Teaching and learning outcomes
advertisement

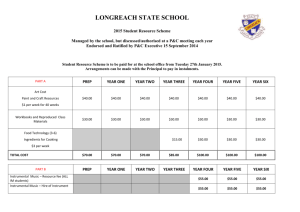
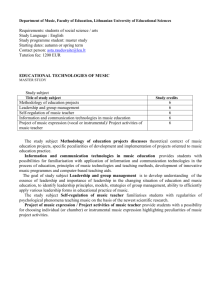
2012/2013 Programme Specification Data Programme Name Programme Number Programme Award QAA Subject Benchmark Statements Pharmaceutical Analysis Programme Aims Programme Learning Outcomes: Knowledge and Understanding MSc Chemistry The aim of this programme is to furnish students with the advanced technical skills and knowledge base that is required in the field of instrumental analysis and which will enable them to pursue careers as analysts in the chemical and/or pharmaceutical industry. More specifically the programme aims to: • extend and deepen the student’s comprehension of key concepts in instrumental analysis and to provide them with an in-depth understanding of the specialised aspects of the subject area. • provide students with the ability to plan and carry out experiments using instrumental techniques independently; to interpret the data; assess the quality of the data and to assess the significance of the outcomes. • develop in the students the skill-set necessary to adapt and apply methodologies to the solution of unfamiliar problems. prepare students effectively for professional employment or further studies at a doctoral level. A Knowledge and understanding of: 1. To develop an in-depth knowledge and critical awareness of the application of modern methods of instrumental analysis that will prepare the student for contemporary professional practice. 2. To extend and deepen the student’s knowledge of and capability in using a range of instruments and instrumental techniques that are of contemporary importance in the chemical and pharmaceutical sciences and, through a programme of practical engagement, provide them with the opportunity to advance their 3. 4. 5. 6. Programme Learning Outcomes: Intellectual Skills practical skills in the use of these instruments in unfamiliar environments Research training. The programme will extend and deepen project specific skills acquired at undergraduate level. These skills include advanced training in the use of literature search engines; the self-directed planning of research and evaluation of hazards and environmental impacts; the oral presentation of key concepts to an expert audience and the writing of reports (including critical evaluation). Advanced studies in instrumental methods of analysis. To extend and deepen the student’s grasp of the advanced concepts underpinning the subject matter and prepare the student to be capable of effectively engaging with the literature of instrumental methods of analysis. Problem solving. The programme will provide the student with structured opportunities to develop strategies including the application of advanced studies to the solution of problems in new or unfamiliar contexts. Professional studies. The programme will inculcate the ethical and social responsibilities of the professional analyst which includes professional adherence to honesty and the keeping of reliable accounts of laboratory work. B Intellectual skills: The student will: 1. Further develop and extend their ability to integrate theory and practice to solve complex problems of a familiar and unfamiliar nature, within multi-disciplinary contexts; 2. Further develop their ability to synthesise key conceptual and factual information and data from a variety of sources in a way that provides evidence of advanced understanding of key concepts; 3. Demonstrate the skills necessary to plan, conduct and report on a piece of original research in an independent and self-directed fashion; 4. Develop the necessary learning skills that permits them to identify learning needs and to undertake study that is autonomous and self-directed; 5. Further develop and extend their personal professional skills. These skills include recognition of their professional duty to comply with codes of good practice in data collection and processing; understand the moral and ethical issues associated with laboratory and field investigations and the need to adhere to strict ethical standards and professional codes of conduct. Programme Learning Outcomes: Subject Practical Skills C Subject Practical skills: 1. Extend and deepen their practical skills so as to be capable of solving practical problems associated with the design and maintenance of analytical protocols within a professional or workplace context 2. Demonstrate the required level of professional competence in the planning, conduct, evaluation and reporting of the results of investigations, including the appropriate use of literature and secondary data. 3. Extend the ability to correctly identify and synthesise advanced concepts that inform the application of appropriate practical techniques to the solution of problems encountered during the project; and to use and develop these advanced theories and concepts to provide the scientific basis for understanding and explaining the science underpinning their practical data and the outcomes of the project. 4. Demonstrate a professional understanding of the need for and regulations encompasses within good laboratory practice. Demonstrate (i) the ability to work safely and responsibly in a laboratory/workplace, including the ability to prepare and use risk and COSHH assessments; (ii) the ability to undertake laboratory investigations in a responsible, safe and ethical manner; and (iii) an awareness of Health&Safety issues and legal responsibilities. Programme Learning Outcomes: Transferable/Key Skills D Transferable/ key skills: The student will: 1. Further develop and extend their written and verbal communication skills so as to permit effective communication and interaction with professionals from other disciplines; 2. Extend and deepen their range of generic skills that they developed at an undergraduate level including the use of IT, presentation skills and their development as selfdirected autonomous learners; 3. Demonstrate an advanced understanding of issues associated with sample selection, accuracy, precision and uncertainty in the collection and analysis of data; 4. Demonstrate the ability to make decisions in complex and unpredictable situations; and to demonstrate an understanding of the dangers of decision-making based on incomplete information; 5. Demonstrate problem solving skills including the demonstration of self direction and originality; 6. Demonstrate a range of professional level personal skills including the ability to work both independently and as part of a team; the ability to plan projects and use time management skills; the ability to exercise initiative and personal responsibility; and recognise the moral and ethical issues associated with their professional practice; 7. Demonstrate an autonomous and reflective approach to lifelong learning; and demonstrate both self-direction and originality. Programme Learning Outcomes: Graduate Attributes Teaching and Learning Methods None A Teaching and learning: Seven taught courses of lectures and tutorials are taken that are designed to communicate advanced knowledge in specific aspects of modern instrumental analysis. The taught courses are relevant to the student’s particular needs, which are appropriate to the outcomes specified in the course outlines. In the research project, which will involve working up to three days a week in the laboratory, full-time students will undertake all the necessary practical work to develop and validate an analytical technique and extend the critical range of computer competencies – acquired at undergraduate level - that are necessary to assess their results and data. B Teaching and learning Intellectual skills are developed through practical/project work, tutorial/seminar work and coursework assignments. Open-ended practical or project work is designed to permit students to demonstrate achievement of all learning outcomes in this section. In tutorial/seminar work acquisition of intellectual skills is achieved through problem solving exercises involving the analysis or interpretation of data. Coursework assignments, particularly at higher levels of the programme, often involve the synthesis of information from a variety of sources in unfamiliar contexts. C Teaching and learning Subject practical skills are developed in a progressive manner throughout the programme. D Teaching and learning Computer, problem-solving, teamwork, practical laboratory and presentation skills are developed in a contextualised manner throughout the programme. These skills are enhanced in seminars, workshops, practical laboratory sessions and coursework assignments. Assessment Methods A Assessment Methods: The assessment methods associated with each course are defined in the individual course specifications. In general each course, apart from the analytical problem solving course and project, is assessed by a combination of examination, practical coursework and problem solving exercises. The nature of the coursework assessment varies from course to course. B Assessment Methods: Intellectual skills are partly assessed through formal examinations but assessment of coursework and practical or project reports also play an important part. A variety of assessment methods are used including formal reports, essays, oral presentations and open-book tests. C Assessment Methods: The practical abilities of the student are assessed in the practical (laboratory) aspects of individual programmes and also in the Research Project – a core course of the MSc programme. This assessment includes their laboratorybased skills, their approach to a critical review of the literature, critical review of techniques used, and evaluation of the resulting data. In addition the abstract, discussion and conclusions of the project are also assessed. D Assessment Methods: A variety of assessment methods are used to assess transferable key skills. These include problem solving. These assessments are contextualised in A, B and C above.