THE B.U.R.P.S LIST - Johns Hopkins University School of Nursing
advertisement

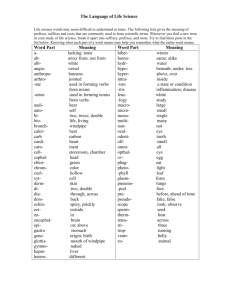
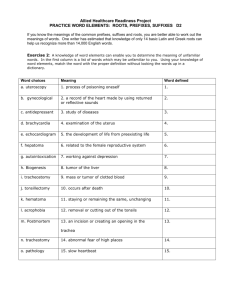
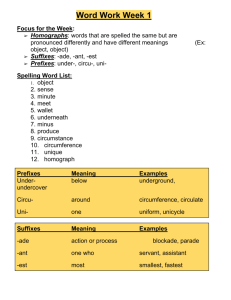
1 April 11, 2011 Welcome to the School of Nursing at the Johns Hopkins University! As a faculty who coordinates one of your first semester courses I am making available to you some helpful and useful information. I have included it below for your reading pleasure! There are two documents: the “B.U.R.P.S.” list (Building and Understanding Roots, Prefixes and Suffixes) and “Talk like a Nurse” handout. These documents list many of the medical terms used in your first semester classes and I believe will ease your transition into a new way of speaking. I look forward to seeing you soon! Kate Lears, Course Coordinator THE B.U.R.P.S LIST Purpose: To become proficient in Building and Understanding Roots, Prefixes and Suffixes Rationale: Building and understanding medical terminology is simpler when the words are broken down into roots, prefixes and suffixes. Steps: Review the B.U.R.P.S. tables and try to determine the definitions of the examples Notice the overlap among the three groups of roots, prefixes and suffixes Make new words by changing one part of the word. For example, if an appendectomy is the removal of the appendix, then a nephrectomy is the removal of a kidney. Tachycardia is a fast heart rate and tachypnea is a fast respiration rate. Log onto http://ec.hku.hk for other interactive exercises in medical terminology Helpful Note: R/T means “related to” TALK LIKE A NURSE Purpose: To become familiar with acronyms commonly used by health care providers Rationale: Different professions have unique languages; medicine and nursing are no exceptions. The acronyms below are used in verbal and written communication in health care settings. Steps: Review the attached list of acronyms (then you can start to critique shows like “House” and “Gray’s Anatomy” for accuracy!) Notice that some acronyms have two different meanings; e.g., ROM stands for “range of motion” and “rupture of membranes” - be careful when using abbreviations Go to www.pharma-lexicon.com and check out the search engines for other acronyms and medical terminology NOTE: All institutions have a list of accepted and “do not use” abbreviations. Always check with the institution before using an abbreviation. 2 THE B.U.R.P.S LIST I. Roots R/T Body Parts Root Angi(o), Vas(o) Brachi(o) Bucc(o) Cardi(o) Carp(o) Cephal(o) Colp(o) Crani(o) Cyst(o) Cyto Dactyl(o) Encephal(o) Enter(o) Gloss(o) Hemo, sanguin(o) Hyster(o) Mast(o), mamm(o) Men(o) Nephr(o), Ren(o) Oophor(o) Ophthalm, Ocul(o) Ot(o), Auri, Aud Phleb(o), Ven(o) Pod Rhin(o) Salping(o) Thorac(o) Thromb(o) Meaning Blood vessel Arm Cheek Heart Wrist Head Vagina Skull Bladder Cell Finger, toe Brain Intestine Tongue Blood Womb, uterus Breast Month, r/t menses Kidney Ovary Eye Ear Vein Foot Nose Fallopian tube Chest Clot Other Roots Root Gluc(o) Hydr(o) Lact(o) Lip(o), adip(o) Therm Meaning Sweet, sugar Water Milk Fat Heat Example(s) Angioplasty, vasoconstriction Brachial Buccal Cardiopathy Carpal tunnel syndrome Cephalic Colposcopy Craniotomy Cystoscopy, cystitis Cytology, cytomegaly Polydactyly Encephalitis Enteritis Glossitis, glossopharyngeal Hemolytic, serosanguinous Hysterectomy Mastitis, mammography Menopause, menarche, dysmenorrheal Nephrectomy, renal Oopherectomy Ophthalmoscope, ocular Otitis, auricle, audiometer Phlebitis, venous Podiatrist Rhinoplasty, rhinorrhea Salpingectomy, salpingitis Thoracotomy, thoracic Thrombosis, thrombolytic Example(s) Glucose, glucometer Hydrocephalus, hydrophobia Lactosuria, lactating Lipoma, adipose Hyperthermia II. Prefixes R/T Colors Prefix Erythr(o) Leuk(o), leuc(o) Cyan(o) Melan(o) Cirrh(o) Meaning Red White Blue Black Yellow Example(s) Erythema, erythrocyte Leukocytes, leukemia Cyanosis Melanin Cirrhosis 3 R/T Descriptions Prefix Ankyl(o) Sten(o), Stric Ortho Kypho Pseudo R/T Measurements Prefix Macro Micro Poly, Hyper, Multi Brady Tachy Oligo, Hypo Iso Diplo, Ambi Hemi Pan R/T Positions Prefix Pro, Ante, Pre Post Super, supra Sub Dors(o) Retro Para Re Later(o) Medi(o) Schizo Inter Heter(o) Hom(o) Ad(o) Ab(o) Anti, Contra Endo, In, Intra Ex(o), Ec(to) Epi Dia, Trans Peri, Circum Sinister(a) Dextr(o) Meaning Stiff, fixed, crooked Narrow Straight position Bent, crooked False Meaning Large Small Many, much Slow Fast Few Equal Both, double Half All Meaning Before After Above Below Back Backwards Beside Again Side Middle Split Between Different Same Towards Away from Against In, within, inside Out Upon, above Through Around Left Right Example(s) Ankylosis Stenosis, stricture Orthopnea, orthopedic Kyphoscoliosis, kyphosis Pseudostrabismus, pseudoaneurysm Example(s) Macrophage, macrocephaly Microscopic, microorganism Polydypsia, hyperthyroidism, multiple Bradypnea Tachycardia Oliguria, hypothermia Isometric, isotonic Diplopia, ambidextrous Hemiplegia, hemisphere Pansystolic, pancytopenia Example(s) Prodromal, antepartum, precapillary Postnatal, posterior Superior, supraclavicular Submandibular, subcutaneous Dorsoflexion, dorsal Retrograde, retrosternal Paramedic, paranasal Rehydrate, recuperate Lateral Medial, mediastinum Schizophrenia Intercostals, interdigital Heterogeneous Homozygous Adduction, adhesion, adrenal Abduction, abnormal Antigen, contraception Endocarditis, inhale, intrapartum Exhale, ectopic Epidermis, epigastric, epiglottis Diameter, transfusion Perinatal, circumcision OS (oculus sinister – left eye) OD (oculus dexter – right eye) 4 R/T the Body Prefix Aden(o) Arthr(o) Cervic(o) Costo Cyto Derm Gastr(o) Glosso Heme Hepat(o) Lingu Litho My Myo, myel Neuro Oto Opti, Ocu Osteo Pneum(o), Pulm Psycho Rhino Thor(a) Vasc Other Prefixes Prefix A(n) Auto Dys Gravida Neo III. Suffixes R/T Surgery Suffix Centesis Ectomy Lysis Ostomy Otomy Plasty R/T Diseases Suffix Algia Cele Emia Gen Itis Meaning Gland Joint Neck Rib Cell Skin Stomach Tongue Blood Liver Tongue Stone Muscle Marrow Nerve Ear Eye Bone Lung Mind Nose Chest Vessel Example(s) Adenoma, adenoids Arthritis, arthroscopy Cervical, cervicitis Costochondritis, costovertebral Cytology, cytomegaly Dermatitis, dermatological Gastritis, gastrointestinal Glossopharyngeal, glossitis Hematuria, hematemesis, hemangioma Hepatitis, hepatocellular Lingual, linguistic Lithotomy, lithotripsy Myoma, myalgia Myelitis Neuromyalgia Otitis, otolaryngology Optician, ocular Osteoarthritis, osteopenia Pneumothorax, pulmonary Psychology, psychopath, psychosomatic Rhinorrhea, rhinitis Thoracic, thoracentesis Vasculitis Meaning Without Self Difficult, painful Pregnant, heavy New Meaning Tap, puncture Removal Separate, destroy Form an opening Cut into Repair Meaning Pain Hernia, swelling Blood Producing Inflammation Example(s) Anemia, avascular Autoimmune Dyspnea, dysuria Gravidity Neonatal, neoplasm Example(s) Thoracentesis Mastectomy, appendectomy Hemolysis Colostomy Tracheotomy, craniotomy Rhinoplasty Example(s) Arthralgia, myalgia Hydrocele, cystocele Leukemia, anemia Carcinogen, allergen Appendicitis, hepatitis 5 Megaly Oid Oma Osis Pathy Penia Phagia Phasia Plegia Phobia Pnea Rrhage Rrhea Sclerosis Spasm Troph(o) Uri(a) Enlargement Resemble Tumor Abnormal condition Disease Deficiency Eating Speech Paralysis Fear Air, breathing Burst forth Flow, discharge Hardening Contraction Nourishment Urine Other Suffixes Suffix Gram Ology Phon(o) Scope Splenomegaly, hepatomegaly Fibroid, keloid Adenoma, myoma Dermatosis Neuropathy, psychopathology Cytopenia, thrombocytopenia Dysphagia Aphasia, dysphasia Paraplegia, quadriplegia Acrophobia, agoraphobia Apnea, dyspnea, orthopnea Hemorrhage Diarrhea Atherosclerosis Bronchospasm Atrophy, hypertrophy Nocturia, dysuria Meaning Example(s) Picture, record Study of Sound Inspect Electrocardiogram Pathology, dermatology Egophony, bronchophony Microscope, laproscopic TALK LIKE A NURSE A-P anterior-posterior BUN blood urea nitrogen ASA acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) BX biopsy A&W alive & well c with (cum) bid 2x/day (bis in dies) CA cancer BKA below-the-knee amputation (AKA-above) CABG coronary artery bypass graft BM bowel movement CAD coronary artery disease BMI body mass index CAGE cut down, annoyed, guilty, eye opener BMR basal metabolic rate CAM complementary alternative medicine BPH benign prostatic hypertrophy CBC complete blood count BR bed rest CBE clinical breast exam BRP bathroom privileges CC chief complaint BS bowel sounds cc cubic centimeter BSE breast self-examination CHF congestive heart failure BSO bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy cm centimeter 6 CN cranial nerve ETOH ethanol (alcohol) CNS central nervous system FB foreign body C/O complains of FBS fasting blood sugar Copd chronic obstructive Pulmonary Disease FUO fever of unknown origin C&S culture & sensitivity FX fracture Csf cerebrospinal fluid GERD gastroesophageal reflux disease Ct computed(computerized) tomography GI gastrointestinal Cta clear to auscultation GU genitourinary Cts carpal tunnel syndrome H&P history and physical Cva cerebrovascular accident (stroke) HA headache Cxr chest x-ray HBP high blood pressure D/C Discharge, Discontinue Hct hematocrit D & C dilatation and curettage HEENT head, eyes, ears, nose, throat DFA difficulty falling asleep hgb hemoglobin DJD degenerative joint disease Hib hemophilus influenza B DM diabetes mellitus h/o history of (or Hx) DNR do not resuscitate HOB head of bed DOA dead on arrival HPI history of present illness DOB date of birth HRT hormone replacement therapy DOE dyspnea on exertion hs hour of sleep, bedtime DPT diphtheria-pertussis-tetanus (vaccine) HTN hypertension DSM diagnostic & statistical manual I&D incision and drainage DTR deep tendon reflexes IM intramuscular DVT deep vein thrombosis I&O intake and output Dx diagnosis IV intravenous ECG electrocardiogram (or EKG) IVP intravenous pyelogram ED emergency department EEG electroencephalogram-gram JCAHO Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations EMA early morning awakening JVD jugular venous distention ENT ears, nose, and throat KUB kidney, ureter and bladder (x-ray) EOM extraocular muscles or movement KVO keep vein open ERT estrogen replacement therapy LE lower extremities ESR erythrocyte sedimentation rate LFTs liver function tests last menstrual period end-stage renal disease LMP ESRD LNMP last normal menstrual period 7 LOC loss or level of consciousness PND paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea or post nasal drip LP lumbar puncture PNS peripheral nervous system MI myocardial infarction (heart attack) PPD purified protein derivative (TB skin test) MMR measles, mumps, and rubella (vaccine) pr per rectum MMSE mini mental state exam PRN as needed (pro re nata) MRI magnetic resonance imaging MS mental status or multiple sclerosis PROM passive range of motion or premature rupture of membranes NAD no acute or apparent distress PSA prostate specific antigen (test) NGT nasogastric tube PT physical therapy NKA no known allergies PTA prior to admission NKDA no known drug allergies PUD peptic ulcer disease NPO nothing by mouth (non peros) PVD peripheral vascular disease NSAID nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug q4h every 4 hours NSR normal sinus rhythm q6h every 6 hours NSS normal saline solution qam every morning NV nausea/vomiting qd every day** NVD nausea, vomiting, diarrhea qh every hour NWB non-weight bearing qhs every night OA osteoarthritis qid 4x/day OC oral contraceptives qod every other day** od right eye (ocular dexter) RA rheumatoid arthritis or right atrium OOB out of bed RBC red blood cell os left eye (ocular sinister) REM rapid eye movements OT occupational therapy RLQ right lower quadrant OTC over-the-counter R/O rule out ou both eyes ROM range of motion or rupture of membranes p after ROS review of systems p.c. after meals RRR regular rate & rhythm PCN penicillin R/T related to PE physical examination or pulmonary embolism s without (sans) PERRLA pupils equal, round, reactive to light and accommodation SBE subacute bacterial endocarditis SC subcutaneous PID pelvic inflammatory disease Sig label PMH past medical history SL sublingual PMI point of maximal impulse (apical pulse) SOB shortness of breath S/P status post (after) (RUQ, LLQ, LUQ) 8 sp.gr. specific gravity UE upper extremities S.Q. subcutaneous(ly) URI upper respiratory infection S/S signs and symptoms UTI urinary tract infection STAT immediately VS vital signs STS serological test for syphilis VSS vital signs stable Sx symptoms WBC white blood cell TCDB turn, cough, deep breathe WD/WN well developed, well nourished TIA transient ischemial attack (mini stroke) WF/BF tid 3x/day TM tympanic membrane TMJ temporomand-ibular joint TNTC too numerous to count TPN total parenteral nutrition TURP transurethral resection of prostate TSE testicular self- examination UA urinalysis white female/black female WM/BM white male/black male WNL y/o within normal limits years old change ** appear on the JCAHO “Do Not Use” list – should write out “daily” or “every other day” Caution against using: < or >