Tutorial Questions (Functional Dependency and Normalization)
advertisement
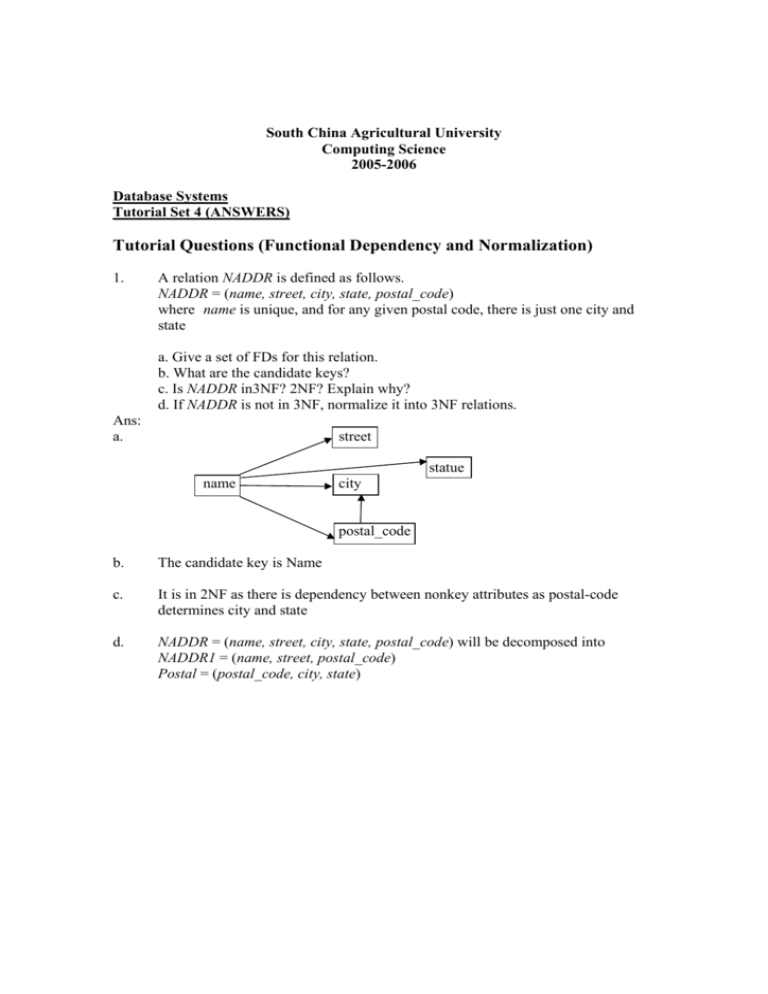
South China Agricultural University Computing Science 2005-2006 Database Systems Tutorial Set 4 (ANSWERS) Tutorial Questions (Functional Dependency and Normalization) 1. A relation NADDR is defined as follows. NADDR = (name, street, city, state, postal_code) where name is unique, and for any given postal code, there is just one city and state a. Give a set of FDs for this relation. b. What are the candidate keys? c. Is NADDR in3NF? 2NF? Explain why? d. If NADDR is not in 3NF, normalize it into 3NF relations. Ans: a. street statue name city postal_code b. The candidate key is Name c. It is in 2NF as there is dependency between nonkey attributes as postal-code determines city and state d. NADDR = (name, street, city, state, postal_code) will be decomposed into NADDR1 = (name, street, postal_code) Postal = (postal_code, city, state) 2. A database used in an order-entry system is to contain information about customers, items and orders. The following information is to be included. For each customer: Customer number (unique) “Ship-to” addresses (several per customer) Balance Credit limit Discount For each order: Heading information: customer number, ship-to address, date of order Detail lines (several per order): item number, quantity ordered For each item: Item number (unique) Manufacturing plants Quantity on hand at each plant Stock danger level for each plant Item description For internal processing reasons a “quantity outstanding” value is associated with each detail line of each order. This value is initially set equal to the quantity of the item order and is (progressively) reduced to zero as (partial) shipments are made. The following semantic assumptions can be made: • No two customers have the same ship-to address. • Each order is identified by a unique order number. • Each detail line within an order is identified by a line number, unique within the order. Draw a functional dependency diagram and design a set of the tables in the third normal form (3NF) for the system. Ans: The functional dependency diagram. BAL ADDRESS CUST # CREDLIM DISCOUNT QTYORD ORD # DATE QTYOUT LINE # DESCN ITEM # QTYOH PLANT # DANGER The tables in third normal form (3NF) CUST (CUST#, BAL, CREDLIM, DISCOUT) PRIMARY KEY (CUST #) SHIPTO (ADDRESS, CUST #) PRIMARY KEY (ADDRESS) ORDHEAD (ORD#, ADDRESS, DATE) PRIMARY KEY (ORD#) ORDLINE (ORD#, LINE#, ITEM#, QTYORD, QTYOUT) PRIMARY KEY (ORD#, LINE#) ITEM (ITEM#, DESCN) PRIMARY KEY(ITEM#) IP (ITEM#, PLANT#, QTYOH, DANGER) PRIMARY KEY (ITEM#, PLANT#)











