part a Body Composition
advertisement

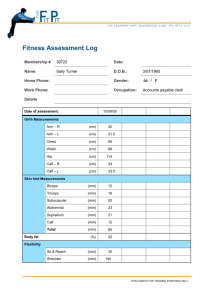
Physiotherapy – Fitness Testing and Prescription Lab Part A Body Composition (25 points) Body Composition Several methods are currently used to determine body fatness or percent body fat including: • Simple methods (Ht/Wt charts; Body Mass Index) • Hydrostatic weighing • Skinfolds and anthropometric measurements • Ultrasound • Photon absorption • Computed tomography • Infrared interactance • Electrical impedance • Total body electrical conductivity • Nuclear magnetic resonance imaging While the gold standard is still hydrostatic weighing, other models, which are based on a multiple compartment model, i.e. Dual energy x-ray absorbmetry – DEXA, are quickly emerging as accurate and reliable methods for the body composition analysis. Body mass index (BMI) We will be using skinfolds and body mass index as a means of measuring body composition. While body mass index (BMI) is simply based on height and weight (kg/m2) and is a simple, fast means of body composition measurement, it tells us little (nothing) about lean muscle mass or body fat percentage and makes most lean individuals overweight simply by definition. Below are standards for grading obesity using BMI, you may also find a nomogram in the ACSM Guidelines book. Body Mass Index (Weight (kg) / Height (m2) 20 – 24.9 Desirable 25 – 29.9 Overweight 30 – 40 Obesity > 40 Morbid Obesity Centers for Disease Control, Waist to Hip Ratio Waist to hip ratio is used to determine risk levels for various types of chronic disease including diabetes and coronary artery disease. A tendency to carry adipose around the torso predisposes an individual to high levels of LDL and glucose as well as hypertension (metabolic syndrome or Syndrome X). Male waist to hip ratio should be at or below 0.90 and females below 0.80. According the Centers for Disease Control guidelines, men are at if they have a waist measurement greater than 40 inches (102 cm) and women are at risk if they have a waist measurement greater than 35 inches (88 cm). Several investigators have shown that higher levels of adipose in the abdominal region are associated with insulin insensitivity, hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, and atherosclerosis. • • • The waist measurement is taken at the narrowest part of the torso (above the umbilicus and below the xiphoid process The hip measurement is taken at the maximal girth of the hips or buttocks region, whichever is larger (above the gluteal fold). Use the “cm” side of the tape measure. To obtain waist to hip ratio, simply divide the mean of the waist measures, by the mean of the hip measures. Skinfolds Skinfold measurement is still one of the most common means of body fat analysis. It is based on a twocompartment model and with proper technique, can be a reliable means of body fat estimation over time. Skinfolds have a relatively high reliability with hydrostatic weighing (r>0.8). This method is based on the assumption that most of total body fat is subcutaneous. This method is inexpensive and less time consuming than other methods, but may be inaccurate if the proper techniques are not used for assessment. Below I have given a brief explanation of the procedure as well as proper techniques to use when taking skinfolds. The key to this measurement as with any other is repetition, repetition, repetition! 1. Calipers - Calipers provide a constant tension applied to the fold by arms within certain spread of distance on jaws of the caliper. The most common and reliable brands are Lange® and Harpenden®. 2. Measurement Technique – a. Site – Making sure that the measurement is taken at the designated anatomical location, in the correction orientation is of utmost importance. Go through for pre-assessment and mark each site before beginning your measurement. Below are the site locations and orientation you will be measuring in this class. i. Biceps: Vertical fold on the anterior aspect of the arm over the belly of the biceps muscle, 1 cm above the level used to mark the triceps site ii. Subscapular: Diagonal fold (45), 1 to 2 cm below the inferior angle of the scapula. iii. Suprailliac: Diagonal fold: in line with the natural angle of the iliac crest taken in the anterior axillary line immediately superior to the iliac crest. iv. Triceps: Vertical fold; on the posterior midline of the upper arm, halfway between the acromion and olecranon processes, with the arm held freely at the side. v. Thigh: Vertical fold; midway between the superior patellar border and the hip, on the anterior portion of the femoris vi. Chest: Males – diagonal fold midway between the nipple and the anetcubetal head on the pectoralis major; Females - diagonal fold 1/3 of the way between the nipple and the anetcubetal head on the pectoralis major vii. Abdominal: Vertical fold one inch from the umbilicus viii. Midaxillary: Vertical fold, Midaxillary line, at the level of the xiphoid process b. Technique – All measurements should be taken on the right side of the body for standardization. • When taking a skinfold, you should hold the fold over handed, with your nondominant hand. The calipers should be placed directly below the fingers (~ .5 inches) at the marked point on the site. • Each site should be measured 2 to 3 times in a rotating fashion. If a subsequent measurement is more than 10% different from the preceding measurement, the site should be repeated a 3rd time. • The average of the 2 closest measurements should be taken as the number (mm) for that site. Body Composition Your Name ASSIGNMENT: 1. Find a subject between the ages of 18 and 25 (or low risk) who is not in this class to perform these measures on. 2. All subjects should be relatively sedentary, and all subjects need to complete a PAR-Q and Informed Consent before testing. If in doubt, please clear them through me. 3. These measurements will be used to develop an exercise program through out the semester for that individual. 4. Due by Dec. 3rd. I will check you off so that you can use this for your prescription. Body Composition Subject #1 Ht (in) Wt (kg) BMI (kg/m2) Waist circumference: Trial 1 Trial 2 Mean Hip circumference: Trial 1 Trial 2 Mean Waist-to-Hip Ratio Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 Site Triceps Subscapular Chest Midaxillary Abdominal Suprailliac Thigh SUM ------------- ----------- Mean of 2 closest trials ------------ Use Box 4-3 to determine body density (BD) and Table 4-4 to determine body fat. Carry body density (BD) to the 5th decimal place. Make sure to use correct equation, i.e. male/ female. Finally use Table 4-5 and 4-6 to determine percentile rank. Use the male/ female skinfold formulas as appropriate. BF (%) Seven Site Formula: BD Three Site Formula : BD BF (%) Three Site Formula : BD BF (%) Percentile Rank – 7 site (Table 4-3 and 4-4)-: Current Weight Desired BF% Goal Weight