State Territorial Change & Spheres of Influence
advertisement
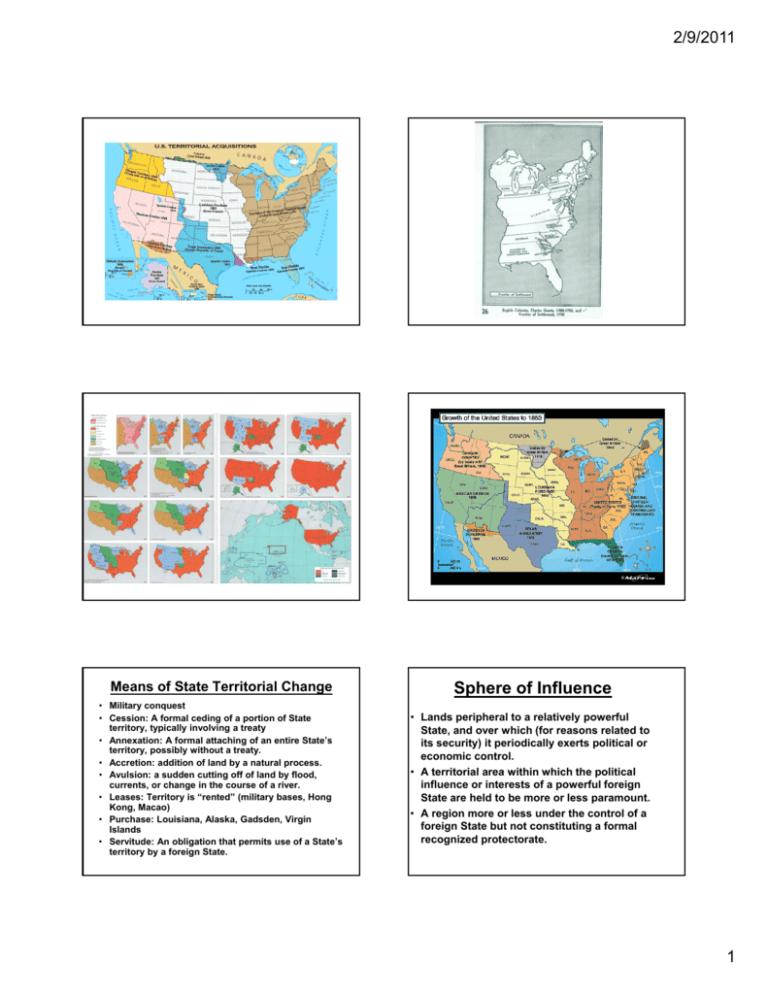
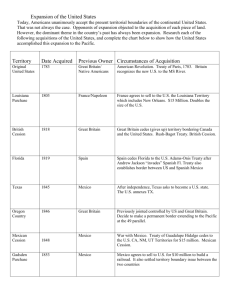
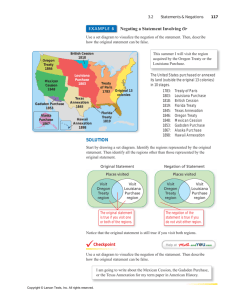
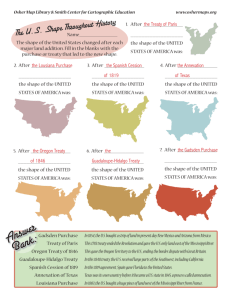
2/9/2011 Means of State Territorial Change Sphere of Influence • Military conquest • Cession: A formal ceding of a portion of State territory, typically involving a treaty • Annexation: A formal attaching of an entire State’s territory, possibly without a treaty. • Accretion: addition of land by a natural process. • Avulsion: A l i a sudden dd cutting i off ff off land l d by b flood, fl d currents, or change in the course of a river. • Leases: Territory is “rented” (military bases, Hong Kong, Macao) • Purchase: Louisiana, Alaska, Gadsden, Virgin Islands • Servitude: An obligation that permits use of a State’s territory by a foreign State. • Lands peripheral to a relatively powerful State, and over which (for reasons related to its security) it periodically exerts political or economic control. • A territorial area within which the political influence or interests of a powerful foreign State are held to be more or less paramount. • A region more or less under the control of a foreign State but not constituting a formal recognized protectorate. 1 2/9/2011 Guantanamo Bay • Largest harbor on south coast of Cuba • 1903 Cuban-American Treaty gives the U.S. a perpetual lease • U.S. regards it as part of its sovereign territory and uses it as a military base. • Cuba regards continued U.S. presence as illegal and the result of coercion. Treaty of 1818 The Spanish Cession, 1819 • Resolved boundary issues between the United States and the United Kingdom • Helped cement Lat. 49° North as a major portion of the future boundary with Canada. • U.S. acquired lands that would become part of ND, SD and MN. • U.S. also ceded land to what is now Canada. • Concerns U.S. acquisition of all of present-day Florida, plus parts of Alabama, Mississippi, Louisiana and Colorado. • Followed un-authorized invasion of Florida by Gen. Andrew Jackson on the pretext that Spain could not control its colony, thus allowing Seminoles and runaway slaves to harass the U.S. borderlands. • U.S. agreed to pay Spain up to $5 million to cover the claims of American citizens against Spain for damages related to the incursions. • Made official by the Adams-Onis Treaty, which redrew the border between the United States and New Spain. 2 2/9/2011 The British Cession of 1842 • The result of the Webster-Ashburton Treaty of 1842 • Used to resolve boundary issues between the United States and the United Kingdom related to map inaccuracies at the time of the Treaty of Paris, 1763 • A major focus was on lands now in Maine and Minnesota Mitchell Map, ca. 1755 Used to help draft the Treaty of Paris, 1763 Mexican Cession, 1848 • Large area formally transferred from Mexico to the U.S. by the Treaty of Guadelupe Hidalgo, following the Mexican War. • Technically purchased for $15 million (more than $300 million in today’s money, but written off to settle preexisting Mexican debts. Annexation of Texas, 1845 • Annexation of the Republic of Texas as the 28th State. • Led to war with Mexico (1846-1848) (1846 1848) and further U.S. expansion. • The culmination of years of negotiation between the U.S. and Texans, most of whom were Americans by birth. 3 2/9/2011 Cession vs. Annexation Hawaiian Annexation, 1898 (formal ceremony shown in photo) • Formerly the Republic of Hawaii • Overthrown with the help of the U.S. to prevent restoration of the monarchy and any possibility of Hawaii’s acquisition by a European power • 1993 U.S. Apology Resolution for overthrowing the government of a sovereign state. • In the case of cession, land is given or sold through treaty. • In the case of annexation, land is seized i d and d held h ld by b a foreign f i State St t and d made legitimate by the approval or recognition of an appropriate agency of that State and/or a recognized foreign body. Rockall Annexations since 1948 Ogaden (by Ethiopia) Rockall (by U.K.) Tibet (by PRC) Goa, Diu and Damao (by India) South Vietnam (by North Vietnam) East Timor (by Indonesia) Western Sahara (by Morocco) Jerusalem, West Bank, Golan (by Israel) Kuwait (by Iraq) Location of Rockall Acquisition of territory by purchase: a form of cession important to the expansion of the United States ---------• • • • The Louisiana Purchase,, 1803 (France) ( ) The Gadsden Purchase, 1853 (Mexico) The Alaska Purchase, 1867 (Russia) The Virgin Islands, 1917 (Denmark) 4 2/9/2011 Gadsden Purchase, 1853 • An area of Arizona and southwest New Mexico purchased from Mexico in 1853 for $10 million. • The brainchild of James Gadsden a South CaroGadsden, Caro linian railroad magnate who dreamed of a southern transcontinental railroad to make the West dependent on the South. • Appointed Minister to Mexico by Pres. Pierce. The U.S. Virgin Islands • Purchased from Denmark in 1916. • An organized, unincorporated U.S. territory. • Has an internal political structure and relation to the U.S. similar to those of Puerto Rico. A Meandering River A meandering river over time Top frame is the oldest Bottom frame is the most recent A Portion of the Mississippi River Boundary between the states of Mississippi (right) and Arkansas and Louisiana 5 2/9/2011 The Meander History of a portion of the Mississippi River Matters of shape and size Compact Prorupted Elongated Framented Namibia: A Prorupted State (Note The Caprivi Strip at top right of Namibia) Thailand An example of a prorupted State Indonesia and Its Provinces And Example of a Fragmented State 6 2/9/2011 Norway: An Elongated State Chile: An Elongated State The Philippines: A Fragmented State Enclave vs. Exclave • Enclave: A sovereign State or a portion of its territory that is enclosed within the lands of another State. portion of a sovereign g State • Exclave: A p separated from the main part, possibly constituting an enclave within a foreign State. • [Embassies and Consulates may be considered as either of the above.] Spain and its exclaves Ceuta and Melilla 7