Most Frequent Questions of Chromogenic Media
advertisement

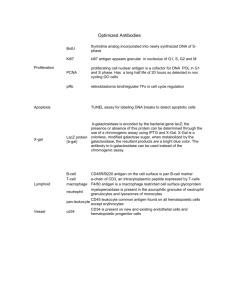
Most Frequent Questions of Chromogenic Media • • • • • ¿What is a chromogenic culture media? ¿How do chromogenic media work? ¿Which are the advantages? Differences between MRSA Agar (Cat. 1493) and MRSA Modified Agar (Cat. Nº 1498) ¿Which of your chromogenic media are under an ISO norm? ¿What is a chromogenic culture media? Chromogenic media are microbiological media suitable for incubation, differentiation, or selection of many microorganisms by using chromogenic substrates and resulting in color production. These colors will be distinctive depending on the target microorganism and it will allow an easier and accurate differentiation. ¿How do chromogenic media work? Chromogenic medias contains nutrients such as peptones, amino acids, yeast extract, minerals and vitamins, as well as inhibitors and solidifiers and chromogenic substrates or chromogens. Chromogenic substrates have been proved to be a powerful toll in the identification of microorganisms due to their detection of specific enzymes produced by the target microorganisms. These chromogenic substrates as ONPG, X-Gal, or X-Glu, together with a specified selectivity of the medium, is the simple principle behind chromogenic media. The target organisms are characterized by specific enzyme systems which are responsible for the cleavage of the substrate inside the chromogen. In order to cleave the substrate the bond between the two parts of the chromogen is broken by the enzyme. Thus, the chromophores are released and they can be visually detected by direct observation of a distinct colour change in the medium. ¿Which are the advantages? 1. Shorter time to result compared with traditional methods for both negative screens and presumptive positives. Some media give confirmed results within 24 hours. 2. On a single medium you can identify more than one organism. If we take one each specific media for more than one organism, the chromogenic media is cheaper. 3. Result interpretation is visually without the need of a special skill or machine. 4. Chromogenic media eliminate the need of subculture and further biochemical test for identification pathogenic agent . 5. The virulence of a certain microorganism can be detected simultaneously with its differentiation and selection. The coagulase and fibrino-lysin tests can also be carried out simultaneously within the medium. 6. Chromogenic media also comprise nutrients and make possible the survival of damaged microorganisms which are about to disappear. Differences between MRSA Agar (Cat. 1493) and MRSA Modified Agar (Cat. Nº 1498) With MRSA Agar (Cat. 1493) you can make the presumptive detection of Methicillin resistant Staphylocossus aureus in clinical sample. Staphylococcus aureus are of particular interest at an international level due to its virulence and resistance to multiple antibiotics. The media will turn out blue colonies when this bacterium is present. Making an improvement MRSA Modified Agar (Cat. Nº 1498) is able to detect and differentiate chromogenically between methicillin resistant Staphyloccus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Staphylococcus aureus grow as magenta colonies. Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis grow as green-blue colonies. The rest of the accompanying flora is inhibited ¿Which of your chromogenic media are under an ISO norm? We have three chromogenic media formulated under an ISO norm. These media are: TBX Chromogenic Agar (ISO 16649-2) Listeria chromogenic Agar Base (ISO 11290) Enterobacter sakazakii Isolation Agar (ISO 22964)