Handout
advertisement

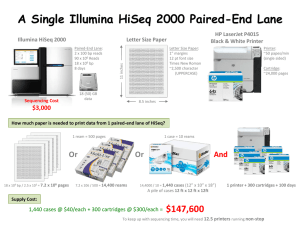
1/6/16 Big Data Why it matters Patrice KOEHL Department of Computer Science Genome Center UC Davis The three I’s of Big Data Big Data is: - Ill-defined (what is it?) - Immediate (we need to do something about it now) - Intimidating (what if we don’t) (loosely adapted from Forbes) Big Data: Volume Byte Kilobyte KB Megabyte MB 1000 bytes 1000 KB Gigabyte GB Terabyte TB Petabyte PB Exabyte EB 1000 MB 1000 GB 1000 TB 1000 PB Zettabyte ZB 1000 ZB Yottabyte YB 1000YB 1 1/6/16 Big Data: Volume One page One song One movie 6 million 55 storeys Data of text books of DVD up to 2003 5 MB 30KB 5 GB 1 TB 1 PB Data in 2011 NSA data center 1.8 ZB 1 YB 5 EB Byte Kilobyte KB Megabyte MB 1000 bytes 1000 KB Gigabyte GB Terabyte TB Petabyte PB Exabyte EB Zettabyte ZB 1000 MB 1000 GB 1000 TB 1000 PB Yottabyte YB 1000 ZB 1000YB Big Data: Volume One page One song One movie 6 million 55 storeys Data of text books of DVD up to 2003 5 MB 30KB 5 GB 1 TB 1 PB Data in 2011 NSA data center 1.8 ZB 1 YB 5 EB Byte Kilobyte KB Megabyte MB 1000 bytes 1000 KB 1s 20 mins 11 days Gigabyte GB Terabyte TB Petabyte PB Exabyte EB Zettabyte ZB 1000 MB 1000 GB 1000 TB 1000 PB 30 years 1000 ZB Yottabyte YB 1000YB 300 30 million 30 billion …. centuries years years Big Data: Volume, Velocity One minute in the digital world (Intel, 2013) 204 million 640 TB e-mails sent IP data transferred 50 GB of data generated at the Large Hadron Collider 3+ million searches launched 6 million users connected 30 hours videos uploaded 1.3 million videos viewed 2 1/6/16 Big Data: Volume, Velocity, Variety Numbers text Images sound Big Data: Challenges ! Volume and Velocity ! Variety ! Structured, Unstructured…. ! Images, Sound, Numbers, Tables,… ! Security ! Reliability, Integrity, Validity Big Data: Challenges Large N: “Any dataset that is collected by a scientist whose data collection skills are far superior to her analysis skills” Computing issues: " Data transfer " Scalability of algorithms " Memory limitations " Distributed computing 3 1/6/16 Big Data: Challenges Vizualization issues: The black screen problem (Matloff, 2013) Big Data: Challenges and Opportunities ! Fourth Paradigm: data driven science Basic Data Translational Knowledge Societal Benefit ! Holistic approaches to major research efforts ! New paradigms in computing ! Digital Humanities Big Data Dreams: Genomics 4 1/6/16 Big Data Dreams: Genomics Genomics: Sequencing costs $100,000,000 Cost per Mbase $1,000.00 $100.00 $10.00 $1.00 $0.10 $10,000,000 $1,000,000 $100,000 11 13 20 09 20 07 20 05 20 20 01 20 20 03 $0.01 $10,000 $1,000 $100 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 Cost per Human Genome $10,000.00 http://www.genome.gov Genomics: Game changing technologies Illumina HiSeq 2000 Capable of 600 Gb per run -> 1,000+ Gb 55 Gb/day 6 billion paired-end reads <$4,000 per human/plant genome <$200 per transcriptome Multiplex 384 pathogen isolates/lane ⇒ $10 (+ $50 library construction)/isolate Challenges: Library preparation & data analysis Gary Schroth (Illumina): “A single lab with one HiSeq is able to generate more sequences than was in GenBank in 2009, every four days”. 5 1/6/16 Genomics @ UC Davis Massively parallel DNA sequencing 2 Illumina Genome Analyzers 1 Illumina Hiseq 2000, 2 Miseq 1 Roche 454 Junior 1 Pacific Biosystems RS GoldenGate SNP genotyping iScan, BeadArray & BeadExpress Cancer Genomics: Molecular Diagnostics Genomics: actual costs “A single lab with one HiSeq is able to generate more sequences than was in GenBank in 2009, every four days.” Gary Schroth (Illumina) 6 1/6/16 Genomics: actual costs Assembling 22GB conifer genome: “A single lab with one HiSeq is able to generate more sequences than was in GenBank in 2009, every four days.” Gary Schroth (Illumina) Data: - 16 billion pair reads (100 bases) Processing: - 10 days for error correction - 11 days for assembling “super-reads” - 60 days to build contigs/scaffold - 8 days to fill in gaps http://www.homolog.us/blogs/2013/05/11/ steven-salzberg-at-bog13-assembling-22gb-conifer-genome/ Social Consequences of Commodity Sequencing ! The danger of misuse predict sensitivities to various industrial or environmental agents discrimination by employers? ! The impact of information that is likely to be incomplete an indication of a 25 percent increase in the risk of cancer? ! Reversal of knowledge paradigm ! Are the "products" of the Human Genome Project to be patented and commercialized? Myriad genetics and BRCA1/2 ! How to educate about genetic research and its implications? Social Consequences of Commodity Sequencing 7 1/6/16 Social Consequences of Commodity Sequencing How to Approach Big Data 8