Arduino Cheat Sheet: Pins, Code, and Functions
advertisement
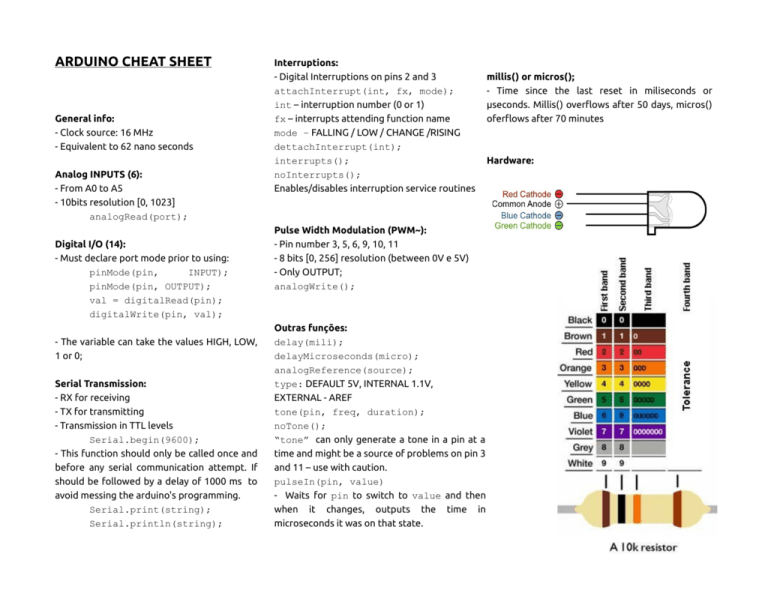
ARDUINO CHEAT SHEET General info: - Clock source: 16 MHz - Equivalent to 62 nano seconds Analog INPUTS (6): - From A0 to A5 - 10bits resolution [0, 1023] analogRead(port); Digital I/O (14): - Must declare port mode prior to using: pinMode(pin, INPUT); pinMode(pin, OUTPUT); val = digitalRead(pin); digitalWrite(pin, val); - The variable can take the values HIGH, LOW, 1 or 0; Serial Transmission: - RX for receiving - TX for transmitting - Transmission in TTL levels Serial.begin(9600); - This function should only be called once and before any serial communication attempt. If should be followed by a delay of 1000 ms to avoid messing the arduino's programming. Serial.print(string); Serial.println(string); Interruptions: - Digital Interruptions on pins 2 and 3 attachInterrupt(int, fx, mode); int – interruption number (0 or 1) fx – interrupts attending function name mode – FALLING / LOW / CHANGE /RISING dettachInterrupt(int); interrupts(); noInterrupts(); Enables/disables interruption service routines Pulse Width Modulation (PWM~): - Pin number 3, 5, 6, 9, 10, 11 - 8 bits [0, 256] resolution (between 0V e 5V) - Only OUTPUT; analogWrite(); Outras funções: delay(mili); delayMicroseconds(micro); analogReference(source); type: DEFAULT 5V, INTERNAL 1.1V, EXTERNAL - AREF tone(pin, freq, duration); noTone(); “tone” can only generate a tone in a pin at a time and might be a source of problems on pin 3 and 11 – use with caution. pulseIn(pin, value) - Waits for pin to switch to value and then when it changes, outputs the time in microseconds it was on that state. millis() or micros(); - Time since the last reset in miliseconds or µseconds. Millis() overflows after 50 days, micros() oferflows after 70 minutes Hardware: