Math 200 Formula Sheet: Statistics & Probability
advertisement
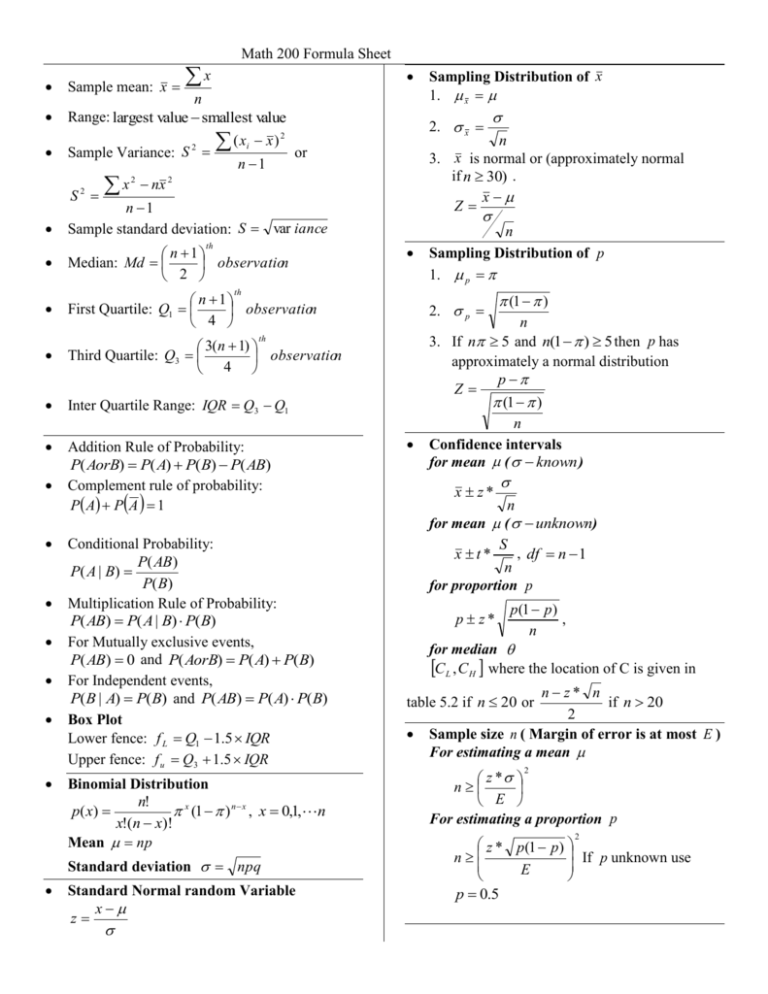
Sample mean: x n Range: largest value smallest value Sample Variance: S 2 S2 x Math 200 Formula Sheet x 2 nx (x i x) 2. x 2 n 1 Sampling Distribution of x 1. x n 3. x is normal or (approximately normal if n 30) . x Z or 2 n 1 Sample standard deviation: S var iance n 1 Median: Md observation 2 n 1 First Quartile: Q1 observation 4 3(n 1) Third Quartile: Q3 observation 4 Inter Quartile Range: IQR Q3 Q1 Addition Rule of Probability: P( AorB) P( A) P(B) P( AB) Complement rule of probability: P A P A 1 th n Sampling Distribution of p 1. p th 2. p th Conditional Probability: P( AB) P( A | B) P( B) Multiplication Rule of Probability: P( AB) P( A | B) P(B) For Mutually exclusive events, P( AB) 0 and P( AorB) P( A) P(B) For Independent events, P(B | A) P( B) and P( AB) P( A) P( B) Box Plot Lower fence: f L Q1 1.5 IQR Upper fence: f u Q3 1.5 IQR Binomial Distribution n! p ( x) x (1 ) n x , x 0,1,n x!(n x)! Mean np Standard deviation npq Standard Normal random Variable x z (1 ) n 3. If n 5 and n(1 ) 5 then p has approximately a normal distribution p Z (1 ) n Confidence intervals for mean ( known ) x z* n for mean ( unknown) S , df n 1 x t* n for proportion p p z* p (1 p ) , n for median C L , C H where the location of C is given in n z* n if n 20 2 Sample size n ( Margin of error is at most E ) For estimating a mean table 5.2 if n 20 or z * n E For estimating a proportion p 2 2 z * p (1 p ) If p unknown use n E p 0.5 Math 200 Formula Sheet Test Statistics for Hypothesis Testing: For a mean x 0 t df n 1 S n For a proportion p Z S 12 S 22 n n 2 1 df 0 (1 0 ) n Inferences about 1 2 (equal Variance) Confidence Interval 1 1 where x1 x2 t * S p n1 n2 Pooled variance is given by (n1 1) S12 (n 2 1) S 22 2 and df n1 n 2 2 . Sp n1 n 2 2 Test Statistics for pooled t-test x x2 d 0 t 1 df n1 n 2 2 1 1 Sp n1 n2 Paired data Confidence Interval S D t / 2 D df n 1 n Hypothesis Testing Test Statistics D d0 t df n 1 SD n 2 2 2 rounded down to the Test Statistics x x2 d 0 t 1 degrees of freedom as above. S12 S 22 n1 n2 Bivariate Data SS ( x) x nx x 2 i 2 2 x 2 2 i SS ( y ) y n y y 2 i i n y 2 2 i SS ( xy) xi yi nx y xi2 Correlation Coefficient r Inference about p1 p 2 Confidence Interval 1 n2 2 2 S S n n 1 2 n1 1 n2 1 nearest integer. 2 1 ( p1 p 2 ) z * S12 S 22 where n1 n 2 x1 x 2 t * p 0 Test Statistics p1 p 2 Z p (1 p ) n11 Inferences about 1 2 (unequal Variance) Confidence Interval SS ( xy) SS ( x) SS ( y) Regression: p1 (1 p1 ) p 2 (1 p 2 ) n1 n2 , where p x1 x 2 n1 n 2 yˆ b0 b1 x where SS ( xy) slope b1 , SS ( x) SS ( y) intercept b0 y b1 x i n x y i i n











