Earth History Exam: Relative Dating, Fossils, Geologic Time
advertisement
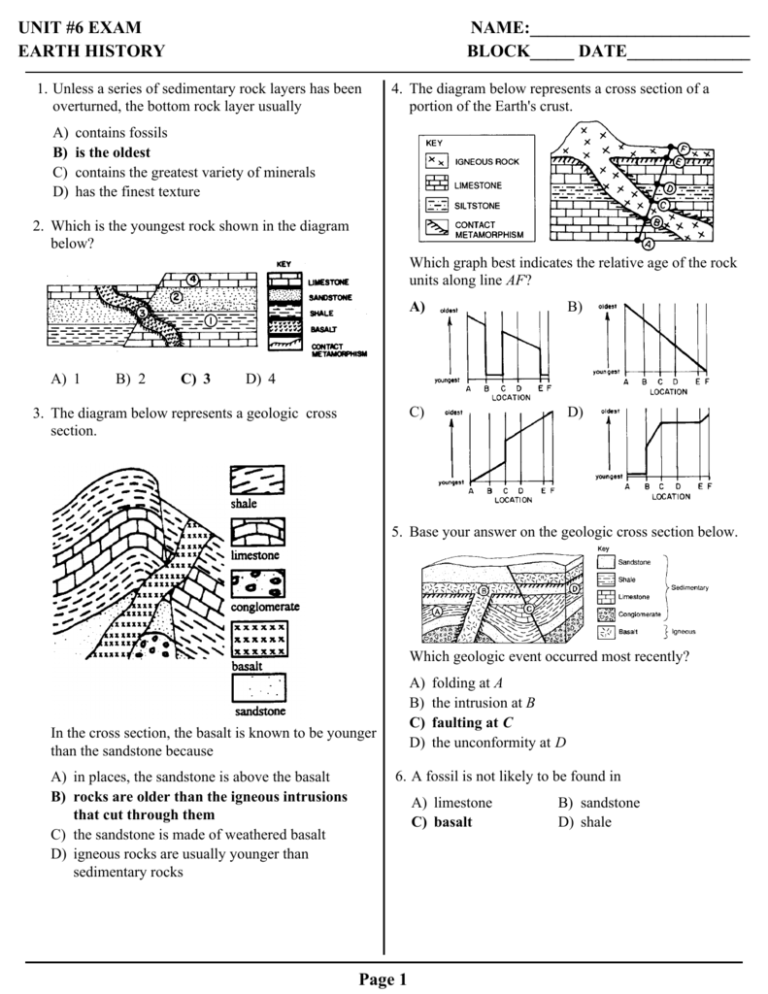
UNIT #6 EXAM EARTH HISTORY NAME:_________________________ BLOCK_____ DATE______________ 1. Unless a series of sedimentary rock layers has been overturned, the bottom rock layer usually A) B) C) D) 4. The diagram below represents a cross section of a portion of the Earth's crust. contains fossils is the oldest contains the greatest variety of minerals has the finest texture 2. Which is the youngest rock shown in the diagram below? Which graph best indicates the relative age of the rock units along line AF? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 A) B) C) D) D) 4 3. The diagram below represents a geologic cross section. 5. Base your answer on the geologic cross section below. Which geologic event occurred most recently? A) B) C) D) In the cross section, the basalt is known to be younger than the sandstone because A) in places, the sandstone is above the basalt B) rocks are older than the igneous intrusions that cut through them C) the sandstone is made of weathered basalt D) igneous rocks are usually younger than sedimentary rocks folding at A the intrusion at B faulting at C the unconformity at D 6. A fossil is not likely to be found in A) limestone C) basalt Page 1 B) sandstone D) shale 7. The geologic cross section below represents a cliff outcrop. Some bedrock layers are labeled as millions of years old (myo). Letters A through E represent different rock types. 10. Which characteristics of a fossil would make it useful as an index fossil in determining the relative age of widely separated rock layers? What is a possible age of igneous rock E? A) B) C) D) 1.5 million years old 12 million years old 28 million years old 40 million years old 8. What is the relative age of a fault that cuts across many rock layers? A) The fault is younger than all the layers it cuts across. B) The fault is older than all the layers it cuts across. C) The fault is the same age as the top layer it cuts across. D) The fault is the same age as the bottom layer it cuts across. 9. Which is the best method of determining the relative ages of a layer of sandstone in western North Carolina and a layer of sandstone in eastern North Carolina? A) Compare the thickness of the two layers. B) Compare the colors of the two layers. C) Compare the size of sand particles of the two layers. D) Compare the index fossils in the two layers. Page 2 A) a wide time range and a narrow geographic range B) a wide time range and a wide geographic range C) a narrow time range and a wide geographic range D) a narrow time range and a narrow geographic range Base your answers to questions 11 and 12 on the diagram below which shows three geologic columns representing widely separated rock outcrops. Letters A through E represent fossils found in the outcrops. Line XY represents a fault in column I. The layers have not been overturned. 11. Which rock would most likely be produced by the metamorphism of the grey limestone? A) quartzite B) slate C) marble D) gneiss 12. What is the oldest layer shown? A) glacial soil C) tan limestone B) brown sandstone D) grey limestone 13. In which way are index fossils and volcanic ash deposits similar? A) B) C) D) 15. Which life-form appeared first? Both can usually be dated with radiocarbon. Both normally occur in nonsedimentary rocks. Both strongly resist chemical weathering. Both often serve as geologic time markers. 14. For which segment of the Earth's geologic history are fossils rarely found? A) Cenozoic C) Paleozoic B) Mesozoic D) Precambrian Page 3 A) trilobite C) coelophysis B) human D) stromatolite 16. Base your answer to the following question on the geologic cross section below. Overturning has not occurred. The dike and sills shown in the cross section are igneous intrusions. Which feature is represented by symbol A along the edges of the dike and sills? A) contact metamorphic rock C) a glacial moraine B) an unconformity D) index fossils 17. The diagram below represents two geologic rock columns. The color and environment of deposition of each sedimentary rock are indicated beside the rock layers. Which rock layer in the West geologic column is most likely the same as rock layer X in the East column? A) A B) B C) C D) D 18. At which location in New York State would one least expect to find fossils in the surface bedrock? A) 42º N. 79º W. C) 44º N. 74º W. B) 43º N. 76º W. D) 42º N. 75º W. Page 4 19. Base your answer to the following question on the geologic cross section below. The large cone-shaped mountain on Earth’s surface is a volcano. Letters A, B, and C represent certain rocks. Which statement correctly describes the relative ages of rocks A and C and gives the best supporting evidence from the cross section? A) B) C) D) A is younger than C, because A is a lower sedimentary rock layer. A is younger than C, because the intrusion of A metamorphosed part of rock layer C. A is older than C, because A has older index fossils. A is older than C, because the intrusion of A cuts across rock layer C. 20. Trilobite fossils may be found in Cambrian rocks. Which statement best explains why trilobite fossils are missing in Triassic rocks? 21. What great orogeny (mountain-building episode) occurred in New York State during the Devonian time period? A) Trilobites became extinct before Triassic time. B) Sedimentary rock did not form during Triassic time. C) Widespread volcanic activity during Triassic time melted Triassic trilobite fossils. D) Uplift and erosion destroyed Triassic trilobite fossils. Page 5 A) B) C) D) Taconian Orogeny Grenvillian Orogeny Alleghenyan Orogeny Acadian Orogeny 22. Base your answer to the following question on the geologic cross section below in which overturning has not occurred. Letters A through H represent rock layers. The folding of rock layers G through C was most likely caused by A) erosion of overlying sediments C) the collision of lithospheric plates B) contact metamorphism D) the extrusion of igneous rock 23. Which column best represents the relative duration of the major intervals of geologic history? A) C) B) 24. The geologic columns A, B, and C in the diagrams below represent widely spaced outcrops of sedimentary rocks. Symbols are used to indicate fossils found within each rock layer. Each rock layer represents the fossil record of a different geologic time period. D) According to the diagrams for all three columns, which would be the best index fossil? Page 6 A) B) C) D) 25. The diagram below represents a cross section of rock layers. Along which line is a former interface between erosion and deposition most likely to be found? A) A B) B C) C D) D 26. When did armored fishes become extinct? A) B) C) D) before the appearance of dinosaurs before the appearance of terrestrial plants after the appearance of reptiles after the appearance of birds Page 7 27. Base your answer to the following question on the diagrams of fossil trilobites shown below. The geologic period in which each trilobite form existed is given. The diagrams below show different geologic cross sections of rock layers in the Earth's crust. Which cross section best shows the relative location of these four types of trilobites if overturning of the rock layers has not occurred? A) B) C) D) 28. An unconformity between two sedimentary layers is most likely produced by A) the deposition of gravel followed by the deposition of sand and silt B) continuous sedimentation in a deep basin over a long period C) uplift followed by extensive erosion, submergence, and deposition D) a period of extrusive vulcanism followed by another period of extrusive vulcanism 29. The changes observed in the fossil record from the Precambrian Era to the Cenozoic Era best provide evidence of A) sublimation C) evolution B) radioactive decay D) planetary motion 30. How many million years ago did the surface bedrock under Watertown, New York, form? Page 8 A) 345 to 395 C) 435 to 500 B) 395 to 435 D) 500 to 570 31. Base your answer to the following question on the map below. The map represents the movement of tectonic plates that resulted in the collision of India with Asia. Scientists believe that 71 million years ago, India was at position A. Which life-forms were living on Earth when India was at position A? A) humans C) trilobites B) dinosaurs D) armored fishes 32. Why are radioactive materials useful for measuring geologic time? A) The disintegration of radioactive materials occurs at a predictable rate. B) The half-lives of most radioactive materials are less than five minutes. C) The ratio of decay products to undecayed material remains constant in sedimentary rocks. D) Measurable samples of radioactive materials are easily collected from most rock types. Page 9 33. Base your answer to the following question on the block diagram and the cross section below. The block diagram shows the present position of Niagara Falls in relation to the Niagara Escarpment. The cross section shows the general bedrock structure of present-day Niagara Falls. What is the approximate age of the Queenston shale? A) 97 million years C) 331 million years B) 220 million years D) 452 million years 34. Which radioactive element would a scientist most likely have used to date the age of a fossil that is 10,000 years old? A) potassium-40 C) uranium-238 B) carbon-14 D) rubidium-87 35. Which radioactive substance has the longest half-life? A) carbon-14 C) rubidium-87 B) potassium-40 D) uranium-238 Page 10 36. The diagram below shows a geologic cross section of 38. The element K 40 radioactively decays to Ar 40. The a region where no faulting has occurred. diagram below shows a model of the relative amounts of K 40 and Ar40 remaining after one half-life. Which diagram best illustrates the relative amounts of K 40 and Ar40 remaining after two half-lives? A) B) C) D) Which statement about the geologic history of the area is best supported by the evidence in the diagram? A) The rocks at A formed before those at B. B) The rocks at D folded after the deposition of rock layer B. C) A long period of erosion took place before the deposition of rock layer B. D) The major agent of erosion acting on the present surface is ice. 37. In the geologic cross section shown below, between which two layers is part of the rock record most likely missing? A) A and B C) C and D 39. Which graph best represents the relationship between the remaining mass of a radioactive element and time? B) B and C D) D and E Page 11 A) B) C) D) 40. Base your answer to the following question on the graph below which shows the rate of radioactive decay of element A and the rate at which decay product B is formed. According to the graph, what is the total percentage of radioactive element A present after 3 half-lives? A) 12.5% C) 75.0 % B) 25.0% D) 87.5% Page 12 Base your answers to questions 41 and 42 on the table below, which shows the results of a student's demonstration modeling radioactive decay. To begin, the student put 50 pennies heads up in a container. Each penny represented one radioactive atom. The student placed a top on the box and shook the box. Each penny that had flipped over to the tails up side was replaced with a bean that represented the stable decay product. The student continued the process until all of the pennies had been replaced by beans. 41. On the grid provided on your answer paper, graph the data shown on the table by following the steps below. a Mark with a dot each number of radioactive atoms (pennies) after each shake. Surround each dot with a small circle. The zero shake has been plotted for you. b Connect all the dots with a solid line. c Mark with an X the number of stable decay atoms (beans) after each shake. The zero shake has been plotted for you. d Connect all the X's with a dashed line. 42. Assume that each shake number represents an additional 100 years. State the half-life of the radioactive material in this model. Page 13 Base your answers to questions 43 and 44 on the newspaper article below. New Fossils Indicate Arctic Climate Used To Be Floridian The frigid Arctic regions were as warm as present-day Florida some 90 million years ago, according to researchers who found fossils of a crocodile-like animal in northern Canada. Six hundred miles from the North Pole, researchers from the University of Rochester found the fossilized remains of the champosaur, a toothy, 8-foot-long extinct crocodile. "We found a whole collection of fossils, from both young and adults," said scientist John H. Tarduno. "The champosaur is a cold-blooded animal that could not have survived in the current climate of the Canadian Arctic where the fossils were found," Tarduno said. Temperatures at the fossil site now routinely drop to minus 60 degrees Fahrenheit in the winter. When the champosaur lived there 86 million to 92 million years ago, winter temperatures rarely dropped to freezing and summer readings of 80 degrees were common. The cold-blooded champosaur depended on the environment for warmth and probably became immobile if the temperature was too cold. Most likely, the champosaur was too small to have migrated seasonally. A field team from the University of Rochester found the fossils in a layer of sandstone located above a layer of basaltic lava. 43. State the geologic time period in which the champosaur lived. 44. Explain why no champosaur fossils were found within the layer of basaltic lava. Page 14 Base your answers to questions 45 and 46 on the geologic cross section and graph provided below, which represents an outcrop of various types of bedrock and bedrock features in Colorado. 45. The shale and sandstone layers both contain fossilized leaves from the Fagopsis tree, an index fossil for the Oligocene Epoch. State a possible age for these rock layers, in million years. 46. Place the geologic events listed in order by numbering them from oldest (1) to youngest (4). __________The fault was formed. __________The shale was deposited. __________The vesicular basalt was formed. __________The sandstone was deposited. Page 15 Base your answers to questions 47 through 49 on the cross section provided in your answer booklet. The cross section represents a portion of Earth’s crust. Letters A, B, C, and D are rock units. 47. Igneous rock B was formed after rock layer D was deposited but before rock layer A was deposited. Using the contact metamorphism symbol shown in the key, draw that symbol in the proper locations on the cross section provided above to indicate those rocks that underwent contact metamorphism when igneous rock B was molten. 48. In relation to rock units A and B in the cross section, when was igneous rock C formed? 49. Describe one observable characteristic of rock A that indicates that rock A is sedimentary. Page 16 50. Base your answer to the following question on the information and diagram below. The diagram represents a cliff of exposed bedrock that was investigated by an Earth science class. After the students examined the cliff, they made three correct inferences about the geologic history of the bedrock. Inference 1: The shale layer is older than the basaltic intrusion. Inference 2: The shale layer is older than the sandstone layer. Inference 3: An unconformity exists directly under the shale layer. Explain how each inference is supported by evidence shown in the diagram. Page 17 Answer Key Earth History Unit Exam 2011 1. B 36. C 50. 2. C 37. A 3. B 38. D 4. A 39. A 5. C 40. A 6. C 41. 7. B 8. A 9. D 10. C 42. 100 years 11. C 43. 12. D The Cretaceous Period 13. D 44. 14. D 15. D 16. A 17. B Examples: The basalt is older than 92 million years. Fossils are not normally found in igneous rock. 18. C 45. 33.7 to 24 million years 19. B 46. 20. A 21. D 22. C 23. A 24. D 4-The fault was formed. 2-The shale was deposited. 3-The vesicular basalt was formed. 1-The sandstone was deposited. 25. B 26. A 27. D 28. C 29. C 30. C 31. B 32. A 33. D 34. B 35. C 47. 48. examples: – C was formed before both B and A. – C is older than both B and A. 49. – Rock A is a mixture of rounded rock fragments of different sizes connected together. – Rock A is a horizontal layer. Page 18 (essay) Answer Key Earth History Unit Exam 2011 50. Inference 1 examples: – An igneous intrusion is younger than the bedrock it intrudes. – The basalt metamorphosed the shale. Inference 2 examples: – The shale layer is below the sandstone layer. – Younger sedimentary bedrock is normally found on top of older sedimentary bedrock. Inference 3 examples: – The limestone layers are folded and tilted but the shale layer is not folded and is horizontal. – The shale layer is not metamorphosed by the granite. – There is an irregular (erosional) surface between the shale and the limestone.






