Biotechnology – Final Exam SG – a look back at this semester! Ch 1
advertisement

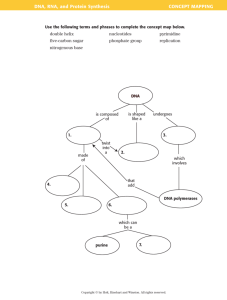
Biotechnology – Final Exam SG – a look back at this semester! Ch 1 Define Biotechnology biotech domains (agricultural., Industrial/Environmental, Medical/Pharmaceutical, Diagnostic) general biotech vocab in chapter 1 see ch 1 review SGQ’s and vocab how to do a serial solution (denim lab) parts of a lab notebook (TOC, numbering pages, writing in ink, signing pages, not erasing or whiting-out) parts of a lab notebook write-up Lab Safety preventative vs responsive safety equipment absorbent material procedure to sanitize lab bench procedure for washing glassware procedure for using glassware off the shelf PPE lab spill clean up protocols broken glassware MSDS ( & what it tells us) (and in the GHS this is called an SDS) GHS HCS OSHA safety signs biosafety levels 1,2,3, 4 Review ch 1 test Review ch 2 bookwork and SGQ’s definitely be able to draw the basic structure of an amino acid and how peptide bonds form eukaryotic vs prokaryotic cells basic cell organelles 4 basic cellular macromolecules Culturing Cells and Tissues what is tissue culturing (TC) history of TC 1902 first culture=?) 1930’s ___ discovered) 1962 = recipe for ?) discovered, 1970’s first commercial __________ TC labs, 1980’s 1st rDNA plant cells why do tissue culture in plants? there are several reason to… conditions for plant TC: sanitary…..sterile (aseptic)…..media…..chamber….tissue… what does each mean &/or why important Laminar Flow Hood (how does one work? and why?) as compared to a chemical hood like we have! Normal vs Cancer cells in vitro vs in vivo tumor benign tumor malignant tumor initiation leads to proliferation due to mutation of gene that regulate___ metastatic cells have acquired what cheacteristics? cancer is of a clonal origin (this means what?) what three things keep tumor formation in check? how is cell culturing important to cancer research? confluency – a culture is out of space to grow subculturing means? why must a biopsy be minced and dissociated with a proteolytic enzyme like Trypsin before it can be cultured? What must be provided for a growing culture? put thwe following llist of terms in order of size: cell, chromosome, electron, cellular nucleus, atomic nucleus, gene, organ, organism, atom, molecule, tissue aneuploid means what about chromosomes (associated with cancer) HeLa is an aneuploid cel line! what are HeLa cells what does it mean if cells will grow in soft agar? What is agar? What do athymic organisms lack? What can athymic organisms not do? Why are athymic organisms important to cancer research? What would you have to do to keep an athymic population alive? ch 3 Equipment and Lab Calculations of Biotechnology Tools for measuring what to use for what? beaker grad cylinder erlymeyer flask, pipette, micropipette types of water – tap, deionized, RGW, sterile autoclave and how to use how to label a prepared chemical how to label a microcentrifuge (eppendorf) tube how to use a pipet with a pump properly how to use micropipets accurately converting between metric unts (primarily base unit to milli to micro) how big is a L mL uL be able to describe each table top vs analytical balances what do you have to do with a table top balance before you use it and before you put it away! it is under the scale!!!!! solution, solute, solvent, (aqueous) concentration (g/mL) X volume (mL) = grams of solute (g) how do you mix a solution (solute + water) without going over the final volume? recording percent as a decimal what is a meniscus what is a hydrogen bond identify the independent variable and the dependent variable identify a negative control vs a positive control what were the controls in the veggie antibiotic resistant bacteria lab? how is molecular (formula) weight determined? can you use: V x FW x M = g final volume x formula weight x Molarity = mass L x g/mol x mol/L = g Try: How do you make 2L of 4 M HCl ? what’s a mole? what’s a coefficient mean in a chemical formula? What’s a subscript mean in a chemical formula? When we say 1M (one molar) what do we really mean? Can you use C1 V1 = C2 V2 ? Our Pipettes are TD to deliver…what does this mean? ch 4 DNA and GE gel electrophoresis (GE) what is is and how it works what would a gel be like with more agarose (high percentage) or less agarose (lower % of agarose?) What are two ways to stain the DNA in an agarose gel? restriction digestion RD enzymes what are they? be able to write the central dogma why is each reagent used in the DNA extraction protocol? (detergent, enzyme, alcohol) why is DNA negative? how is this important to GE? what causes Huntington’s disease and thus how were you able to determine which family members had the disease by using GE? if a RD enzyme cut lambda DNA in 6 pieces then how many cuts did the RD enzyme make? what does using semilog graph paper allow us to do? extrapolating data vs interpolating data what is an Rplasmid? (i.e. it is a bactieral plasmid which contains the genes for _______________) When bacteria has taken up foreign DNA it is called ________________________ what is a virus? non-pathogenic bacteriophage can you still label the beast? what is a phosphodiester bond? where do hydrogen bonds form in DNA? how does DNA bond: purine to purine? & pyrimidine to pyrimidine? OR purine to pyrimidine? what does it mean to say the 5’ end of DNA? the 3’ end? how is 5’ to 3’ important in replication? what does it mean that DNA replication is semi-conservative? two terms we used before, but which came up again – lysis and medium we did not get to transcription of prokaryotic (operons promoters operators) and eukaryotic DNA (introns and exons…enhancers, silencers, transcription factors and histones) what is a light box used for? what is a rocker platform (or tilt-table) used for?