Digestion: Other Animals
advertisement

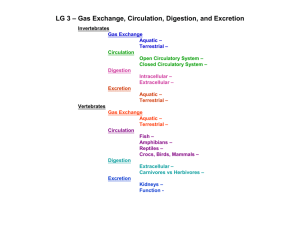
CP p.86-89 Unicellular No Digestive system Intracellular digestion Example: Amoeba Pseudopods engulf food Food vacuole formed Lysosome fuses with vacuole Hydrolytic enzymes released into food vacuole to digest food Nutrients absorbed into cytoplasm Bag system Extracellular digestion, followed by intracellular digestion Example: Hydra, Jellyfish Tentacles bring prey to mouth Prey is stuffed into gastrovascular cavity Different types of cells line gastrovascular cavity: ◦ Some cells release digestive enzymes to breakdown food (extracellular digestion) ◦ Other cells with flagella keep contents of cavity moving ◦ Still other cells engulf food particles for intracellular digestion Lining cells can absorb nutrients Nutrients diffuse to outer layer of cells Waste is expelled through the mouth Tube system ◦ Digestive tract allows the separation of processed (ingestion, digestion, absorption, and egestion) into different regions ◦ Extracellular digestion ◦ Example: Earthworm, Bird, Cow Muscular pharynx sucks food and soil into mouth Muscles in wall of esophagus push food to crop Crop stores and moistens food Food is broken down by small particles of sand and gravel in the muscular gizzard (physical digestion) Food is broken down chemically and absorbed in the intestine (chemical digestion) Waste is eliminated through the anus Esophagus carries food to crop Crop stores food Small pebbles in muscular gizzard grinds food Stomach begins chemical digestion Intestine absorbs food Waste removed through anus abomasum omasum Stomach has four chambers to help digest cellulose Food travels first to rumen then to reticulum of stomach where bacteria start to help break down cellulose Cow regurgitates and re-chews food to help soften and break down plant fibres Food then travels to last two chambers of stomach and onto the intestine Waste removed through anus