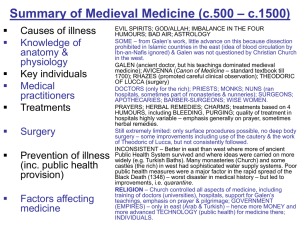
Medical Revolution - Revision

MEDICINE IN THE
INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION
1750-1900
REVISION NOTES
PROBLEMS FOR HEALTH AT THE
TIME OF INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION
People move from the countryside into big cities like Manchester and
London. ( URBANISATION )
Conditions in the new FACTORIES led to ill health eg POOR
VENTILATION and FIBRES in the air in cotton factories caused lung problems
Working with the UNGUARDED MACHINES often caused accidents eg children had to get inside the machines to fix the cotton threads
The new factories caused massive POLLUTION – of the AIR and WATER
– which damaged health
Workers’ houses were cramped and UNHYGIENIC . DISEASE SPREAD
EASILY
The new factory houses did not have modern facilities like RUNNING
WATER (it had to be got from a pump in the street)
Sewers and factory effluent ran into the rivers – CONTAMINATING THE
WATER SUPPLY.
There was LESS FRESH FOOD in the cities
WHY WAS SO MUCH PROGRESS
MADE (1)?
INDIVIDUALS – Work of RENAISSANCE thinkers such as VESALIUS and HARVEY did not help treatment in Renaissance period but helped
PAVE THE WAY for further DEVELOPMENTS. They proved ideas of
GALEN and HIPPOCRATES to be WRONG. The Medical Revolution witnessed the work of key individuals like Jenner, Pasteur, Koch, Hunter,
Nightingale, Garret-Anderson.
TECHNOLOGY – INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION began a RADICAL
CHANGE and led to following EFFECTS ON MEDICINE
Provided MONEY to use to tackle ill-health (eg BUILDING HOSPITALS)
Produced LARGE CITIES that became BREEDING GROUNDS for
KILLER DISEASES and EPIDEMICS – This had to be solved and led to
BREAKTHROUGHS
Improved KNOWLEDGE of how to build structures such as SEWERS and
WATER SUPPLIES
SCIENTIFIC DISCOVERIES – New DISCOVERIES led to
IMPROVEMENTS (such as GERMS CAUSING DISEASES)
INVENTION of NEW EQUIPMENT such as THERMOMETERS and SYRINGES
WHY WAS SO MUCH PROGRESS
MADE (2)?
COMMUNICATION – TRAVEL meant that SCIENTISTS could meet and DISCUSS NEW IDEAS EASIER THAN BEFORE
More EDUCATION and BOOKS could be spread around
QUICKER THAN BEFORE
GOVERNMENT – In 1800, politicians DID NOT CARE about
HEALTH AND MEDICAL PROBLEMS (Laissez-Faire)
With the middle classes getting the vote in 1832 and the working classes in 1867, they then had to.
By 1900, they took health
SERIOUSLY and PASSED A NUMBER OF LAWS to IMPROVE the HEALTH OF PEOPLE
WAR – The need to LOOK AFTER WOUNDED SOLDIERS (e.g.
Crimean War in mid C19th) led to BETTER HOSPITALS and
NURSING
INNOCULATIONS
Invented through OUTBREAKS of SMALLPOX that were responsible for up to 1/5 OF ALL
DEATHS
INNOCULATIONS were developed by LADY
MONTAGUE in 1721
People DELIBERATELY INFECTED themselves with a MILD FORM of SMALLPOX
Doctors used this idea during OUTBREAKS and it
WORKED!
HOWEVER!
INNOCULATIONS DID NOT ALWAYS WORK
SOME DIED from even a SMALL DOSE
EDWARD JENNER AND
VACCINATIONS
JENNER found that FARMERS often caught a disease called COWPOX – very MILD DISEASE
Those who got COWPOX never got SMALLPOX
JENNER took COWPOX from a girl and put it into a couple of cuts in a boy
The boy developed a MILD ILLNESS and then recovered.
JENNER then INNOCULATED the boy and he did NOT get SMALLPOX – this was REPEATED and it WORKED
JENNER’S VACCINATION was DEVELOPED and given through SYRINGES
SPREAD HIS IDEAS THROUGH BOOKS
GOVERNMENT gave JENNER £30,000 to set up a
VACCINATION CLINIC IN LONDON.
WHO WERE AGAINST
VACCINATION?
People were FRIGHTENED by the idea of being
INJECTED WITH DISEASE
Many DID NOT BELIEVE cowpox could protect you against SMALLPOX
DOCTORS resisted change as they were making
LOTS OF MONEY from INNOCULATIONS
VACCINATIONS had to be given CAREFULLY
Some DOCTORS ADMINSTERED the
VACCINATIONS INCORRECTLY
PASTEUR AND GERMS
BEFORE PASTEUR
People knew DISEASE was CONNECTED with DIRTY and UNHYGIENIC conditions
Thought that rubbish on streets gave off MIASMA (BAD AIR)
To stop getting the disease, people PROTECTED
THEMSELVES using HERBS AND MASKS
WHAT WAS DISCOVERED?
1.
GERMS were finally discovered in 1800s due to:
INVENTION OF MICROSCOPE
2.
3.
4.
5.
IMPROVED MICROSCOPES
LOUIS PASTEUR MAKES BREAKTHROUGH
1.
2.
Employed by a brewing firm to find out why alcohol went stale
Found TINY MICROBES in STALE BEER
DEFEATING SPONTANEOUS GENERATION THEORY
1.
PASTEUR attacked this theory by saying that MICROBES
WERE IN AIR AROUND US and caused food to ROT
LINKING GERMS WITH HUMAN DISEASE
1.
GERMS got into our bodies through CUTS or the MOUTH OR
NOSE
WHY WAS PASTEUR’S WORK
IMPORTANT?
BIG SCIENTIFIC BREAKTHROUGH
Found out what CAUSED DISEASE for the FIRST
TIME
Might be possible to TREAT DISEASES properly through VACCINATIONS
There were still some PROBLEMS
Each disease was caused by ONE TYPE OF GERM
This took TIME as there were MANY DIFFERENT TYPES
OF GERMS
FLORENCE NIGHTINGALE AND THE
DEVELOPMENT OF NURSING
In 1854 Britain went to war with Russia in the CRIMEAN WAR
The British army fighting in the Crimea had HARDLY ANY
MEDICAL SUPPORT – half of the soldiers wounded in battle died in hospitals
This was because the hospitals were DIRTY and there were NO
PROPER NURSES
When Florence arrived she RE-ORGANISED MILITARY
HOSPITALS
New wards were built
The wards were scrubbed and kept CLEAN
Sheets were BOILED to make them clean
PROPER FOOD was given to the soldiers.
Results -
The DEATH RATE for the wounded FELL from 42% to just 2%.
This was done through VERY SIMPLE MEASURES but also proper nursing
She became a HERIONE back in Britain where she was called
‘THE LADY WITH THE LAMP because of her night visits to the wards.
HOW NIGHTINGALE CHANGED
NURSING IN BRITAIN
CHANGES
She PUBLISHED A BOOK on improving army hospitals
1859 she published ‘Notes on
Nursing’ about how nurses should work in hospitals – she argued strongly for FRESH AIR,
CLEANLINESS, AND PROPER
FOOD
1860 she set up the FIRST
PROPER TRAINING SCHOOL
FOR NURSES– she trained
‘MATRONS’’ who would then train ordinary nurses
She helped set up a school for
MIDWIVES at Kings College
Hospital in 1861
Her work was reported in newspapers so she got GOOD
PUBLICITY
RESULTS
People were NO LONGER
AFRAID of being treated in hospitals. The SUCCESS RATE
HAD MASSIVELY IMPROVED
ATTITUDES to nurses changed – they were now PROPERLY
TRAINED AND RESPECTED
CHANGES IN TRAINING OF
DOCTORS
BEFORE 1750
Doctors were NOT WELL
TRAINED
Still trained by using the books of
GALEN – whose ideas were wrong (4 HUMOURS)
They RARELY did
DISSECTIONS of bodies to learn about them
You trained for years at
University
The you were accepted at the
‘Royal College of Surgeons’, the
‘Royal College of Physicians’
(physician = another word for doctor) or the ‘Society of
Apothecaries’ (APOTHECARY – someone who makes medicines – a CHEMIST)
BY 1900
Improvements in TECHNOLOGY
Improvements in the
UNDERSTANDING of disease.
Improvements in the understanding of ‘PHYSIOLOGY’
– how the human body works
Improvements in the TRAINING of doctors
Improvements in
COMMUNICATION – new ideas could spread
Work of individuals such as
JOHN HUNTER
Hunter felt that
EXPERIMENTS should be undertaken rather than reading books
New Medical schools were set up in major cities
Doctors began to use dissections to give better understanding of how body works
CHANGES
TO
TRAINING
Inventions such as stethoscope helped doctors improve
Pasteur’s Germ
Theory gave doctors better understanding
HOW DID HOSPITALS CARE FOR
THE SICK 1750-1900?
There were 300 ‘COTTAGE HOSPITALS – normally in your local area’ –Your own Doctor will provide you with
MEDICATION and you were then looked after by NURSES
There were also 18 hospitals in LONDON with 4000 BEDS
BUT – the chances of being treated or looked after depended on how RICH you were
Well off upper class or middle class people who had money would be treated AT HOME and the doctor would visit them
WORKING CLASSES like factory workers (who were the biggest group in Britain) COULD NOT AFFORD
DOCTORS OR TREATMENTS
Many ended up in WORKHOUSES
Conditions were POOR and you had to WORK but at least they would feed you and give you a bed.
WHY DID THINGS CHANGE?
In 1850s many EDUCATED people became concerned how poor working class people were being treated when they were ill –
Newspapers like THE TIMES ran a PUBLICITY
CAMPAIGN to do something for these people
1865 Louisa Twining set up the ‘WORKHOUSE
VISITING SOCIETY’ to campaign to get things
CHANGED
At the same time there was PUBLIC PRESSURE on LOCAL AUTHORITIES
The pressure groups were called ‘Poor Law Unions’
HOW DID THINGS CHANGE?
The GOVERNMENT finally took action to improve treatment for the poor
1867 it ordered the POOR LAW UNIONS to join together and build ‘INFIRMARIES’ (another name for a hospital) for poor people which had TRAINED DOCTORS.
They were paid for by the GOVERNMENT so the poor did not have to pay.
But there was still NOT ENOUGH SPACE in these new hospitals and many sick poor people had to stay in the
WORKHOUSE
Even so the new ‘infirmaries’ were the first real hospitals and founded the hospitals we use today
WHAT HELPED THE NEW HOSPITALS WORK
FLORENCE NIGHTINGALE’S work in TRAINING
NURSES – who now worked in the new hospitals
PASTEUR’S breakthrough in discovering GERMS
JOSEPH LISTER’S work on ANTISEPTICS
WHAT HELPED CHANGE BETWEEN
1750-1900?
CHANGE
Great amounts of change happened due to:
Breakthroughs by INDIVIDUALS –
JENNER, PASTEUR, KOCH,
NIGHTINGALE
ATTITUDES AND PUBLIC PRESSURE- usually from educated people for change and improvement eg the changes in the way poor sick people were treated
GOVERNMENT ACTION action – which responded to public pressure by building new hospitals and regulating pills and drugs
BUT – some people still RESISTED change due to ATTITUDES –
Some people did not like Jenner’s vaccinations and still would not take them.
Some people still refused to believe in
Pasteur’s germ theory and would not give up their old ideas
Many doctors still refused to adopt the new ideas because they had been trained in the old ideas
Many still refused to accept the important role women now played in medicine and as nurses in hospitals
CONTINUITY
The new ideas of Pasteur and Koch were still resisted by many old, traditional doctors
The poor were still not all looked after in the new system of hospitals – you still got better treatment if you had MONEY and doctors still charged HIGH FEES for their services
Medicines were MASS-PRODUCED but still based on OLD IDEAS about herbs and potions and NOT REALLY EFFECTIVE.
They were not yet based on SCIENTIFIC
IDEAS.