Units Of Measure Commonly Used In A Microbiology Laboratory
advertisement

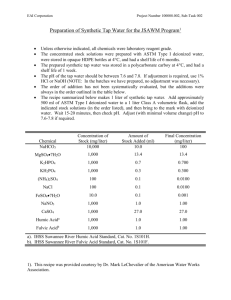
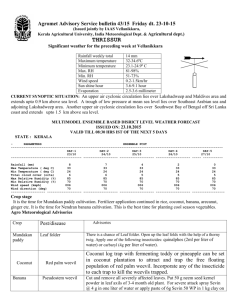
Units Of Measure Commonly Used In A Microbiology Laboratory Molarity (M): Molarity is the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. A 1M solution contains 6.023 x1023 molecules per liter. To calculate M, you need to know the molecular weight of the material. For Example: Glucose (dextrose), a carbohydrate, has a formula (molecular) weight of 180.16 g. This means that 6.023 x1023 molecules would weight 180.16 g. The molecular weight number comes from the formula for D-glucose: CH2OH(CHOH)4CHO 6 carbons @ 12 g each 72 12 hydrogens @ 1 g each 12 6 oxygens @ 16 g each 96 TOTAL 180 If you were to weight out 180.16 g of D-glucose and dissolve it in enough water to give a final volume of 1 liter, you would have a 1 M solution. [Note that solid material will contribute to the final volume of a solution. Therefore, it is important initially to dissolve the glucose in less than 1 liter and then add water to adjust the final volume to 1 liter (1000 ml).] More dilute solutions are written as follows: 1 mmole (millimole) 1 µmole (micromole) 1 nmole (nanomole) 1 pmole (picomole) 1 mM 1 µM 1 nM = 10-3 moles (1/1000 of a mole) = 10-6 moles (1/1000000 of a mole) = 10-9 moles (1/1000000000 of a mole) -12 = 10 moles (1/1000000000000 of a mole) = 10-3 M = 1 mmole/liter = 1 µmole/ml = 10-6 M = 1 µmole/liter = 1 nmole/ml = 10-9 M = 1 nmole/liter = 1 pmole/ml To make a 1 mM solution of D-glucose, you could weigh out 0.180 g (or 180 mg) of D-glucose and dissolve it in enough water to give a final volume of 1 liter, you would have a 1 mM solution. % Weight or Volume: The conventions above are the same for other measurements (i.e. grams): 1 gram 1 milligram = 10-3 g 1 µgram = 10-6 g Some recipes call for a certain percentage of material. For most purposes in microbiology, this will be a weight/volume (w/v) or volume/volume (v/v) recipe. A X% (w/v) means X grams per 100 ml A X% (v/v) means X ml per 100 ml For Example: A 10% (w/v) D-glucose solution contains 10 g in 100 ml of liquid (usually water). You can covert this to molarity (M) as follows: 10 g/100 ml is the same as saying 100g in 1000 ml (100 g per liter). Because a 1M solution of glucose is 180 g/liter, a 100 g/liter solution = 100/180 or 0.55 M solution of D-glucose. Therefore 10% (w/v) glucose is approximately equal to 0.55M glucose Summary Of Most Common Abbreviations weight (based on gram, abbreviated g) length (based on meter, abbreviated m) volume (based on liter, abbreviated l or L) DNA (based on base pairs, abbreviated bp) time (based on second, abbreviated sec) smaller----------------------------------to-------------------------------------larger 10-12 10-9 10-6 µ 10-3 103 K microg picog (pg) nanog (ng) millig (mg) g Kilog (Kg) (µg) microm millim (mm) m Kilom (Kg) (µm) microl l nanol (nl) milli (ml) (µl) (L) Kilobp bp (Kbp) nanosec microse millisec picosec (psec) sec (nsec) c (µsec) (msec)