AP U.S. History - Mr. Cain's US History Classes
advertisement

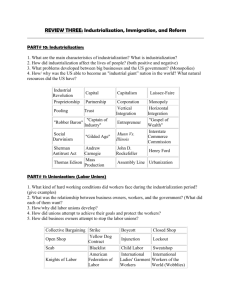
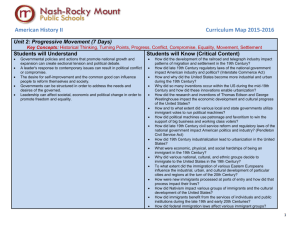
AP U.S. History Unit 6: The Gilded Age & the Progressive Era (1865-1916) Required Reading: Kennedy Chapters 23-26, 28, 29 (part); AMSCO 16-19, 21 Unit Test Date: Tuesday, February 2 COLLEGE BOARD KEY CONCEPTS 6.1) Technological advances, large-scale production methods, and the opening of new markets encouraged the rise of industrial capitalism in the United States. 6.2) The migrations that accompanied industrialization transformed both urban and rural areas of the United States and caused dramatic social and cultural change 6.3) The Gilded Age produced new cultural and intellectual movements, public reform efforts, and political debates over economic and social policies. 7.1) Growth expanded opportunity, while economic instability led to new efforts to reform U.S. society and its economic system. ACT QUALITY CORE STANDARDS C.1.A. Evaluate the impact of new inventions and technologies of the late 19th century. C.1.B. Identify and evaluate the influences on business in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. C.1.C. Identify labor and workforce issues of the late 19th century, including perspectives of owners/managers and Social Darwinists. C.1.D. Explain the challenges and contributions of immigrants of the late 20th century. C.1.E. Explain the causes and impact of urbanization in the late nineteenth century. C.1.F. Compare and contrast the experiences of African Americans in various U.S. regions in the late 19th century. C.1.G. Identify and evaluate the influences on the development of the American West. C.1.H. Analyze significant events for Native American tribes, and their responses, in the late 19th century. C.2.A. Identify and explain significant issues and components of the Populist movement and their impacts. C.2.B. Explain the origins and accomplishments of the Progressive Movement. C.2.C. Analyze the efforts to achieve women’s suffrage in the early 20th century. KEY TERMS For any 50 of the terms listed below, indicate the most specific date possible relative to the term, briefly describe which Thematic Learning Objective the term best fits with, and write a clear, concise statement detailing the term’s main idea and significance. Note – all terms on this list are important and are good examples to include when writing the Short Answer Questions, Long Essay, and DBQ on the AP Exam. Remember, key terms must be hand written on individual index cards. (1 point each; extra credit for completing more than 50) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 16th Amendment 17th amendment 18th Amendment 19th Amendment Alexander Graham Bell Alice Paul American Federation of Labor Andrew Carnegie Angel Island Anti-Saloon League Atlanta Compromise Barbed wire Benjamin Harrison Bessemer process Booker T. Washington Boss Tweed Bull-Moose Progressives Carrie Chapman Catt Chester Arthur Chinese Exclusion Act Clayton Anti-Trust Act Company towns Cornelius Vanderbilt Cowboys Coxey’s Army Crazy Horse 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. Credit Mobilier Scandal “Cross of Gold” speech Dawes Act Direct primaries Election of 1912 Ellis Island Eugene Debs Farmers Alliance Federal Reserve Federal Trade Commission Food and Drug Act George Custer George W. Carver Gospel of Wealth Grover Cleveland Haymarket Riot Homestead Act Homestead Strike Horatio Alger Horizontal integration Hull House Ida B. Wells Ida Tarbell Initiative (political term) Interstate Commerce Act of 1887 Interstate Commerce Commission 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. 69. 70. 71. 72. 73. 74. 75. 76. J.P. Morgan Jacob Riis James Garfield Jane Addams Jay Gould John D. Rockefeller Keating-Owens Child Labor Act Knights of Labor Little Big Horn Lochner v. New York Meat Inspection Act Muckrakers Munn v. Illinois National Association for the Advancement of Colored People National American Woman Suffrage Association National Labor Union Nativism Old/New Immigrants Pendleton Act of 1883 Plessy v. Ferguson Political machines Populist Party Progressivism Prohibition 77. 78. 79. 80. 81. 82. 83. 84. 85. 86. 87. 88. Pullman Strike (1894) Railroad Strike of 1877 Referendum Robert La Follette Rutherford B. Hays Samuel Gompers Sears & Roebuck Sherman Antitrust Act Silverites and Goldbugs Sitting Bull Social Darwinism Social Gospel 89. 90. 91. 92. 93. 94. 95. 96. 97. 98. 99. Square Deal Tammany Hall Teddy Roosevelt Tenements The Grange The Significance of the Frontier in American History Thomas Edison Thomas Nast Transcontinental Railroad Trust-busting Tuskegee Institute 100. United States v. E. C. Knight Co. 101. Upton Sinclair 102. Vertical Integration 103. W.E.B. DuBois 104. Wabash v. Illinois 105. William Howard Taft 106. William Jennings Bryan 107. Women’s Christian Temperance Union 108. Woodrow Wilson 109. Wounded Knee 110. Yellow-dog contracts CHAPTER QUESTIONS Chapter questions are designed to get you to extensively examine the main topics of each chapter while citing specific historical examples and evidence. These are required to be answered in 5-7 sentences each and must be hand written. (5 points each) Chapter 23 1. 2. 3. 4. Explain the rise of class conflict between business and labor in the 1870s and the growing hostility to immigrants, especially the Chinese. Describe the economic crisis of the 1870s, and explain the growing conflict between hard-money and soft-money advocates. What were the causes and political results of the rise of agrarian protest in the 1880s and 1890s? Why were the Populists’ attempts to form a coalition of white and black farmers and industrial workers ultimately unsuccessful? Chapter 24 1. 2. 3. 4. Describe how the economy came to be dominated by giant “trusts,” such as those headed by Carnegie and Rockefeller in the steel and oil industries AND what problems emerged as a result. Indicate how industrialists and their supporters attempted to explain and justify great wealth and increasing class division through “natural law” and the “Gospel of Wealth.” Explain social changes brought by industrialization, including the altered position of working men and women. What strains did the new industrialization bring to the American ideals of democracy and equality? Was the growth of huge corporations and great fortunes a successful realization of American principles or a threat to them? Chapter 25 1. 2. 3. How did the “New Immigration” differ from the “Old Immigration,” and how did Americans respond to it? Discuss the efforts of social reformers and churches to aid the New Immigrants and improve urban problems. Explain the areas of the growing national debates about morality in the late 19th century, particularly in relation to the changing roles of women and the family. Chapter 26 1. 2. 3. Explain the development and changes of federal policy toward Native Americans during the second half of the 19th century. Explain how westward settlement ultimately led to the “closing of the frontier” and what role technology and the federal government played in this development. Describe the economic forces that drove farmers into debt, and how the Grange, the Farmers Alliance, and the Populist Party organized to protest their opposition. Chapter 28 1. 2. 3. Explain how Progressivism was a response to the development of the new urban and industrial age in America. Explain the critical role women played in progressive social reform, noting some of the major women reformers. Compare the major policies and achievements of the three Progressive Presidents: Roosevelt, Taft, and Wilson. Chapter 29 1. 2. Discuss the key issues of the 1912 election and the basic principles of Wilsonian Progressivism. What were the results of Wilson’s great reform assault on the “triple wall of privilege”—the tariff, the banks, and the trusts?