the mines act and development of mine safety legislation

THE MINES ACT AND DEVELOPMENT OF
MINE SAFETY LEGISLATION
IN INDIA.
Prasanta Kumar Sarkar
India-EU Seminar, 19-20 September, 2011 1
Development of Mines Safety Legislation
Back ground
Mineral is important for development of a nation
India is endowed with rich mineral deposits
Today India is one of the leading countries in production of coal, iron ore, bauxite and other minerals.
About one million persons are engaged in mining industry
India-EU Seminar, 19-20 September, 2011 2
Development of Mines Safety Legislation
Back ground
• At present India produces 87 minerals
• Mineral sector is growing at a rate of about 7.5%
• The contribution of mining sector to
Gross Domestic Product(at current price) for 2010-11 is estimated as
2.51% of GDP.
India-EU Seminar, 19-20 September, 2011 3
MINERAL INDUSTRY IN INDIA
569Coal Mines 67 Oil & Gas Projects
Over 8000 Non-Coal Mines
Employing over one (1) million persons directly on a daily average basis
India-EU Seminar, 19-20 September, 2011
Development of Mines Safety Legislation
Back ground
Mining is a hazardous profession
The credit for establishing the principle of state regulation goes to France. In
1781
Louis XVI created the first inspectorate of mines.
In
1849
State of Pennsylvania, in USA enacted law for the benefit of miners.
India-EU Seminar, 19-20 September, 2011 5
Development of Mines Safety Legislation
Back ground
India has completed
109 years of State intervention for protecting persons at work in mines
Required safeguards for the persons working in mines have been provided in Indian constitution
The Constitution of India has empowered the parliament to frame law concerning regulation of labour and safety in mines
India-EU Seminar, 19-20 September, 2011 6
Constitutional obligation
Article 246 (entry 55 of the seventh schedule)
“regulation of labour and safety in mines and oilfields”.
Article 24
“No child below the age of fourteen years shall be employed to work in any factory or mine or engaged in any other hazardous employment”
India-EU Seminar, 19-20 September, 2011 7
Constitutional obligation
Article 39
“the state shall, in particular, direct its policy towards securing -
(e) that the health and strength of workers, men and women, and the tender age of children are not abused and that citizens are not forced by economic necessity to enter a vocations unsuited to their age or strength;”
Article 42
“The state shall make provision for securing just and humane conditions of work and for maternity relief”
India-EU Seminar, 19-20 September, 2011 8
History of Development of OSH legislation in
India
1890
The ILO, at its meeting in Berlin considered the issues related to improvement in the working conditions of miners
Following it the Govt. of UK requests Govt. of India to consider the advisability of undertaking legislation for inspection of mines in general and coal mines in particular
1894
P reliminary study of mining conditions in India by one HM Inspector of Mines, Mr. James Grundy 1895
India-EU Seminar, 19-20 September, 2011 9
History of Development of OSH legislation in
India
1895
A Committee was appointed by the Govt. of India to
Frame suitable legislation to afford full protection to persons working in mines in such matters in which they have a reasonable claim on the State for protection
- Committee Submitted report in 1896
In 1897 two disaster took place one at Kolar Gold field & another at Khost coal mine in Baluchistan
India-EU Seminar, 19-20 September, 2011 10
History of Development of OSH legislation in
India
1901
This efforts led to the enactment of the First Indian Mines
Act which came into force on 22 nd March, 1901
Some of the important provisions of the Mines Act:
Inspectors empowered to enter mines and inspect & make enquires
Minimum age of employment as 12 years.
Supervision by competent manager holding manager's certificate
Penalties prescribed for various contraventions.
The Act was amended in1910 &1914
Bureau of Mines Inspection was formed with Calcutta as HQ on Jan 7, 1902
India-EU Seminar, 19-20 September, 2011 11
History of Development of OSH legislation in
India
1923
New Indian Mines Act 1923 came into force
The Act was amended in 1925, 1927, 1928, 1931, 1935, 1936,
1937, 1940 and 1946.
The 1928 amendments made the following additional provisions:
– Overlapping of shifts was prohibited
– same set of workers not to work more than 12 hours
– required to maintain a register of workers and their hours of work.
India-EU Seminar, 19-20 September, 2011 12
History of Development of OSH legislation in
India
The amending Act of 1935 made the following new provisions:
• The age of children was raised to 15 years
• Medical examination for employment of adolescents (15-17 years) belowground.
• The limit of weekly hours of work for both surface and underground workers was equalized at 54
• the maximum spread over on any day was fixed.
• Mining Boards were required to be set up by provincial governments.
The amendment Act of 1936 provided the following provision:-
• Establishment of Rescue Stations and formation, training and duties of rescue brigades.
India-EU Seminar, 19-20 September, 2011 13
History of Development of OSH legislation in
India
The 1937 amendment enlarged the powers of the Inspectors
The 1940 amendment stipulated
-salaries and wages of manager, supervisory staff etc should be paid by the owner of the mine and not by the ‘raising contractor’.
The 1946 amendment required the construction and maintenance of pithead baths.
India-EU Seminar, 19-20 September, 2011 14
History of Development of OSH legislation in
India
1952
The Mines Act 1952 superseded earlier legislation
Some of the important provisions of the Mines Act, 1952 are :
Definition of mine was enlarged
The minimum age for employment as 18 years
Compulsory weekly day of rest
Weekly hours of work limited to 48
Daily maximum work -8 hrs in underground & 9 hrs on surface
Restriction on employment of women below ground
Provision of first-aid, ambulance, drinking water and other medical facilities.
India-EU Seminar, 19-20 September, 2011 15
History of Development of OSH legislation in
India
Payment of overtime wages and leave with wages
Constitution of tripartite committees in place of mining board
Serving of improvement notice
Imposition of prohibitory orders for unsafe mines
Mine inspectorate empowered to undertake safety and occupational health surveys
Govt. empowered to frame rules and regulations on
Workmen's Inspectors, Safety Committee, Emergency plan etc
Notification of occupational diseases.
Punishment both imprisonment & fine
India-EU Seminar, 19-20 September, 2011 16
History of Development of OSH legislation in
India
The Mines Act 1952 amended in 1959 and in 1983
The 1959 amendment stipulated
The definition of the term “mine” was again amended
Inspectors were empowered to prohibit employment of persons if the mine failed to comply with the notice for remedying anything
A first-aid room to be maintained in every mine employing more that 150 persons (instead of 500 as prescribed earlier).
The 1983 amendment stipulated
• A new section 9A empowered the Inspectors to undertake safety and occupational health surveys in mines.
• constitution of a single tripartite Committee for the whole country in place of several Mining Boards and for constitution of one or more Committees
India-EU Seminar, 19-20 September, 2011 17
History of Development of OSH legislation in
India
The 1983 amendment stipulated
• Clearly re-define the duties and responsibilities of the owner, agent and manager.
• Section 22 was amended to clarify that any prohibitory order issued under sub-section (3) would remain valid until the Chief
Inspector or Inspector was satisfied that the danger had been removed.
• A new section 22A empowered the Chief Inspector to prohibit employment of persons in cases where despite warnings the owner, agent or manager did not show any improvement in regard to safety matters.
• Section 57 and 58 were amended to widen the scope of making regulations and rules.
India-EU Seminar, 19-20 September, 2011 18
History of Development of OSH legislation in
India
Regulations framed under the Mines Act
Three separate codes of regulations were framed under the Mines Act, 1952
The Coal Mines regulations, 1957
The Metalliferous Mines Regulations, 1961
The Oil Mines Regulations, 1984
India-EU Seminar, 19-20 September, 2011 19
History of Development of OSH legislation in
India
Regulations made provisions for:
supervision of mines by competent personnel,
maintenance of up-do-date plans,
general precautions against every conceivable hazard
permission for-
commencing certain operations
working beneath and in the vicinity of bodies of water or surface buildings and structures,
using new machines generating any kind of risk in underground mines
submission of notice in every case of accidents etc.
precautions against air-borne dust
India-EU Seminar, 19-20 September, 2011 20
History of Development of OSH legislation in
India
Mines Rules 1955 framed under the Mines Act 1952
A set of rules covering health & welfare provisions was promulgated.
Some of the provisions are:
Certifying Surgeons
Health & Sanitation
First aid
Employment of persons, Leave with wages, Overtime etc.
The Mines Rules were amended in 1978 and in 1986 & provided for :
Medical examination of persons employed or to be employed in mines
Prescribed medical standards of fitness
Appointment of Workmen's Inspectors
Constitution of safety committees.
India-EU Seminar, 19-20 September, 2011 21
History of Development of OSH legislation in
India
Vocational Training Rules 1966 framed under the Mines Act 1952
Recognizing the need for educating mine workers about the dangers of working in mines, the Mines Vocational
Training rules were framed in 1966.
The rules provided for:
Initial, refresher and specialized training to mine workers.
India-EU Seminar, 19-20 September, 2011 22
History of Development of OSH legislation in
India
Mines Rescue Rules framed under the Mines Act 1952
Keeping in mind the occurrence of emergencies in mines, particularly in belowground mines due to explosion, fires etc.
Coal Mines Rescue Rules , 1939 were framed
Mines Rescue Rules, 1985 , replaced the Coal Mines
Rescue Rules 1939
India-EU Seminar, 19-20 September, 2011 23
History of Development of OSH legislation in
India
Mines Rescue Rules framed under the Mines Act 1952
set-up of rescue stations/rescue rooms
appoint superintendent, instructors, rescue personnel, rescue room in-charge etc
specify the duties and responsibilities of these persons, organization,
Maintenance of equipment in mines, conduct of rescue work etc.
India-EU Seminar, 19-20 September, 2011 24
History of Development of OSH legislation in
India
Under the Mines Act ,
Mines Crèche Rules 1966
&
Coal Mines Pit Head Bath Rules, 1959 were framed
India-EU Seminar, 19-20 September, 2011 25
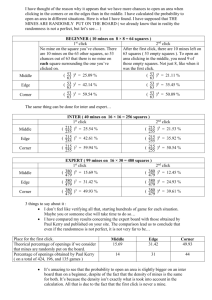
Period
Trend in fatal accidents & fatality rates
per 1000 persons employed
1901-10
1921-30
1941-50
1951-60
1961-70
1971-80
1981-90
1991-00
2001-10
295
259
264
185
170
107
Coal
Av. No of fatalities
92
219
273
Fatality rate
0.93
1.24
1.01
0.82
0.62
0.55
0.34
0.33
0.27
81
85
74
73
77
65
Non-coal
Av. No of fatalities
23
50
31
Fatality rate
0.67
0.66
0.29
0.34
0.33
0.30
0.31
0.36
0.40
India-EU Seminar, 19-20 September, 2011 26
300
250
200
150
100
50
0
Trend in Fatal Accident
(no of accident)
Oil
Metal coal
India-EU Seminar, 19-20 September, 2011 27
TREND IN FATALITY RATE / 1000 PERSONS
EMPLOYED, 10 YEARLY AVERAGE
India-EU Seminar, 19-20 September, 2011 28
Trend in Fatal Accident-Coal
India-EU Seminar, 19-20 September, 2011 29
Amendment of Statute
These laws are constantly upgraded based on
the experience gained while implementing law
The recommendations of the Courts of Inquiries
The ILO conventions and recommendations
The recommendations of the Conferences on
Safety in Mines
International experiences, their standards and legislation
Research and development
India-EU Seminar, 19-20 September, 2011 30
Existing Mining Scenario
•
Quantum jump in mineral demand
•
Complex Geo Mining Conditions
•
New innovative Technology
•
Privatization and outsourcing
•
Entry of Multinational players
•
Social issues
India-EU Seminar, 19-20 September, 2011 31
Amendments in Safety Legislation
In view of recent development and changed scenario in mining industry various amendments of statutes are under process -
Mines Act, 1952,
Coal Mines Regulations, 1957,
Metalliferous Mines Regulations, 1961
Oil Mines Regulations, 1984.
India-EU Seminar, 19-20 September, 2011 32
India-EU Seminar, 19-20 September, 2011 33