Lab2 - Electrical and Computer Engineering
advertisement

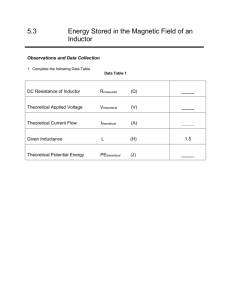
Lab #2 First Order Circuits Due: End of THIS Lab Session Name / SN:____________________________________ TA: __________ Name / SN:____________________________________ TA: __________ A) Pick up the following components from the TA: 1. 2. 3. 4. 100 resistor (1) 1K resistor (1) 100nF capacitor (2) 100mH inductor (1) B) Connect the capacitor and 1K resistor in series with a 5V power supply. 1. Measure the voltage across the resistor and capacitor and compute the current in the circuit. Ans: ____________________________________ Resistor Ans: ____________________________________ Capacitor Ans: ____________________________________ Current C) Replace the power supply with a signal generator. Set the signal generator to a 5Vpeak, 300Hz square wave. Adjust the offset so that Vmin=0. Adjust the duty cycle so that the signal stays high for 1ms. Use one scope probe to display the input signal and the other scope probe to display the voltage across the capacitor. TA: ____________________________________ 1. Compute the time constant. Read the time constant from the scope. Ans: ____________________________________ Computed Ans: ____________________________________ Measured ECE 251 - Circuit Analysis I Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering, UBC 2. Reduce the duty cycle as much as possible and adjust the frequency so that the on time is equal to 1x the computed time constant. Record the maximum voltage measured across the capacitor. Compute the percentage of the steady state voltage (the voltage across the capacitor if it were given a very long time to charge up). Ans: ____________________________________ Voltage Ans: ____________________________________ Percentage D) Use the RCL meter to measure the actual inductance of the inductor and the Multimeter to measure the resistance of the inductor. Replace the resistor and capacitor with the 100 resistor and the inductor. Repeat steps B and C. TA: ____________________________________ 1. Compute and measure all of the corresponding values. Ans: ____________________________________ Inductor Inductance Ans: ____________________________________ Inductor Resistance Ans: ____________________________________ Resistor Ans: ____________________________________ Inductor Ans: ____________________________________ Current Ans: ____________________________________ Computed Ans: ____________________________________ Measured Ans: ____________________________________ Voltage Ans: ____________________________________ Percentage 2. In this circuit, is it reasonable to model the inductor as an ideal inductor? Propose a more accurate ideal circuit model. Recompute using your new model. Ans: ____________________________________ Better Model Ans: ____________________________________ Computed ECE 251 - Circuit Analysis I Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering, UBC E) Make a voltage divider out of the two capacitors. Drive it with a 5Vpeak, 20KHz square wave. Use one scope probe to display the input signal and the other scope probe to display the voltage between the two capacitors. TA: ____________________________________ 1. Sketch the input waveform with the voltage divider connected and dis-connected. Explain why the two are not the same and whether or not capacitors make a good voltage divider. 2. Theoretically, you can also make a voltage divider out of two inductors. Would this make a better or worse voltage divider than 2 capacitors? Explain (assume near ideal behaviour). ECE 251 - Circuit Analysis I Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering, UBC