A “Toolbox” for Improving NBME Subject Examination Performance
advertisement

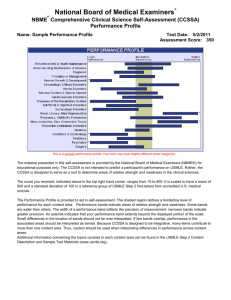
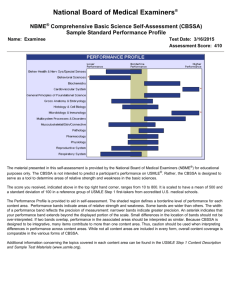
A “Toolbox” for Improving NBME Subject Examination Performance John Spollen, M.D., Brandi Hankins, M.D., Shanna Palmer, M.D. Department of Psychiatry, College of Medicine, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences Background Psychiatry NBME Subject Examination Scores • NBME Subject Examinations are a useful measure of basic psychiatry knowledge - Only one of the competencies, but still important • Areas of poor performance indicate areas for improvement in curriculum • Scores likely correlate moderately (r~.6) with USMLE Step II - In schools with poorer test performance, NBME exam preparation may improve pass rates on USMLE examinations • In 2000-01 at UAMS, Psychiatry NBME scores were 28th percentile and last among the 6 clerkships • Psychiatry had never finished better than 3rd among the 6 clerkships • The clerkship directors were challenged to improve performance Clinical NBME Subject Examinations 2000-01 2001-02 2002-03 2003-04 2004-05 2005-06 2006-07 National % Rank 28 33 53 42 63 55 65 6th of 6 5th 3rd 2nd 1st 1st 1st Strategies Used: The “Toolbox” Curriculum Change Faculty review the NBME yearly and update lectures Specific test review handouts Online (WebCT) modules Flashcards and Review Questions Team-based Learning (TBL) for lectures Year Added 2002-03 Self-Directed Learning Modules Using Blackboard© • Handouts developed with the help of senior students and current residents • Updated yearly based on student and faculty feedback • Expanded in 2006 to include - Test bank of 180 NBME-like questions, using Articulate Quizmaker© - >100 Flashcards of “high yield” information, using Respondus Studymate© Example of NBME-like Questions Using Articulate Quizmaker© Team-Based Learning • Well-defined, evidence-based instructional strategy • Allows a single instructor to teach using multiple small groups simultaneously in the same classroom 2003-04 2004-05 2006-07 2007-08 • Class time is shifted away from learning facts and toward application and integration of information Conclusions Review of the NBME Exam • Annually review a copy of a previous year’s subject exam under proctored conditions - Probably the 1st step, as you learn a lot from it *2007-08 is calculated Exam Review Materials Self-Directed Learning Modules • Get as many faculty as possible to do this - Strongly encouraged for all clerkship lecturers • Opportunity to provide students with additional information without a lecture • Shows what is nationally expected knowledge - Points out holes in the curriculum - Curriculum deficiencies can be addressed with self- directed learning modules • NBME-like quizzes give students practice answering case format questions seen on the exam and helps to incorporate new knowledge • Gives students control over how and when to cover material • Strategies used, in aggregate, appear to be effective for improving the “medical knowledge” competency, as measured by the NBME subject examination • May have an effect on Step II pass rates - In 2004-05, 06-07 and 07-08, the 2 highest subscales on Step II at UAMS were “Mental Disorders” and “Psychiatry” • Residents and medical students are a frequently untapped resource in education - As “experts” in NBME exams, they can be a valuable asset in developing review materials