Prevost's Squirrel
advertisement

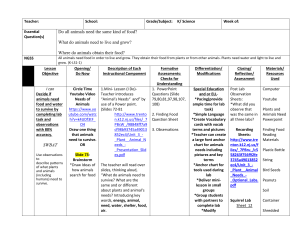
Prevost’s Squirrel Fast Facts What do they look like? Prevost’s squirrels are a strikingly-colored species, typically with black backs from the nose to tail, a chestnut-colored belly, and white-striped sides. Different subspecies have some variations in their coloring. Their body is 7-10 inches long, and their bushy tail is of a similar length. Like all rodents, they have a pair of strong incisors which grow continuously throughout their lives and are worn down by gnawing on tough foods. They have bulbous eyes which are adapted to vertical vision, peering intently up and down tree trunks as they climb. How do they behave? Common Name: Prevost’s Squirrel, Asian Tri-Colored Squirrel Scientific Name: Callosciurus prevosti Family: Sciuridae Order: Rodentia Class: Mammalia Range: Southeast Asia Primarily arboreal, they spend most of their time high in the trees of forests. Prevost’s squirrels are diurnal, most active during the day, and spend most of their time foraging for food. They are very agile climbers and can leap 8-10 feet between branches! Prevost’s squirrels communicate with each other with a variety of vocal trills and whistles, along with shaking, waving, and twitching their tails. What’s on the menu? Prevost’s squirrels eat mainly fruit, nuts, seeds, flowers, and occasionally insects. At the Zoo, they eat specialized pelleted food, fruit, vegetables, and seeds. How are they born? Prevost’s squirrels reach sexual maturity around one year of age. The female squirrel builds a spherical nest from leaves and twigs, called a drey. Alternatively, she may line the hollow of a tree with leaves. She bears a litter of one to four young after a gestation period of around forty days, and may have up to three litters each year. The young are born altricial (requiring nourishment): hairless, toothless, and with their eyes closed. They grow and develop very quickly, cared for by the female, and leave the nest at 6 to 8 weeks of age. What should you know about them? Squirrels are vital to the survival of the forests in their native range. They disperse the seeds by carrying the fruit away from the tree, eating the flesh and then dropping the seeds to the ground. This helps replant the trees, to create a healthy and diverse forest. The Prevost’s squirrel is part of the genus Callosciurus, which means “the beautiful squirrels” due to their striking coloration. Habitat: Forests Lifespan: 8-10 years in the wild; 10-15 years in captivity Conservation Status: Lower Risk What can you do to help? Although Prevost’s squirrel populations are currently stable, habitat loss and deforestation threaten this species’ future. To prevent habitat destruction, you can help by buying wood that is sustainably harvested, coffee that is shade grown, and produce that is grown locally. These products do not require the destruction of forest land to grow crops.