NACHA Operating Rules:
What Do They Mean to You?
© 2015 NACHA — The Electronic Payments Association. All rights reserved.
No part of this material may be used without the prior written permission of NACHA. This material is not
intended to provide any warranties or legal advice and is intended for educational purposes only.
Agenda
• Who is NACHA and What is ACH?
• Originator Obligations for Authorization
and Authentication
• Authorization Requirements by SEC Code
• Resources
2
NACHA as Industry Association
• As a not-for-profit association, NACHA represents more than
10,000 financial institutions – some are Members directly, and
some are represented via 16 Regional Payments Associations
– Direct Financial Institution Members
– Regional Payments Associations
• Through its industry councils and forums, NACHA brings
together payments system stakeholders to foster dialogue
and innovation to strengthen the ACH Network
– Affiliate Program
– Risk Management Advisory Group
– Payments Innovation Alliance
– Government Relations Advisory
Group
– Communications & Marketing
Advisory Group
NACHA as Network Administrator
• ACH Logical Network
– ACH rules set, and associated
payment types and formats owned
by NACHA
– Allows counterparties to logically
and confidently pass transactions
to each other, knowing how they
will be recognized and dealt with
• NACHA holds the role of the
Network…
–
–
–
–
–
–
Administrator
Rules Creator
Rules Enforcer
Educator
Supporter
Protector
• ACH Physical Network
– The physical environment required to
move transactions
– The technology and communications
environment, and associated product
set, needed to initiate, clear and
settle ACH transactions between
counterparties
• ACH Operators take the role of…
– Processing and routing transactions
• Maintaining access to all sending and
receiving endpoints
• Inter-operator exchanges
– Services to help financial institutions
manage ACH volume and risk
management
– Interbank settlement
– Network reporting to NACHA
What is ACH?
AUTOMATED CLEARING HOUSE
Batch-oriented, store-and-forward
processing system
Safe, secure, electronic network
for consumer, business, and
government payments
Used by more than 11,000 participating FIs and millions of
businesses and consumers
What is ACH?
ACH Credit Payment: Entry and Funds Flow
Authorization
ACH Debit Payment: Entry and Funds Flow
Authorization
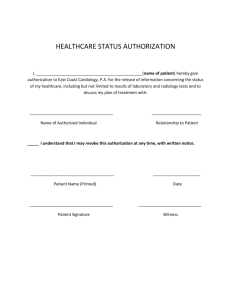
Authorizations
“An Originator must obtain authorization from
the Receiver to originate one or more Entries
to the Receiver’s account.”
2015 NACHA Operating Rules, Article Two, Subsection 2.3.1
9
Authorizations
• Authorization occurs when Originator and the
Receiver enter into an agreement to allow the
Originator to initiate a debit entry to the
Receiver’s account
• An authorization to debit an account is only valid
if the person who authorized the debit is an
owner on the account
• Requirements specified
in the Rules are
MINIMUM
requirements
10
Electronic Authorizations
• Similarly authenticated standard allows signed, written
authorizations to be provided electronically
• Writing and signature requirements in the NACHA
Operating Rules can be satisfied by compliance with the
E-sign Act (Electronic Signatures and Global National
Commerce Act)
• To satisfy Reg E and NACHA Rules,
must evidence both the customer’s
identity and assent to authorization should provide the same assurance
as a signature in the physical world
11
• Electronic authorizations must be
visually displayed in a way that
allows the consumer to read it
Corporate Authorizations
• Corporate Authorizations
– Business Receiver must authorize
all credits and debits
– Originator / Receiver must enter
into agreement with each
business receiver of ACH Entries
(other than ARC, BOC and POP
Entries to non-consumer
accounts)
– Agreement must bind the Receiver to the NACHA
Rules
12
Consumer Debit Authorizations
• Authorization must:
– Be readily identifiable
– Have clear and readily understandable terms
– Provide for revocation (for recurring payments or
payments scheduled in advance)
• Authorization should contain:
–
–
–
–
Express authorization language
Amount of transaction
The date(s) and/or frequency of the transaction(s)
The consumer’s account number and financial
institution’s routing number
– Account Type
• Authorization of a debit entry must be in writing and signed
or similarly authenticated, except where expressly provided
in the Rules for specific types of Entries
13
Consumer Debit Authorizations
Originators must:
• Provide the Receiver with electronic or hard copy of
Receiver’s authorization
• Retain the original or a copy for two years from
termination or revocation of authorization
• At the request of the ODFI, provide original or copy to
ODFI in such time and manner as to allow the ODFI to
deliver it to the RDFI within 10 banking days of the
RDFI’s request for a copy of the authorization
14
Consumer Debit Authorizations
• Notice of Change of
Amount
• Written notification of
amount and date
• No notice required for
change within agreed
upon range
• Notice of Change to
Scheduled Date
• Written notification of
new date
15
10 CALENDAR
DAYS
prior to debit date
7 CALENDAR
DAYS
prior to debit date
Authorization Requirements by SEC Code
PPD
Prearranged Payment or Deposit Entry
Written Authorization Credit or Debit
• Writing that is signed OR Receiver may similarly
authenticate the written authorization previously
delivered by Originator
• Example of similarly authenticated:
– Originator delivers written terms of authorization.
– Receiver authenticates agreement to terms of
authorization by key entering into a VRU or speaking to
a recorded line a PIN provided with the authorization
that identifies the consumer
• Proof of authorization would be a copy of the
written authorization and the consumer’s use of
the authorization code provided by the
Originator.
16
credit
debit
PPD
PPD
Authorization Requirements by SEC Code
TEL
Telephone Initiated Entry
Electronic Authorization (Similarly Authenticated) Debit Only
• Oral Authorization only
• Single Entry or recurring consumer
debits
• If no relationship exists, the
consumer must initiate the phone
call
• Record authorization and/or provide
written notice before settlement
17
TEL
Authorization Requirements by SEC Code
TEL
Telephone Initiated Entry
Electronic Authorization (Similarly Authenticated), Debit Only
• Minimum Authorization Information
– Date on or after which debit will occur (single) or timing –
including start date – number and/or frequency (recurring)
– Amount of the transaction(s) or method of determining amount
– Receiver’s Name and account to be debited
– Telephone number for Receiver inquiries
– Revocation method
– Date of oral authorization
– Statement by Originator that authorization is for single entry ACH
debit (single only)
• REMEMBER: Key entry on a VRU to input data and
respond to questions does not qualify as oral
authorization. Actual authorization must be oral.
18
Authorization Requirements by SEC Code
WEB
Internet/Mobile Initiated Entry
Electronic Authorization (Similarly Authenticated)
• Single or Recurring consumer debit and credit
entries
• Use when authorization was given via the
internet or entry was initiated via wireless
device
• Use for P2P – Credit WEB only for payments
exchanged between consumers
• Example of records of authorization
– Screen shot of authorization language and
date/time stamp of the Receiver log-in and the
authorization process that evidenced both the
consumer’s identity and assent to the authorization
19
WEB
Authorization Requirements by SEC Code
CIE
•
•
•
•
Consumer Initiated Entry
Electronic Authorization (Similarly Authenticated) Credit Only
Consumer is Originator
Used primarily for bill payment
Credits only (except for reversal)
Individual payments only
CIE
Authorization Requirements by SEC Code
RCK
Re-Presented Check Entry
Notice = Authorization, Debit Only
• Single entry debit initially presented as a paper check
• Consumer check must have been returned insufficient
or uncollected funds and be less than $2,500
• Limited to a combination of three presentments (paper
and ACH)
• Notice must be provided
RCK
21
Authorization Requirements by SEC Code
CCD
Corporate Credit or Debit
Written Authorization (recommended), Credit or Debit
• Single or recurring payments
• Agreement between trading
parties
• One addenda record
• Used for the distribution or
consolidation of funds intracompany or between two
corporate entities
CCD
Authorization Requirements by SEC Code
CTX
Corporate Trade Exchange Entry
Written Authorization (recommended) Credit or Debit
• Debit or credit transfer
between trading
partners, single or recurring
• Agreement between trading
parties
• May contain up to 9,999
addenda records
CTX
Authorization Requirements by SEC Code
ARC
Accounts Receivable Entry
Authorization = Notice + Receipt of Source Document, Debit Only
• Regular lockbox check converted into an
ACH transaction
• Must have been received through the mail
or at a drop-box or in-person for bill payment
• “When you provide a check as payment, you
authorize us either to use information from your
check to make a one-time electronic fund
transfer from your account or to process the
payment as a check transaction”
• Must post/place in prominent and conspicuous
location
24
CHECK
RECEIVED AT
LOCKBOX
ARC
Authorization Requirements by SEC Code
BOC
Back Office Conversion Entry
Authorization = Notice + Receipt of Source Document, Debit Only
• Requires written notice to Receiver prior to
receipt of each source document
• “When you provide a check as payment, you
authorize us either to use information from
your check to make a one-time electronic fund
transfer from your account or to process the
payment as a check transaction. For inquiries,
please call (retailer phone number).”
• Must post in prominent and conspicuous
location and provide copy of notice at the time
of transaction
25
CHECK IS RECEIVED AT
POINT OF SALE, BUT
CONVERTED
AT A LATER TIME
BOC
Authorization Requirements by SEC Code
BOC
Back Office Conversion Entry
Authorization = Notice + Receipt of Source Document, Debit Only
• Verification of Receiver’s Identity
– Must use commercially reasonable procedure to
verify the Receiver’s identity
– Examples include:
• Photo identification
• Retailer preferred card
• Check verification services
26
Authorization Requirements by SEC Code
POP
Point-of-Purchase Entry
Authorization = Notice + Receipt of Source Document AND
Written Authorization, Debit Only
• Merchant must provide notice and
consumer signs
authorization at point of purchase
• Check is scanned by merchant to capture
account information, voided, and returned
to the customer
• Must post in prominent and conspicuous
location and provide copy of notice at the
time of transaction
27
POP
Resources
• NACHA Operating Rules
– Board Policy Statements
– Formal Rules Interpretations
– Summary of Revisions from
previous year and any Supplements
– Operating Rules
• NACHA Operating Guidelines
– do not supersede the Rules but provide
additional information
Resources
1. Online Rules access
With full-featured search, bookmarking,
save search, and a host of FAQs!
www.achrulesonline.org
2. NACHA’s Website
–
–
–
–
Upcoming amendments
Proposed changes
eStore
News and education
www.nacha.org
QUESTIONS?
Danita Tyrrell, AAP
Director, Network Rules
NACHA-The Electronic
Payments Association
dtyrrell@nacha.org