hormones 2
advertisement

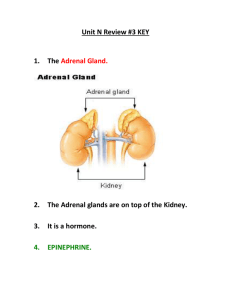
Hormonal coordination 2 Hormones produced by Anterior Pituitary and Hypothalamus Pituitary Pituitary (hypophysis) • Pea shaped structure 1-1.5cm diameter, • Attached to hypothalamus through a stalk (infundibulum) • Anterior pituitary • Posterior pituitary – contain axons Hypothalamus Neurons of Hypothalamus Pituitary stalk Posterior pituitary Anterior pituitary Anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis) • Secretes seven hormones • Five main types of cells in the Anterior pituitary Somatotrophs, thyrotrophs, gonadotrophs, lactotrophs, corticotrophs • Somatotrophs produce hGH • Thyrotrophs produce TSH • Gonadotrophs produce FSH & LH • Lactotrophs produce Prolactin • Corticotrophs produce ACTH & MSH hGH (human growth hormone) Most abundant pituitary hormone Target tissue: all body cells specially - bone, - cartilage, - liver - muscle Effects of hGH on target tissues 1. cause body cells to grow 2. regulate metabolism - stimulate protein synthesis & inhibits protein breakdown, - stimulate lipolysis, - slow down use of glucose for ATP production 3. Promote synthesis & secretion of “insulin like growth factors” (increase growth) Disorders associated with hGH • Pituitary dwarfism (under production of hGH during growth years,) slow bone growth, & other organs • Giantism (over production of hGH during childhood), abnormal increase in length of long bones • Acromegaly (over production of hGH during adulthood), bones of hands, feet, cheeks, jaws thicken, other tissues also grow, enlarged eye lids, lips, nose TSH (Thyroid stimulating hormone) • Target tissue : thyroid gland • Stimulate synthesis & secretion of thyroxin & triiodothyronin from thyroid gland FSH (follicle stimulating hormone) • Target tissues: ovary & testes • Ovary – Initiate development of follicles each month – Stimulate follicular cells to secrete estrogen • Testes – Stimulate sperm production LH (Luteinizing hormone) • Target tissues: ovary & testes • Ovary – together with FSH stimulate – secretion of estrogens by ovarian cells – Ovulation – Stimulate formation of corpus luteum in the ovary – Secretion of progesteron by corpus luteum LH (Luteinizing hormone) • Testes – Stimulates interstitial cells in testes to develop & secrete testosterone Prolactin • Target tissue : mammary glands • Effect: Together with other hormones, initiate & maintain milk secretion by mammary glands • Disorders: overproduction causes absence of menstrual cycles in females, impotence in males ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic hormone) • Target tissue : adrenal cortex • Effect: Stimulates adrenal cortex to produce & secrete glucocorticoid hormones MSH (melanocyte stimulating hormone) • Target tissue : melanocytes in the skin • Excessive MSH increases skin pigmentation Regulation of anterior pituitary hormones Regulation of secretion of anterior pituitary hormones 1. Hormones secreted by hypothalamus • • five hypothalamic releasing hormones, two release inhibiting hormones 2. By negative feed back from target endocrine gland hormones Hypothalamic releasing hormones 1. GHRH (growth hormone releasing hormone) –stimulate release of hGH 2. TRH (thyrotropin releasing hormone) – stimulate release of TSH & hGH 3. GnRH (gonadotropin releasing hormone) stimulate release of LH & FSH 4. PRH (prolactin releasing hormone) 5. CRH (Corticotropin releasing hormone) stimulate release of ACTH & MSH Hypothalamic release inhibiting hormones 1. GHIH (growth hormone inhibiting hormone) - inhibits release of hGH & TSH 2. PIH (prolactin inhibiting hormone) - Inhibits secretion of prolactin Hypothalamo-pituitary portal system • Releasing or release inhibiting hormones synthesized in hypothalamus and secreted by neuro-secretary cells of hypothalamus • They are carried in portal veins to anterior pituitary where they stimulate or inhibit secretary cells Neurons of the hypothalamus Median eminence Portal veins Hypothalamic hormones Ant. Pituitary hormones Endocrine cells of Ant. pituitary Ant. Pituitary hormones _ Higher brain centers _ Hypothalamic neurosecretary cells Two Release inhibiting hormones Five Releasing hormones _ Anterior pituitary hGH +/-, Prolactin +/MSH + Non-endocrine target tissue TSH +/-, ACTH + FSH & LH (+) Endocrine target tissue -ve feedback Hormones released by posterior pituitary • ADH, Oxytocin • Hormones synthesized by cell bodies of the neurosecretory cells in the hypothalamus • Axons of these neurons ends in posterior pituitary Hypothalamus Neurons of Hypothalamus Pituitary stalk Posterior pituitary Anterior pituitary Oxytocin Target tissues (During & after delivery of a baby) • Mother’s uterus-smooth musclesDuring delivery oxytocin enhances contraction of the wall of the uterus • Mother’s breasts-mammary glands Stimulates milk ejection from the mammary glands in response to the mechanical stimulation provided by the suckling infant ADH Target tissues • Kidney-distal convoluted tubules, collecting ducts reabsorb more water from the urine (decrease urine volume) • Sweat glands -decrease water loss by perspiration from skin • Arterioles-constrict arterioles which increase blood pressure