Structures of the Heart (Lab Check 12th edition)
advertisement

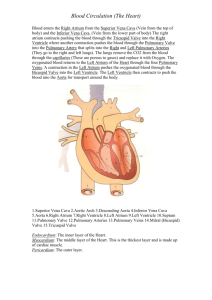
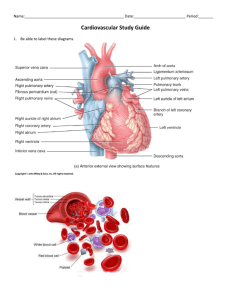
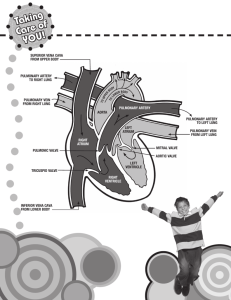
LAB MANUAL: 12th Edition LABORATORY EXERCISE 38 HEART STRUCTURE Instructional Suggestions 1. You may want to have the students use colored 3. pencils to color the features of the heart and blood vessels in figure 38.3. This activity should help them observe the illustrations more carefully and locate the 4. various features shown from different views in the figures. They can check their work by referring to the corresponding figures in the textbook, which are presented in full color. 2. Instead of using preserved sheep hearts, you might want to provide fresh pig hearts for dissection. To reduce the cost of specimens used, you might provide predissected, preserved sheep hearts for observation and save the specimens for use with other classes. Fresh beef hearts are sometimes available from meat-packing houses. You might want to demonstrate the dissection of this large heart. Try to make sure that the atria and large blood vessels are left attached for this purpose. Figure Labels FIG. 38.1 1. Aorta 2. Superior vena cava 3. Right atrium 4. Right coronary artery 5. Right ventricle 6. Inferior vena cava 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Pulmonary trunk (artery) Left atrium Left coronary artery Great cardiac vein Left ventricle 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Apex Superior vena cava Right atrium Inferior vena cava Right ventricle FIG. 38.3 1. Aorta 2. Superior vena cava 3. Aortic valve 4. Right atrium 5. Tricuspid valve 6. Chordae tendineae 7. Inferior vena cava 8. Left pulmonary artery 9. Pulmonary trunk 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. Left pulmonary veins Left atrium Pulmonary valve Mitral (bicuspid) valve Papillary muscle Interventricular septum Left ventricle Right ventricle FIG. 38.4 1. Superior vena cava 2. Aorta 3. Right atrium 4. Aortic valve 5. Tricuspid valve 6. Right ventricle 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Interventricular septum Left atrium Mitral valve Left ventricle Apex 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. e g i b c a FIG. 38.2 1. Aorta 2. Left pulmonary artery 3. Left pulmonary veins 4. Left atrium 5. Left ventricle Laboratory Report Answers PART A 1. h 2. l 3. j 4. f 5. k 6. d 45 PART B 1. The right atrioventricular valve is composed of three 4. relatively large cusps that contain chordae tendineae; the pulmonary valve is made up of three smaller pocket-like cusps that lack chordae tendineae. 2. The cusps of the right atrioventricular valve move upward into a horizontal position and close the opening 5. between the right atrium and the right ventricle. 3. The chordae tendineae and papillary muscles prevent the cusps of the right and left atrioventricular valves from swinging into the atria when the ventricles contract. The thicker wall of the aorta allows it to withstand the higher pressure of the blood pumped out from the left ventricle. The thinner wall of the pulmonary trunk (artery) is related to the lower pressure of the blood that leaves the right ventricle. Vena cava, right atrium, right atrioventricular valve, right ventricle, pulmonary valve, pulmonary trunk, pulmonary artery, capillary of the lungs, pulmonary vein, left atrium, left atrioventricular valve, left ventricle, aortic valve, aorta. Critical Thinking Application Answers The thicker wall of the left ventricle allows it to contract with greater force and create the high pressure needed to move blood to all parts of the body (systemic circuit) except the lungs. The thinner wall of the right ventricle creates the lower pressure needed to move blood a relatively short distance to the lungs (pulmonary circuit). 46