Method for Computation of Displacement by proper draught
advertisement
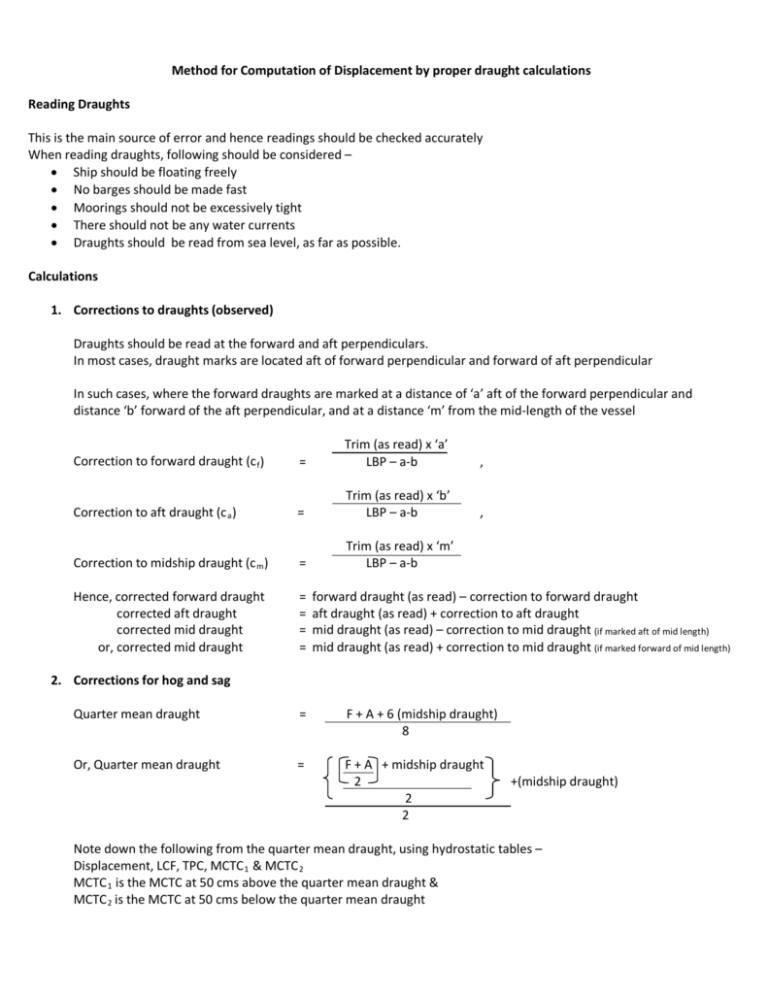
Method for Computation of Displacement by proper draught calculations Reading Draughts This is the main source of error and hence readings should be checked accurately When reading draughts, following should be considered – • Ship should be floating freely • No barges should be made fast • Moorings should not be excessively tight • There should not be any water currents • Draughts should be read from sea level, as far as possible. Calculations 1. Corrections to draughts (observed) Draughts should be read at the forward and aft perpendiculars. In most cases, draught marks are located aft of forward perpendicular and forward of aft perpendicular In such cases, where the forward draughts are marked at a distance of ‘a’ aft of the forward perpendicular and distance ‘b’ forward of the aft perpendicular, and at a distance ‘m’ from the mid-length of the vessel Correction to forward draught (c f ) = Trim (as read) x ‘a’ LBP – a-b , Correction to aft draught (c a ) = Trim (as read) x ‘b’ LBP – a-b , Correction to midship draught (c m ) = Trim (as read) x ‘m’ LBP – a-b Hence, corrected forward draught corrected aft draught corrected mid draught or, corrected mid draught = = = = forward draught (as read) – correction to forward draught aft draught (as read) + correction to aft draught mid draught (as read) – correction to mid draught (if marked aft of mid length) mid draught (as read) + correction to mid draught (if marked forward of mid length) 2. Corrections for hog and sag Quarter mean draught = F + A + 6 (midship draught) 8 Or, Quarter mean draught = F + A + midship draught 2 2 2 +(midship draught) Note down the following from the quarter mean draught, using hydrostatic tables – Displacement, LCF, TPC, MCTC 1 & MCTC 2 MCTC 1 is the MCTC at 50 cms above the quarter mean draught & MCTC 2 is the MCTC at 50 cms below the quarter mean draught 3. 1st trim correction ( from mean of mean draught – quarter mean draught – to hydrostatic draught) Hydrostatic draught is the correct draught at the center of floatation (i.e., center of water plane area) 1st trim correction = LBP – LCF 2 x trim x TPC x 100 LBP Apply 1st trim correction to Displacement to give Displacement at hydrostatic draught st 1 trim correction is (+) if trim is by stern and (-) if trim is by head 4. 2nd trim correction (for trim correction) 2nd trim correction = 50 x trim2 x (MCTC 1 - MCTC 2 ) LBP Apply 2nd trim correction to the obtained Displacement at hydrostatic draught 2nd trim correction is always (+) 5. Heel correction (for heel or list) Draught changes with heel / list. Since the vessel is ship shaped, the volume of immersed wedge is more than emerged wedge. But since displacement and density is the same, the ship rises up and draught reduces. Heel Correction = 6 (D 1 -D 2 ) ( TPC 1 -TPC 2 ) D 1 and D 2 are the corrected mid-ship draughts on the port and starboard sides TPC 1 and TPC 2 are the TPCs at draughts D 1 and D 2 , respectively. 6. Density correction (due to density difference between salt water and dock water) New displacement = Old displacement Old density ( = 1.025) x new density Old displacement is the displacement obtained after heel correction. Approved formula for calculation of constant 0.5% Deadweight + 0.05% (age of the vessel)