What to Know for the Evolution Test
advertisement

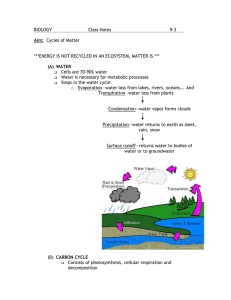
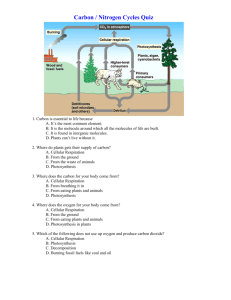
Biology 1st Semester Final Study Guide: DeBroux Scientific Method (Chapter 1) Hypothesis: measurable prediction and rationale Manipulated (independent) variable, responding (dependent) variable and controlled variables Be able to explain why it is critical that an experiment only test one manipulated variable at a time. Reliability and validity Know that to assess the reliability of your results your experiment needs to have multiple samples or repeated trials. Know that some methods for improving the validity of an experiment include having all the necessary controlled variables, controlling for sample bias, and improving measuring techniques. Ecology (Chapters 13 and 14) Biotic, abiotic, population, community, ecosystem, habitat, niche, trophic level Be able to define population density, know the formula and be able to calculate it and give the correct unit. Autotroph (producer), heterotroph (consumer). Types of heterotrophs: herbivore, carnivore, omnivore, decomposer Be able to define biodiversity and know that tropical rainforest typically have the highest level of biodiversity (for terrestrial biomes). Know that biodiversity contributes to the stability of an ecosystem. Energy pyramid. Explain why available energy decreases in a food chain (and how this is consistent with Law of Conservation of Energy) Exponential growth graph, logistic growth graph, carrying capacity Symbiotic relationships: mutualism, commensalism, parasitism Be able to explain the overall equation for photosynthesis, knowing the reactants and products. Know that glucose has greater energy than the reactants and that this chemical energy comes from sunlight. Know the overall equation for cellular respiration (reactants and products). Know that the purpose of cellular respiration is to use the chemical energy stored in a sugar molecule to produce ATP (the energy currency of the cell). Carbon cycle: know the basic cycling of carbon including the role of photosynthesis, cellular respiration and combustion and be able to explain the two causes for increasing carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Nitrogen cycle: know that all organisms need nitrogen to build DNA and proteins but that most organisms cannot use atmospheric nitrogen (N2). Know that nitrogenfixing bacteria can convert atmospheric nitrogen (N2) into nitrogen compounds that plants can use. Water cycle: including transpiration Be able to define eutrophication and explain the effects. Be able to define thermal pollution and explain the effects. Biomagnification of toxins Invasive species (also known as introduced species) Be able to define sustainability for resource use. Be able to define ecological succession. Evolution (Chapters 10, 11 and 12) Be able to explain the process of natural selection and give three requirements for natural selection. Know that the variation required for natural selection to occur results from random mutations in genes, which produces changes that may be harmful or beneficial. Be able to explain that an adaptation is a characteristic that makes a species suited for its niche, and is the result of natural selection. Divergent evolution and speciation (new species). Homologous structure and vestigial structure. Be able to define convergent evolution and explain why it would occur. Be able to define biochemical evidence for evolutionary relationships (DNA sequence of nucleotides and protein sequence of amino acids) and explain why this is considered to be the best evidence. Know why using anatomical comparisons to compare evolutionary relationships might be misleading. Be able to define coevolution and be able to identify examples. Chemistry of Life (Chapter 2) Know that water takes extra energy to heat compared to most substances and therefore resists temperature changes. Acids, bases (alkaline), pH scale Know the basic characteristics and possible functions of the following organic molecules: carbohydrates (monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides), lipids, proteins (building blocks= amino acid) Enzyme, active site, substrate. Know that each type of enzyme is specific to a certain chemical reaction. Understand that enzymes are not changed in the reaction so can catalyze the same reaction many times. Be able to explain the effect of temperature and pH on enzyme catalyzed reactions and why this occurs. Cells (Chapter 3 Sections 1 and 2) Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic cells Differences between plant and animal cells Be able explain the effect of increased size on the surface area to volume ratio (amount of surface area per unit of volume) and why the ratio changes. Effect of internal organization on maximum cell size Function and basic shape of the following organelles: plasma membrane, cell wall, cilia, nucleus, ribosome, flagellum, mitochondrion, chloroplast, rough ER and Golgi Be able to define the Endosymbiotic Theory