GL11: Descriptive Geometry
advertisement

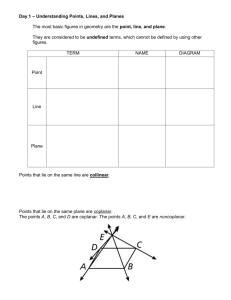
436-105 Engineering Communications GL11: Descriptive Geometry • Elements • Primary auxiliary views • Rotations Elements of DG • Orthographic projection – parallel projectors Top (plane 1) a1 b1 a1 b1 Fold line 1-2 1 b2 a2 Projection of line AB on plane 1 B A 2 Fold line 1-2 (or reference line) b2 a2 Front (plane 2) Projection of line AB on plane 2 Elements of DG • Geometric elements – points – lines – planes • Relationships – angles – distances Point Line Plane b1 C B c1 a1 1 2 A 2 3 c2 c3 b3 b2 a2 a3 Fundamental views • Lines – – – – seen in true length (TL) if parallel to projection plane seen as a point if perpendicular to projection plane an inclined line is seen in TL in one principal view an oblique line is foreshortened in all principal views TL TL Fundamental views • Planes – seen in true shape (TS) if parallel to projection plane – seen as a line if perpendicular to projection plane – an inclined plane is seen as a line (edge view) in one standard view – an oblique plane is ‘similar’ in all standard views TS edge view Summary of fundamental views Geometry Lines: • Point View • True Length (TL) view Planes: • Edge View • Dihedral angle view • True Shape (TS) view Projection plane • ⊥ to line • // to line • ⊥ to plane • ⊥ to plane • // to plane Auxiliary views • Often an object has significant features inclined to the principal projection planes • Primary auxiliary view – projection on to an auxiliary plane which is orthogonal to one of the principal projection planes • Secondary auxiliary view – the auxiliary plane is inclined to all the principal projection planes Top view Primary auxiliary view Front view Depth 1 True shape view of sloping surface Top view 2 Reference line = edge view of auxiliary plane 4 2 Front view th p De ry a i il x Au view Review • Principal views – projections onto principal planes of the orthographic box (top, front, left side, right side, back, bottom) – placed on one sheet of paper by unfolding top and sides about fold (or hinge) lines • Primary auxiliary view – projection onto an auxiliary plane which is orthogonal to a principal plane of the orthographic box – placed on drawing sheet by unfolding about fold (or hinge) line • Reference lines – represent edge views of projection planes (fold lines, or hinge lines) • Adjacent views – share a common reference line; hence are orthogonal to each other • Related views – share a common adjacent view (e.g., top and side views are related because they are both adjacent to the front view) – points in related views are at the same distance from their respective reference lines Rotation of elements to find true size • To find true size we can: – introduce an auxiliary projection plane parallel to the element of interest (a line or plane), or – rotate the element until it is parallel to a principal plane a1 b1r A True length of a line by rotation b1 1 Axis of rotation 2 a2 B Br TL b2 b2r Axis of rotation 120º Ø 11 m 15º Exam question Semester 1, 1998 120º Find TL and angle of guy wires to the ground 11 m 15º 120º 15º 1 3 a1 p1 O1 120º Ø 11 m b1 p3 1. PA by auxiliary view TL 1 2 TS of triangle PAO angle a3 o3 p2 11 m a2 o2 b2 15º 120º 15º a1 b1r p1 120º Ø 11 m b1 1 2 p2 2. PB by rotation TS of triangle PBO 11 m TL a2 angle o2 b2 b2r 15º A r1 q1 s1 p1 c1 d1 b1 B X a1 Simple shadow problem: Find true size and shape of shadow cast by B on A 10º Plan view 30º A r2s2 p2q2 d2c2 a2b2 A B Front elevation p3 s3 r3 q3 View on X Primary aux. view Another shadow problem: What is true size of shaded region of roof on A? 1. Find shadow limits 2. Edge view of roof plane (primary aux. plane 4 _|_ ridge) 3. Secondary aux. plane 5 parallel to roof plane 1 4 TL x4 y4 15º x1 TL 4 5 y1 x5 TS 1 y5 2 Secondary aux. view 35º x2 y2 A B Follow up • Read Bertoline: – Ch 11: Auxiliary views – Ch 12: Fundamentals of descriptive geometry • Do problems from Bertoline: – Probs 11.1(1)(6), 12.7-10