International Logistics Management Overview
advertisement
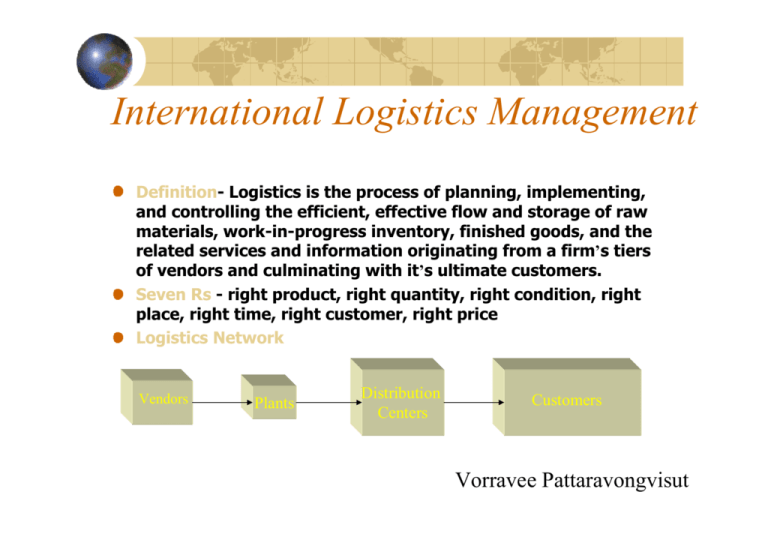
International Logistics Management Definition- Logistics is the process of planning, implementing, and controlling the efficient, effective flow and storage of raw materials, work-in-progress inventory, finished goods, and the related services and information originating from a firm’s tiers of vendors and culminating with it’s ultimate customers. Seven Rs - right product, right quantity, right condition, right place, right time, right customer, right price Logistics Network Vendors Plants Distribution Centers Customers Vorravee Pattaravongvisut What What is is aa Distribution Distribution Channel? Channel? A set of interdependent organizations (intermediaries) involved in the process of making a product or service available for use or consumption by the consumer or business user. Channel decisions are among the most important decisions that management faces and will directly affect every other marketing decision. Distribution Distribution Channel Channel Functions Functions Risk Risk Taking Taking Information Information Financing Financing Promotion Promotion Physical Physical Distribution Distribution Contact Contact Negotiation Negotiation Matching Matching Consumer Consumer Marketing Marketing Channels Channels & & Levels Levels Channel Level - A Layer of Intermediaries that Perform Some Work in Bringing the Product and it’s Ownership Closer to the Buyer. Channel 1 Direct Direct M M CC Indirect Indirect Channel 2 M M RR ฎ CC RR ฎ CC RR ฎ CC Channel 3 M M ฎ W W Channel 4 M M ฎ W W ฎ JJ ฎ Channel Channel Behavior Behavior & & Conflict Conflict The channel will be most effective when: each member is assigned tasks it can do best. all members cooperate to attain overall channel goals and satisfy the target market. When this doesn’t happen, conflict occurs: Horizontal Conflict occurs among firms at the same level of the channel. Vertical Conflict occurs between different levels of the same channel. For the channel to perform well, conflict must be managed. Types Types of of Vertical Vertical Marketing Marketing Systems Systems Greater Corporate Corporate Common Common Ownership Ownership at at Different Different Levels Levels of of the the Channel Channel Degree Degree of of Direct Direct Control Control Contractual Contractual Contractual Contractual Agreement Agreement Among Among Channel Channel Members Members Administered Administered Lesser Leadership Leadership is is Assumed Assumed by by One One or or aa Few Few Dominant Dominant Members Members Vertical Vertical Marketing Marketing Systems Systems Vertical Vertical Marketing Marketing Systems Systems (VMS) (VMS) Contractual Contractual VMS VMS Corporate Corporate VMS VMS Wholesaler Wholesaler Sponsored Sponsored Voluntary VoluntaryChain Chain Retailer Retailer Cooperatives Cooperatives ManufacturerManufacturerSponsored Sponsored Retailer Retailer Franchise FranchiseSystem System ManufacturerManufacturerSponsored Sponsored Wholesaler Wholesaler Franchise FranchiseSystem System Administered Administered VMS VMS Franchise Franchise Organizations Organizations Service-FirmService-FirmSponsored Sponsored Franchise FranchiseSystem System Channel Channel Design Design Decisions Decisions Analyzing Analyzing Consumer Consumer Service Service Needs Needs Setting Setting Channel Channel Objectives Objectives & & Constraints Constraints Identifying Identifying Major Major Alternatives Alternatives Intensive Intensive Distribution Distribution Selective Selective Distribution Distribution Exclusive Exclusive Distribution Distribution Evaluating Evaluating the the Major Major Alternatives Alternatives • Provide a Targeted Level of Customer Service at the Least Cost. • Maximize Profits, Not Sales. Higher Distribution Costs/ Higher Customer Service Levels Lower Distribution Costs/ Lower Customer Service Levels Logistics Logistics Systems Systems Order OrderProcessing Processing Costs Costs Submitted Submitted Processed Processed Shipped Shipped Minimize MinimizeCosts Costsof of Attaining AttainingLogistics Logistics Objectives Objectives Logistics Transportation Functions Warehousing Warehousing Storage Storage Distribution Distribution Water, Truck, Rail, Pipeline & Air Inventory Inventory When Whento toorder order How much to How much toorder order Just-in-time Just-in-time Transportation Transportation Modes Modes Rail Rail Nation’s Nation’slargest largestcarrier, carrier,cost-effective cost-effective for forshipping shippingbulk bulkproducts, products,piggyback piggyback Truck Truck Flexible Flexiblein inrouting routing&&time timeschedules, schedules,efficient efficient for forshort-hauls short-haulsof ofhigh highvalue valuegoods goods Water Water Low Lowcost costfor forshipping shippingbulky, bulky,low-value low-value goods, slowest form goods, slowest form Pipeline Pipeline Ship Shippetroleum, petroleum,natural naturalgas, gas,and andchemicals chemicals from fromsources sourcesto tomarkets markets Air Air High Highcost, cost,ideal idealwhen whenspeed speedis isneeded neededor orto to ship shiphigh-value, high-value,low-bulk low-bulkitems items Choosing Choosing Transportation Transportation Modes Modes Checklist for Choosing Transportation Modes 1. Speed. 2. Dependability. 3. Capability. 4. Availability. 5. Cost. Integrated Integrated Logistics Logistics Management Management Concept Recognizes that Providing Better Customer Service and Trimming Distribution Costs Requires Teamwork, Teamwork Both Inside the Company and Among All the Marketing Channel Organizations. Cross-Functional Cross-Functional Teamwork Teamwork inside inside the the Company Company Building Building Channel Channel Partnerships Partnerships Third-Party Third-Party Logistics Logistics Supply Chain Activities Demand Forecasting Order Processing Procurement Plant and Warehouse Site Location Warehousing and Storage Traffic and Transportation Production Planning Materials Handling Inventory Control Customer Service Industrial Packaging Distribution Communications Return Goods Handling Parts and Service Support Salvage and Scrap Disposal Supply Chain Management SCM entails managing the flow of material and information in a sequence beginning with supplier and ending with customers. For the purpose clarity and transparency the SCM sequence is often broken up into smaller segments beginning with inbound logistics (materials management), followed by operational logistics which concerns the issues while the goods are being produced, and ending with outbound logistic (customer service and distribution channels) Materials Management Functions Materials management concerns the planning and control of inbound materials, the work-in-process, and the storage of the finished goods. Typical activities include the following: Materials planning and control Procurement Transportation Material receiving Inbound quality control Inbound warehousing Production planning and control Outbound quality control Outbound warehousing Salvage and scrap disposal Procurement Activities Needs analysis Define user requirements Make or buy analysis Identify type of purchase (rebuy, modified rebuy, new buy) Market analysis on supply source Generate supplier list Prescreen suppliers Evaluate suppliers Select supplier Delivery and performance measurement Performance evaluation Vendor Selection Criteria Necessary Criteria Quality Reliability Capability Financial considerations Desirable Criteria Location Reputation Training Support Final selection of vendors can be facilitated by scoring vendors based on a factor-based scoring system Warehousing Issues in warehousing for inbound raw materials, sub-assemblies and supplies is similar to issues in warehousing outbound finished goods warehousing. They differ primarily in terms of the following: type of facility used value of material perish ability Production Planning and Control Demand Forecasting Production Scheduling- quantities, timing Resource Allocation machines labor material budget Transportation The transportation activities concern bridging the spatial and temporal gaps between the vendor and the firm and the firm and it’s customers. Some issue that need to be addressed include: control transportation mode rates and cost analysis routes carrier services claims handling Receiving and Quality Control Receiving Inspection- variance checking between order and shipment Physical damageclaims, legal issues Quality Control quality benchmarks variance measurement and analysis statistical quality control Channels of Distribution A series of cooperating entities who facilitate the flow of goods and services from the producer to the end user. Wholesaler, retailers, producers sales branches, agents, brokers etc are examples of such entities Primary benefits include cost efficiencies and customer convenience Conventional channel versus Vertical Marketing System Intensive, Exclusive and Selective Distribution Cooperation, conflict and Competition within and between channels People Training – Learning - Knowledge Team Work – Cross-Functionality Buy-in Management Workers Technological Information Substitution E-commerce E-logistics E-procurement Materials Substitution Greener Materials Packaging Advances Delivery Mechanisms











