Ch. 6 Working with single protein sequence Designing a protein on
advertisement
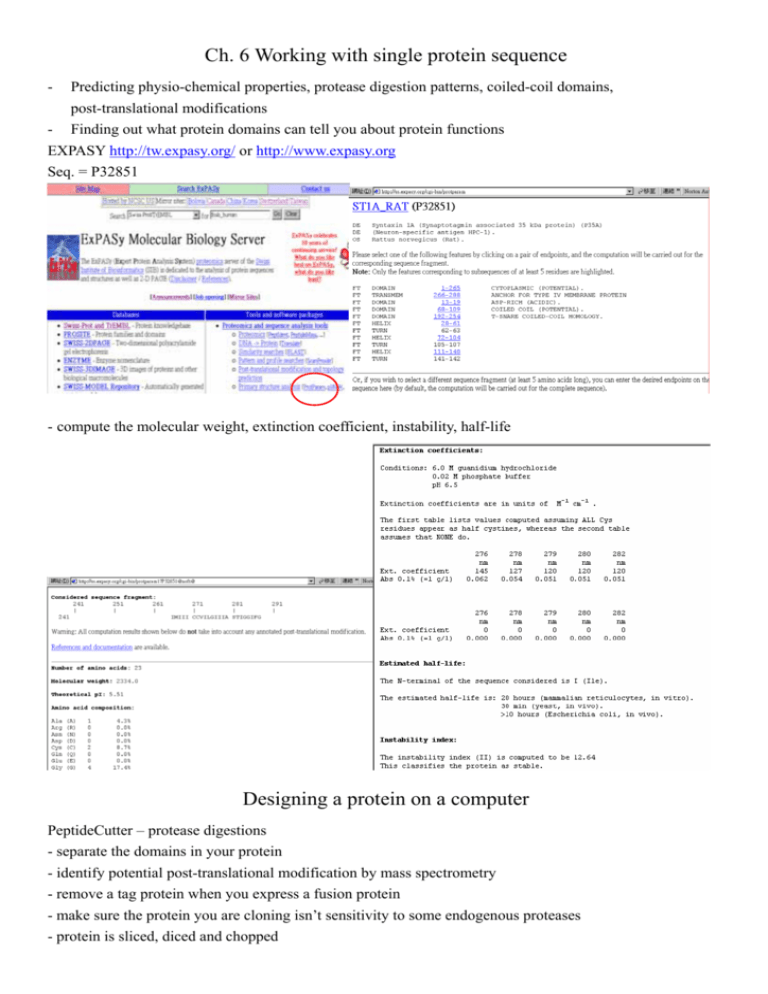
Ch. 6 Working with single protein sequence - Predicting physio-chemical properties, protease digestion patterns, coiled-coil domains, post-translational modifications - Finding out what protein domains can tell you about protein functions EXPASY http://tw.expasy.org/ or http://www.expasy.org Seq. = P32851 - compute the molecular weight, extinction coefficient, instability, half-life Designing a protein on a computer PeptideCutter – protease digestions - separate the domains in your protein - identify potential post-translational modification by mass spectrometry - remove a tag protein when you express a fusion protein - make sure the protein you are cloning isn’t sensitivity to some endogenous proteases - protein is sliced, diced and chopped 2 http://www.expasy.org/tools/#proteome Doing primary structure analysis - sliding window approach, hydrophoblic regions, coiled-coil regions, hydrophilic region - strong signals, robustness, window size problem - transmembrane domains ~ 21 a.a. - globular proteins, size ~ 7 – 11 a.a. Looking for transmembrane segments - hydrophoblic regions are characteristic of transmembrane proteins ProtScale Seq. = P78588 3 TMHMM http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services Identify 5 segments and fail to predict another 2 segments Looking for coiled-coil regions COILS server http://www.ch.embnet.org/software/COILS_form.html - protein-protein interaction involve coiled-coil regions Predicting post-translational modification site PROSITE http://www.expasy.ch/tools/scanprosite - a collection of short motif seqs. db, which associated with some biological function - regular expression representation, i.e. [RK]-x-[ST] Æ RGT, KCS or KET - compare your protein seq. with the list of pattern in PROSITE Finding domains in your protein - domains are independent globular folding units - may interact with other proteins, bind an ion like calcium or zinc, or it may contain an active site - InterProScan, CD server, Pfscan 4 InterProScan http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/scan.html Seq. = FOSB_HUMAN or P53539 All agree on the presence of Leucine zippers understanding InterProScan report - yellow box, domain name, IPR###, PS00138, - inconsistency Æ consult all the dbs - domain collection library - BLOCKS contains many short multiple alignments (blocks) - Prodom, collection of domains through seq. comparison on NR - Pfam, high quality manually (PfamA) and machine (PfamB) annotated domains Finding domains with CD server - report a score in the output - CD doesn’t integrate as many dbs as InterProScan -NCBI Æ BLAST Æ use RPS-BLAST Æ P53539 -deselect the low complexity box, because many domains are rich in certain amino-acids, i.e. the leucine zippers, glycine-rich domains, - E-value <0.01 mean significant, the lower the better - Red domains are from SMART, blue domains are from Pfam, ragged ends indicate partial matches 5 - Watch out for False positive (FP) and False Negative (FN) results Finding domains with Pfscan http://hits.isb-sib.ch/cgi-bin/PFSCAN Seq. = P53539 Only score > 7 are consider Green/Red or bar above/below Æ (conserved/not expected to be here) amino acid at this position - Pfscan found two domains not detected by InterProScan and CD, Proline-rich and Arginine-rich Exercise 6 Name: _______________ Class:________________ Student ID:_______________ Point your browser to SWISS-PROT, http://tw.expasy.org/, or http://www.expasy.ch, or http://ca.expasy.org, or http://us.expasy.org. 1. 2. We need to predicting the physio-chemical properties of a well-known protein called Calmodulin (SWISS-PROT ID, P06787), which mediates the control of a large number of enzymes by Ca(++). Among the enzymes to be stimulated by the calmodulin-Ca(++) complex are a number of protein kinases and phosphatases. Use the tool, ProtParam, in which you can find it in the SWISS-PROT web page, to predict the following properties of this protein; (i) (ii) (iii) the theoretical pI value ______________ instability index ______________ is this protein stable ? (when the index is below 40, the protein is consider to be stable) ______________ (iv) Grand average of hydropathicity value ______________. In question 2, we will study the pattern and domain structures of calmodulin, using PROSITE (http://www.expasy.org/tools/scanprosite/), InterProScan (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/scan.html), and Pfscan servers (http://hits.isb-sib.ch/cgi-bin/PFSCAN). For PROSITE search, remember to deselect the “scan profiles and rules boxes”. You will obtain several patterns after the search. z z z z Do you think short patterns are reliable ? Yes, it is reliable. No, it is not reliable. What is the domain name of the longest pattern ? _________________________________ How long is the longest domain pattern ? _________________________________________ Write down the sequence positions of all the longest domains. _________________________________________________________________________ For InterProScan search, what is the name of the identified domain ? _______________________ For Pfscan search, how many predicted domains sequences have a score larger than 7 ? _________








