* (” ) Ribosymes , ( ) * ” , , ,” ” ” *
advertisement

'*!#2&.)2 '!)!*+,
!"!#$%& '!()() '!)!*+,
,”+- %*.+!/ ,'!&0 '!!1
-2&!3 ,$!40+, !#24#!4 ,,”+02
2"2 '!.!#2&.)2 '!+2&#1
:'!*+,
/6#7)26 2, 82&#1 "”0-& *
(,”+0) Ribosymes (! #&, ,!+2&#1
'!!.!#.6 '!+-42+2
(9()$& -23) 02.*!#.6" ()() *
Chemical reactions and energy changes
reactants
If energy of reactants is greater
than energy of products, energy is
give out (released) during the
reaction: EXERGONIC
!"#$%&'(
products
If energy of reactants is less than
energy of products, energy is taken in
(absorbed) during the reaction:
ENDERGONIC
!"#$%)*(
reactants
INCREASING ENERGY
”!"#$%$&"'()”* +"#,$&
$!5&!.6, %!!40+, *
1%7)-#23+) *
#!37 0%, *
Km 2 Vmax *
'!!%201% '!&"3) *
'!!0./2#,2
Energy is released to
the surroundings
products
products
Energy is absorbed
from the surroundings
reactants
Reaction profile
Reaction profiles
transition state
following the course of a one-step exergonic
chemical reaction
(or activated complex)
e
n
e
r
g
y
bonds
breaking
activation
energy, Ea
reactants
bonds
forming
exergonic
reaction
e
n
er
g
y
reactants
exergonic
reaction
products
Course of reaction
Reaction profiles
following the course of a one-step endergonic
chemical reaction
products
e
n
er
g
y
products
Click for endergonic
exergonic
reaction
reactants
Replay Close window
”!"#$%$&"'()”* +"#,$&
$!5&!.6, %!!40+, *
1%7)-#23+) *
#!37 0%, *
Km 2 Vmax *
'!!%201% '!&"3) *
'!!0./2#,2
1%7) -#23+) %),%$
1%7) -#23+) %),%$
(...'!)37#)
ATP
O
O
P
O
O
O
P
O
P
O
N
O
O
P
O
O
P
O
O
H
H
OH
H
H
O
N
NH
N
N
O
O
GTP
NH2
N
O
N
O
O
O
P
O
NH2
O
O-
H
H
OH
H
H
H
N
H
ATPase:
ATP
GTP
X
ADP + Pi
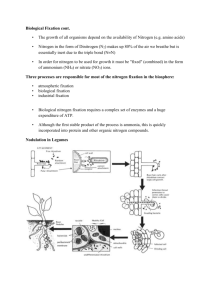
Nitrogen fixation
All living organisms need
nitrogen
• Nucleotides
• Amino acids
• Other bio-molecules
But, although earth atmosphere is 78% N2
most organisms can not use it, and need
fixed nitrogen - NH3, NO3, Urea etc.
3&26) 86+1# %2026) $(2#(
!)!" 8('2!" .('-, !-! $(3)) %!/1! (-1 *
.$-( !#2-!4& 86+1$) 18%"
Haber-Bosch 9!#$%& 052!) *
Fixed nitrogen can come from a
three sources
Fixed nitrogen can come from a
three sources
• Fertilizers
• Fertilizers
• Decaying bio-material
• Biological
Nitrogen Fixation
• Decaying bio-material
• Biological
#( %2!367
Nitrogen Fixation
!3&. 8(- - /2)02%
rhizobium
Nostoc
Fixed nitrogen can come from a
three sources
• Fertilizers +"",-$. +"/0"".* 1/(. 2$*"/
• Decaying bio-material
• Biological
Nitrogen Fixation
Azotobacter
Trichodesmium
2 3
N2+3H2->2NH
Fritz Haber (Nobel 1918) and Carl Bosch (1/2 nobel
1931)
Haber-Bosch process:
Mix gaseous H2 and N2 under:
* high temperature (~500oC)
* high pressure (~250 atmospheres, ~351kPa)
* In the presence of a catalyst (porous iron prepared by
reducing magnetite, Fe3O4).
(N2->NH3) $!+2),# 86+1 02*!1
!)0%2/6, 9!#$% ,2$
!42#2!& 86+1 32&!6
kJ/mol 92.4 !$!40+, 001()
$"2)+ $!40+, %)0& (NH3) 052%$( 822!"
(N2-2 H2) '!.0./&2/$) 0%2!
?!"#3() !*3! 45 %5 4"36 2$0& ')
• Only by bacteria (both archaea and eubacteria)
• It is done by the nitrogenase multi-protein complex
(NifH, D and K). A large protein hetro-oligomer
• Although energetically favorable, it is bib-energetically
expensive due to the very stable triple N N bond
N2+10H++8e-+16ATP -> 2NH4++ H2+16ADP*
*) As measure in-vitro
• Other triple bond substrates cyanide (H!C N), azide (N3;
both to NH3), and acetylene (HC CH) among others evolutionary origin?
• The complex contain multiple metal centers, Fe-S, Mo
etc. Also alternative complexes
2 3
N2+3H2->2NH
Fritz Haber (Nobel 1918) and Carl Bosch (1/2 nobel
1931)
Haber-Bosch process:
Mix gaseous H2 and N2 under:
* high temperature (~500oC)
* high pressure (~250 atmospheres, ~351kPa)
* In the presence of a catalyst (porous iron prepared by
reducing magnetite, Fe3O4).
Biological nitrogen fixation:
* 1 atm
* ~ room temperature
* Catalyst? = enzyme - Nitrogenase
!" #$%$&'( #$($)*"
$+,&*"- #'./(-
1/2 N2->N
e
n
e
r
g
y
activation
energy, Ea
3/2 H2->3H
N+3H>NH3
reactants
%20)# ,'2!$# 82"+
061+ *+420.!+$ /6#7)26(
2#( $#237$ 82+4+) ,%2&0
.020& !0)4# ,#
exergonic
reaction
1/2 N2, 3/2 H2
NH3
Course of reaction
'!)!*+,$ 9!, *,
”?$* %, '!(23“
”!"#$%$&"'()”* +"#,$&
$!5&!.6, %!!40+, *
2,0 - '!)37#) 1%7)-#23+) *
(*+420.!+
#!37 0%, *
Km 2 Vmax *
'!!%201% '!&"3) *
'!!0./2#,2
'!*2*!#
- .0./&2/
86!#42-!.77
(cleft) ”36(”& ,5)+ '!*2*!# #( #!37$ 0%,$
+"'()
352 52 ,”1 - #!37$ 0%,# &# 2)!(
82+4+)
$#237$
#(
'!*2*!#
+"'$'"% %, !%$2-! 1$(#(&
'!!.40+, '!#26!(
%!.)!*+, $!56,0# !#)!/ 425!
Enzyme + Substrate ⇌ ES ! E + Product
352 52 ,”1 - #!37$ 0%,# &# 2)!(
E + S ⇌ ES ! E + P