF as a primary planning model to organize prevention efforts. DFC Program Requirements DFC Requirement Establish and strengthen collaboration Reduce substance abuse among youth Effect community-level change How PCF Can Fulfill PCF provides a framework for the coalition to work through together. Specific PCF Tools Step 1 Workplan The positive frame often energizes stakeholders and decreases defensiveness. For example, schools are often more likely to share data if they know it will be used to say what is right about the students instead of what is wrong. PCF maximizes the effectiveness of prevention efforts by guiding communities through a process of targeting the most pressing local factors that contribute to youth substance abuse. Stakeholder ID and Recruitment Toolkit PCF is grounded in strong behavioral models to develop a more robust understanding of beliefs leading to behaviors. A cultural approach inherently focuses on community level (instead of individual level) change. Using the Social Ecological Model and the 7 Step Process, ensures a comprehensive plan to assess culture and promote positive change across the multiple layers of community. Use of the Seven Strategies for Community Change PCF encourages the selection of a variety of strategies at each layer of the social ecology to impact cultural factors and local conditions. 7 Step Framework & Step by Step Workplans Leadership Skill: Thinking across social ecology Portfolio Map Asking Critical Questions about System Interactions Using PCF with Seven Strategies for Change document Portfolio Map 1 How the Positive Culture Framework can Enhance Local Drug-Free Communities Efforts Use of the SPF: Assessment Use of the SPF: Capacity Building Use of the SPF: Planning Use of the SPF: Implementation Use of the SPF: Evaluation Use of the SPF: Cultural Competence Use of the SPF: Sustainability 12 Sector Representation Assessment is a critical PCF step and focuses on developing a strong understanding of cultural factors that influence substance use. PCF builds capacity among the coalition as a whole to engage in a thoughtful, data-driven prevention planning process. Establishing common language and shared understanding among coalition members is critical for an effective coalition. PCF engages in planning efforts during several steps especially Step 1, Step 4, Step 5, and Step 7. PCF separates implementation into two parts – Step 5 Pilot Test and Refine and Step 6 Implementation. Pilot testing on a smaller scale first, leads to better final implementation of the strategy. PCF encourages evaluation throughout each of the 7 steps to ensure lasting change and transformation and to inform future needs. Developing cultural competence is critical. PCF is based on a cultural approach where prevention is viewed through a cultural lens. All steps involve developing a better understanding of the cultures within the community. By embedding improved health and safety in the local culture, efforts are much more likely to be sustained. PCF seeks to address sustainability at every step. A cultural approach requires engagement across the social ecology. Thus, participation by stakeholders representing the social ecology is critical. A cultural approach helps reveal how these stakeholders play an integral role in addressing youth substance use. Step 2 Workplan Assessments available across the social ecology 7 Step Framework & Step by Step Workplans 7 Step Workplans Sample PCF Timelines Pilot testing guidance and tools Tips and talking points to guide implementation Step 5 and 6 Workplans Tips for Engaging with Program/Community Evaluators Step 7 Workplan Inclusive Communities –Diversity Worksheet 7 Step Workplans Stakeholder Asset Development Worksheet Sample PCF Worksheets include: Inclusive Communities – Sector List Inclusive Communities –Diversity Worksheet How the Positive Culture Framework can Enhance Local Drug-Free Communities Efforts Cross-site Evaluation/Data Collection: 4 Core Measures: past 30- day use, perception of risk, perception of parental disapproval, and perception of peer disapproval Monitoring of alcohol, tobacco, marijuana, and prescription drugs in three grade levels (6th – 12th grade) every two years Cost sharing/financial match requirement Target multiple drugs of abuse (2+) Attend National Coalition Academy Because PCF takes a widespread and inclusive approach to assessment, repetitive and comprehensive data collection with the focus audience is essential. Various PCF tools exist to collect reliable data, including the 4 Core DFC Measures. Measures exist for all of the required substances, as well as many others. PCF helps coalitions identify a broad range of stakeholders, as well as, guides leaders through the assessment of stakeholder and community assets that may be useful to the coalition. Expanding implementation of strategies into new sectors and levels of the social ecology creates a broader pool of partners from whom resources may be leveraged. PCF acknowledges that many community concerns coexist and that some substance use problems may actually be contributing factors for other substance use problems. Additionally, many cultural factors impact the use of multiple substances. Because PCF attempts to create true, community-level transformation, it is necessary to be as comprehensive as possible, without stretching capacity and resources too thin. PCF Guide Service can support coalitions in achieving this balance. PCF provides step-by-step guidance in the development of products the National Coalition Academy requires coalitions develop. Stakeholder Start List Assessment across layers of social ecology including 4 Core Measures Stakeholder Asset Development Worksheet Step 2 and 3 Workplans Causal Factors Across the Social Ecology Worksheet 7 Step Workplans How the Positive Culture Framework can Enhance Local Drug-Free Communities Efforts The table below is intended to assist those responding to the Fiscal Year 2016 DFC FOA. It provides specific examples of how PCF can help applicants respond to the questions being asked in the Project Narrative section of the proposal. Proposal Organization: Project Narrative Project Narrative Section Coalition history and coalition member involvement: Discuss the coalition’s capacity to create community change concerning youth substance use Formation and history of the coalition Coalition’s organizational structure Sector member identification, selection, and role Cultural competency Coalition’s current and proposed role Statement of the problem: Discuss how the community youth substance use issues are How PCF Can Fulfill PCF helps coalitions build common language and a better understanding of the power of a cultural approach, which relies on the social ecological model. It focuses capacity-building efforts around three necessary skills to be successful in implementing a DFC grant or any prevention initiative: leadership, communication, and the integration of effective prevention strategies. A cultural approach requires engagement across the social ecology. When coalition members embrace a cultural approach, they better understand how they can contribute and the need for their involvement. PCF provides a process for assessing (Step 2) and prioritizing (Step 3) substance use problems and local conditions; assessment tools, Sample Ideas for Responding to this Section Be creative and write a brief story explaining how your coalition came to be. Include the vision/mission statement that drives your efforts. Include a visual depicting your coalition’s organizational structure and/or the different levels of involvement people have with the coalition. Use tables or other visuals to demonstrate who (which sector) has been and currently is represented or involved in the coalition. Describe the coalition’s current and potential “sphere of influence.” Discuss how you have created and trained (or will create and train) members on common language and/or Coalition Talking Points. Explain how shared hopes and concerns were identified, and discuss plans to continually reinforce what “brings people to the table.” Discuss how the coalition’s relationships and sector representatives allow for prevention efforts to be implemented across the social ecology to create community-level change. Specific PCF Tools Sample PCF Worksheets include: Inclusive Communities – Sector List Inclusive Communities –Diversity Worksheet Stakeholder Start List Stakeholder Asset Development Worksheet Discuss data measures within the context of the various levels of the social ecology. Use a logic model or similar visual to outline the consequences, primary substance use problems you will be addressing, and the PCF Step 2 and Step 3 Workplans Assessment tools across the social ecology which How the Positive Culture Framework can Enhance Local Drug-Free Communities Efforts impacting public health and public safety Youth substance use problems & effects Unique local conditions, absence of protective factors, associated consequences Related youth data Four Core Measures data Substances to be addressed & specific problems related to those substances data collection services, and technical assistance are also available. 12-Month Coalition Action Plan that will address youth substance use in the community Goal 1: Increase Community Collaboration Goal 2: Reduce Youth Substance Use Goal 1 Action Plan: PCF fosters collaboration by mobilizing all sectors, emphasizing the importance of working across the social ecology, and helping key partners understand and own their roles in creating a safe and healthy community. Engaging a broad group of stakeholders in the implementation of PCF builds capacity to engage in effective prevention and create community-wide transformation. A cultural approach seeks to move beyond just substance use at the individual level, but also acknowledges problems and opportunities across the social ecology (e.g., within enforcement, school policies, parent resources, etc.). underlying local conditions that contribute to each primary substance use problem. Use a table to clearly display data on the Four Core Measures. Explain how these problems were identified and how the coalition was involved in the process. Explain that local conditions will be revisited as new data become available and you move through the PCF and SPF step of assessment. Explain how a data workgroup or sub-committee of the coalition will be responsible for guiding the direction of future assessment, identifying and filling data gaps, and monitoring of indicators. In the introduction of this section (or included as an additional goal), consider explaining that PCF was utilized as a prevention planning framework, in combination with the SPF and the Seven Strategies for Community-level Change, to develop the 12-month Action Plan. Develop a table or dedicate a brief sub-section to explain the coalition’s actions taken preparing this application within each of the following steps: o Planning and Advocacy (e.g. created a shared sense of concern; developed a coalition resource, interests, and skills inventory; connected with unengaged members and/or recruited new members). o Assessment of Culture (e.g. became familiar with the wellresearched risk and protective factors for your particular substance use problem, developed a list of assessment questions, gathered existing data from within the community, identified existing strategies). include DFC Core Measures Prioritization tools for selecting indicators Sample PCF Worksheets: Data Guidelines: Seven Criteria for Baseline Data Matched Perception Questions Across the Social Ecology Interpreting Baseline Data Worksheet Causal Factors Across the Social Ecology PCF Step 1 – Step 7 Workplans Using PCF with the Seven Strategies for Change document Portfolio Map Sample PCF Worksheets: Developing Measurable Objectives Guidelines for Pilot Testing How the Positive Culture Framework can Enhance Local Drug-Free Communities Efforts Goal 2 Action Plan: PCF guides coalitions through an intentional, data-driven process to create a comprehensive and outcome-based plan to reduce youth substance use. o Establishment of Common Purpose & Prioritization (coalition Preparing for the consensus on overall goals, identified criteria and processes for Public Response prioritizing local conditions, implemented the prioritization process). o Development of a Portfolio of Strategies (developed a strategy selection committee; conducted literature reviews to identify strategies proven to be effective in addressing the prioritized local conditions; trained the strategy selection committee on evidence-based prevention, the Seven Strategies for Community-level Change, and Institutes of Medicine Model; updated the Portfolio Map and developed a comprehensive logic model). Goal 1: Increase Community Collaboration o In developing objectives, use assessment findings to identify sectors for which relationships could be strengthened, or to identify unengaged stakeholders who have the ability to impact change (especially relative to your prioritized local conditions). o Include strategies and/or activities for meeting with and discussing individual sector or stakeholder interests, level of readiness, barriers to doing prevention, vision for the future, etc. o By engaging these stakeholders in the planning process, identify appropriate, mutually agreed upon ways to meet their needs and include strategies or activities to do so. o Include strategies or activities to improve the satisfaction and meaningful involvement of currently engaged coalition members (e.g. develop coalition job descriptions, offer timelimited volunteer opportunities, provide training that’s of interest to members, co-present with members, etc.). o Address how new members will be brought on to the coalition (e.g. describe any new member orientation procedures or materials). How the Positive Culture Framework can Enhance Local Drug-Free Communities Efforts Evaluate effectiveness: Discuss how the coalition will assess the effectiveness of the 12- PCF encourages evaluation throughout each of the 7 steps to ensure lasting change and o Discuss how data can be used to build relationships (data use agreements can be a great first step to collaboration). o Address the various ways community members can be involved, even if they aren’t able to attend coalition meetings. o Discuss how you will seek alignment across and between systems. Goal 2: Reduce Youth Substance Use o Include more specific goals for each primary substance use problem. Make sure your goals are specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). o Use assessment findings to draft SMART objectives related to your priority local conditions. o For each priority local condition, include details for at least one or two strategies selected to address that local condition (some local conditions may require multiple strategies in order to create true transformation). o In selecting strategies and drafting activities, attempt to incorporate as many of the Seven Strategies for Communitylevel Change as appropriate. o Include activities around key fidelity components, essential best practices, and/or core program components of each strategy (these should have been researched prior to strategy selection). o Include activities related to building the necessary capacity, readiness, and sustainability, including securing resources (e.g. in-kind or matching contributions), relationship building, technical assistance, and training. o Within each strategy, detail activities around leadership, communication, and integration. Work with an evaluator to determine how you will measure progress specific to the strategies outlined in your Action Plan. Steps 5, 6, and 7 Workplans How the Positive Culture Framework can Enhance Local Drug-Free Communities Efforts Month Action Plan, disseminate findings, and engage the community in moving the plan forward Monitoring & evaluation processes Sector member roles & evaluation tools Processes for making improvements and enhancements Evaluation dissemination plans How evaluation findings will be used to engage the community transformation and to inform future needs. Successful implementation of the DFC Grant: Discuss how the coalition and/or community will determine successful implementation of this five-year grant Coalition/ community’s unique characteristics that strengthen the likelihood of successful implementation PCF offers many tools to ensure successful implementation. The 7 Step Process itself, however, may be the most important factor to success, as it guides coalitions through the necessary steps taken prior to implementation. PCF also offers training and a Guide Service to support coalitions in implementing the framework. PCF is unique in that it emphasizes the need to raise both hope and concern, which While PCF staff members do not serve as program evaluators, they do have expertise in data collection methods, and PCF offers many tools that are useful in monitoring the effectiveness of prevention efforts. In this section, discuss the roles and responsibilities of your evaluator, strategy partners, coalition leaders, data workgroup, and anyone else who will be involved in monitoring effectiveness. Include a master data collection plan that outlines the methods, timeline, who is responsible, and tools used to evaluate strategies and measure changes in the local conditions/objectives, goals, the 4 Core Measures, and potentially other measures such as consequence data. Discuss how both process and outcome measures will be tracked and utilized. Though pilot testing activities should be included in your 12-month Action Plan for each strategy, detail plans again in this section. Directly discuss how the implementation team, data workgroup, or coalition will analyze the results and decide on enhancements for moving forward. Be sure to include these efforts in the master data collection plan. Use the 7 Step Communication Process as a framework for developing an evaluation dissemination and community engagement plan. Discuss the shared values and strengths of your community. Include examples of how the community has come together and created transformation in the past. Discuss how key fidelity components, essential best practices, and/or core program components were determined and how they will be maintained throughout implementation. Explain how the Seven Strategies for Community-level Change were considered and written into your 12-month Action Plan. Discuss how the coalition has the necessary relationships and influence to work across the social ecology to create alignment across and between systems. Explain how coalition members and those implementing each strategy are prepared to respond to the public discussion after implementation begins. Evaluation Success Worksheet (tips for engaging with program/ community evaluators) Assessments across the social ecology 7 Step Communication Process Step 6 and Step 7 Workplans Stakeholder Influence/Interest Grid Preparing for the Public Response Worksheet How the Positive Culture Framework can Enhance Local Drug-Free Communities Efforts Key indicators, factors, leads to more mobilization and collaboration in the and/or practices implementation stage. important to successful implementation How the coalition will work with community systems, protocols, and procedures Necessary coalition key practices for successful implementation How the coalition will measure key successes Discuss the strengths of the coalition. Address why your coalition is highly functional. Elaborate on your organizational structure, how meeting agendas maximize members’ time, coalition materials that have been developed, procedures that have been established, how roles and responsibilities are well understood and members have taken active ownership, etc. Explain how coalition leaders will ensure all individuals responsible for implementation are adequately prepared prior to implementation, are carrying out the strategy as intended, and are supported throughout implementation. Include plans to hold an annual meeting to review the year’s successes and opportunities, ensure objectives are being met, and review your community’s Strategy Portfolio. To learn more about the Positive Culture Framework, visit www.CHSCulture.org or email mail@CHSCulture.org.