Class activities
advertisement
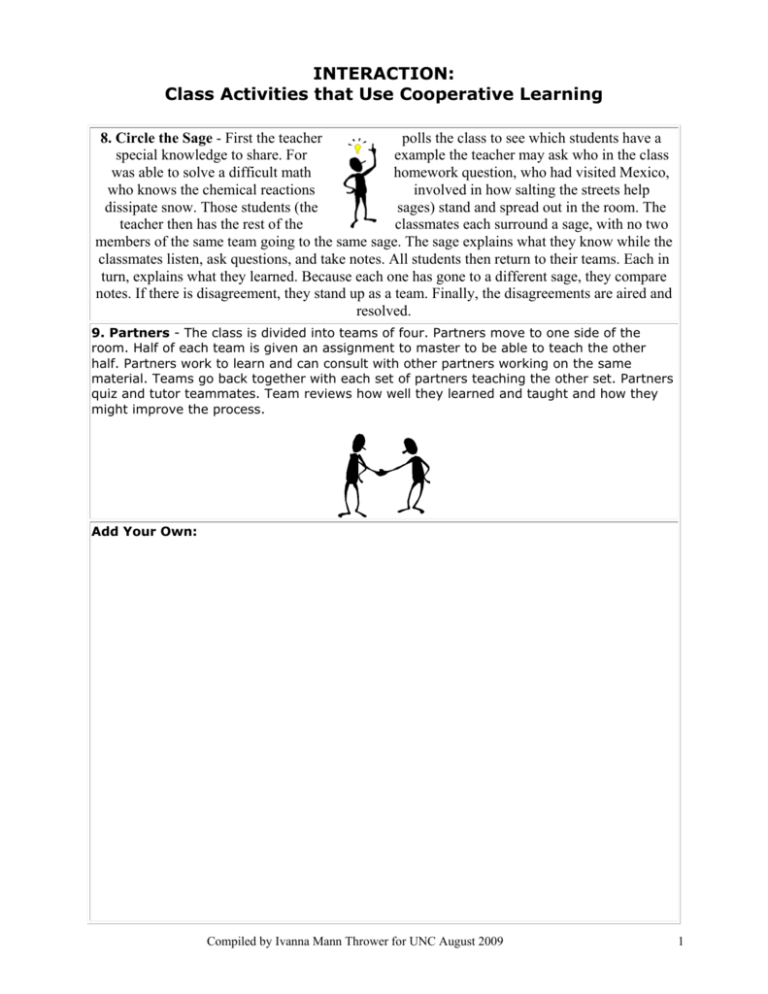
INTERACTION: Class Activities that Use Cooperative Learning 8. Circle the Sage - First the teacher polls the class to see which students have a special knowledge to share. For example the teacher may ask who in the class was able to solve a difficult math homework question, who had visited Mexico, who knows the chemical reactions involved in how salting the streets help dissipate snow. Those students (the sages) stand and spread out in the room. The teacher then has the rest of the classmates each surround a sage, with no two members of the same team going to the same sage. The sage explains what they know while the classmates listen, ask questions, and take notes. All students then return to their teams. Each in turn, explains what they learned. Because each one has gone to a different sage, they compare notes. If there is disagreement, they stand up as a team. Finally, the disagreements are aired and resolved. 9. Partners - The class is divided into teams of four. Partners move to one side of the room. Half of each team is given an assignment to master to be able to teach the other half. Partners work to learn and can consult with other partners working on the same material. Teams go back together with each set of partners teaching the other set. Partners quiz and tutor teammates. Team reviews how well they learned and taught and how they might improve the process. Add Your Own: Compiled by Ivanna Mann Thrower for UNC August 2009 1 Practice/Application Quick Write How do you integrate activities in your classroom? 20. Provide hands-on materials and/or manipulatives for students to practice using new content knowledge. 21. Provide activities for students to apply content and language knowledge in the classroom. 22. Provide activities that integrate all language skills (i.e., reading, writing, listening, and speaking). Lesson Delivery: Teacher Behaviors Avoid Assuming prior knowledge Yes or no questions! Building Background • • Self-Correcting • Immediately correcting the student Self-Evaluation • Only grading for correct answers Peer Interaction • Always giving the answer Imitation • Silent classrooms Native Language Resources • Assuming students will know how to use their dictionaries and glossaries Focus On Discovering prior knowledge Context clues Relating shared experiences Wait time • • • • • • • • Journals (can be illustrated!) KWL Charts Rubrics Phone a friend’, ‘poll the audience’ • Pairing higher & lower level ELLs • • • • • Listen to the radio Interviews Guest Speakers Clarification Teaching students when and how to use these resources Compiled by Ivanna Mann Thrower for UNC August 2009 2 Assessment Modification: It’s NOT Unfair! It’s Essential! 1. Give students objective tests (matching, multiple choice, T or F) instead of subjective tests (essays). 2. Provide extra testing instructions or rephrase directions. 3. Test key concepts or main ideas (not specific points). 4. Make a simplified language test. 5. Supply ELLs with word banks for tests. 6. Reduce the number of test responses. 7. Simplify test directions. 8. Assess ELLs on their effort to understand content area material at their level of language ability. 9. Provide highlighted tests. 10. ________________________________________________________ 11. _________________________________________________________ 12. _________________________________________________________ OUTCOME SENTENCES zI feel … zI wonder … zI think … zI learned … WARNING!! No Teacher should FAIL an LEP student if that teacher has not offered instructional and testing accommodations to the student. Compiled by Ivanna Mann Thrower for UNC August 2009 3