More on Hormones
advertisement
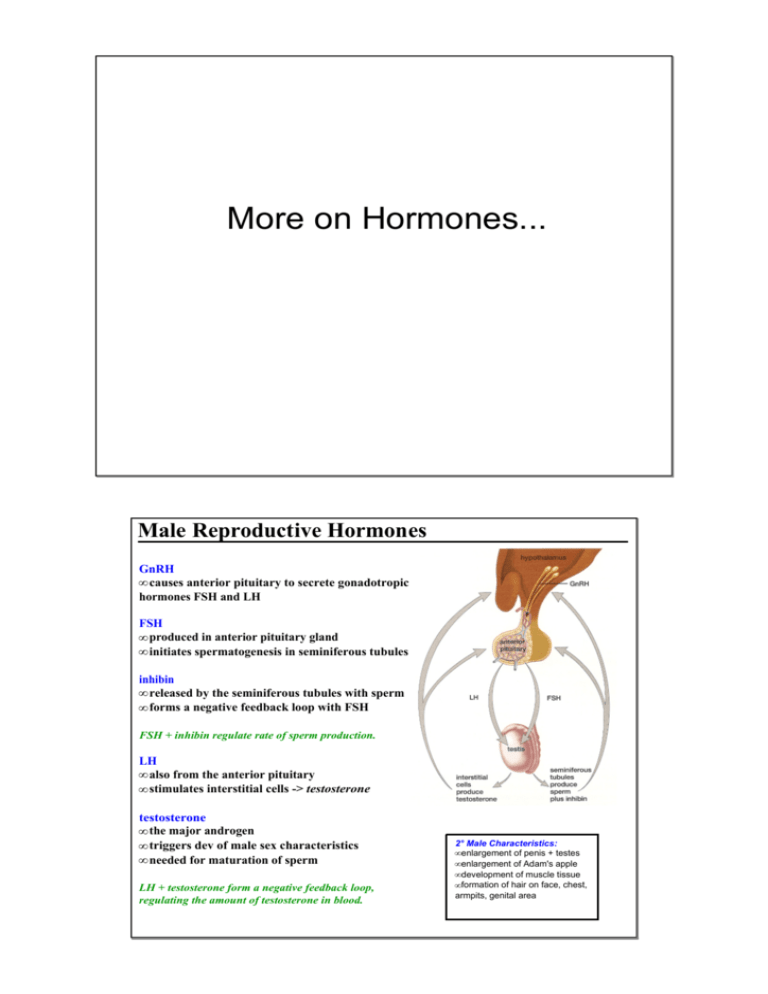
More on Hormones... Male Reproductive Hormones GnRH • causes anterior pituitary to secrete gonadotropic hormones FSH and LH FSH • produced in anterior pituitary gland • initiates spermatogenesis in seminiferous tubules inhibin • released by the seminiferous tubules with sperm • forms a negative feedback loop with FSH FSH + inhibin regulate rate of sperm production. LH • also from the anterior pituitary • stimulates interstitial cells ­> testosterone testosterone • the major androgen • triggers dev of male sex characteristics • needed for maturation of sperm LH + testosterone form a negative feedback loop, regulating the amount of testosterone in blood. 2° Male Characteristics: • enlargement of penis + testes • enlargement of Adam's apple • development of muscle tissue • formation of hair on face, chest, armpits, genital area Produced by Role GnRF FSH testosterone LH inhibin Female Reproductive Hormones The human reproductive system does not follow a seasonal pattern, but it is cyclical. The release of an ovum is timed so that the uterus is prepared to accept and sustain a developing embryo. This pattern is called the menstrual cycle, and is under the control of the hypothalamus. It is usually about 28 days long, but can vary from 20 ­ 45 days and can differ from month to month. Female Reproductive Hormones The ovaries are composed of follicles, each containing a single ovum. 1st Stage of Menstrual Cycle: follicular stage • GnRH from hypothalamus causes release of FSH from anterior pituitary • levels of FSH increase • in ovary: FSH stimulates follicles to develop and produce estrogen Estrogen causes • in uterus: endometrium to thicken and increase blood supply • in various tissues: dev of 2° female chars Estrogen forms a negative feedback loop with FSH. What will be the result of the increased estrogen levels on levels of FSH? Female Reproductive Hormones Levels of estrogen increase causing: • less FSH to be produced (negative feedback) • release of large amounts of LH from anterior pituitary • in ovary: LH triggers ovulation (day 14) *i.e. the release of an ovum from one of the ovaries Female Reproductive Hormones 2nd Stage of the Menstrual Cycle: luteal stage • Ovulation marks the beginning of the luteal stage • Immediately following ovulation, the follicle becomes the corpus luteum • this group of cells produces progesterone and estrogen Progesterone • • • • inhibits LH production (negative feedback) inhibits ovulation from other follicles (so only 1 ovum) inhibits uterine contractions continues preparation of endometrium for embryo As LH levels fall, the corpus luteum degenerates. Female Reproductive Hormones As corpus luteum breaks down, • • • • • progesterone and estrogen levels drop blood supply to endometrium decreases endometrial tissue is deprived of nutrients and O2 + breaks down contractions of uterus cause endometrium to pull away from uterine wall excess blood + tissue passes through the vagina and out as menstrual flow This marks the beginning of menstruation which coincides with the start of the next follicular stage. Menstruation usually lasts about 5 days. Animation­ Interactive Good Animation Awesome Animation Label the stages of the Menstrual Cycle on the diagram below. Levels of Pituitary Hormones 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 Label Stages Luteal Stage Follicular Stage Ovulation Levels of Ovarian Hormones 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 Label Phases Proliferative Menstrual Secretory 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 Day Levels of Pituitary Hormones 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 Follicular Stage Ovulatory Luteal Stage Stage Levels of Ovarian Hormones 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 Secretory Proliferative Menstrual 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 Day Produced by Role GnRF FSH estrogen LH progesterone Homework Questions: What are some signs of ovulation? Name and describe 2 prediction kits used to predict ovulation. Attachments Endrocrine Gland Function.wpd