Europe before WW1 PDF - EAL Nexus
advertisement

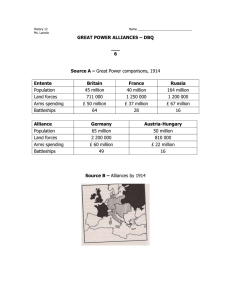
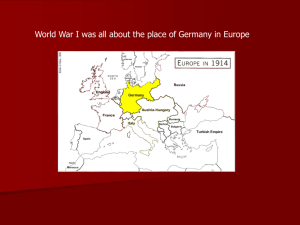
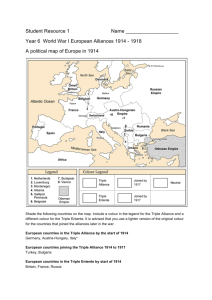
This project and its actions were made possible due to co-financing by the European Fund for the Integration of Third-Country Nationals EAL Nexus resource Events leading to World War I Europe before World War I Subject: History Age groups: 12–14, 15–16, 17–18 Topic: World War I Licence information | This resource is free to use for educational purposes. ©British Council 2014 Source | This resource was originally developed by Sabine Matzak and has been adapted by EAL Nexus. Words you need to know The opposite of peace is war If something is made up of three parts, it is called triple Materials needed in order to manufacture (make) goods you can sell (e.g. coal, iron, wood, wool, cotton) are called raw materials A country which is controlled by a more powerful country is a colony The head of state in the German Empire (1871–1918) was called the Kaiser A group of ships (e.g. in an army) is called a fleet A group of countries that are formally united and working together because they have similar aims is an alliance Somebody who inherits a title and the belongings of somebody who dies is their heir A written agreement between countries in which they agree to do a particular thing or to help each other is a treaty A formal word for taking something (e.g. an army or money) away or removing it is to withdraw To enter a country by force with an army is to invade Europe at the beginning of World War I Russia Germany France AustriaHungary Bulgaria Ottoman Empire Central Powers Triple Alliance Germany Austria-Hungary Italy (until 1915) after 1914 Bulgaria Ottoman Empire (Turkey) Allied Nations Triple Entente France Russia Britain (since 1904 with France and since 1907 with Russia) after 1914 Serbia, Montenegro, Belgium, Romania, Portugal, Greece, Italy Neutral countries Norway Sweden Denmark Netherlands Switzerland Spain Albania World leaders 1914 Triple Alliance Triple Entente • Germany: Kaiser Wilhelm II • France: President Raymond Poincaré • Austria: Kaiser Franz Josef I • Russia: Tsar Nicholai II • Italy: Vittorio Emmanuele III • Britain: George V The real causes of WWI Germany became a successful industrial power. Germany needed raw materials and wanted power. It competed for colonies with Britain, France and other colonial powers. The Kaiser was envious of the British fleet and started to build battleships. An arms race began. Europe split up in alliances. The events leading to WWI (1) The Austrian heir to the throne, Archduke Franz Ferdinand, was murdered by Serbian terrorists in Sarajevo (Bosnia). 28th June 1914 Germany Austria-Hungary declared war on backed AustriaHungary. Serbia. Russia backed Serbia. 28th July 1914 The events leading to WWI (2) Germany declared war on Russia. 1st August 1914 France prepared its army to support Russia. Germany declared war on France. Germany invaded Belgium. 3rd August 1914 The events leading to WWI (3) Britain, who had a treaty with Belgium, set Germany an ultimatum to withdraw from Belgium. Germany did not withdraw its troops. Britain declared war on Germany. 4th August 1914