Interphase Before mitosis begins four events take place in

Interphase
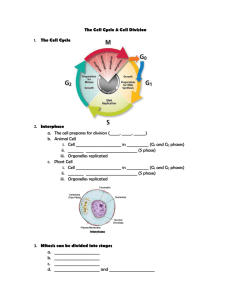
Before mitosis begins four events take place in interphase; the G1, S, and G2 phases. All of which are necessary for a successful mitotic division.
* Two centrioles located close to the nucleus have replicated, making two pairs of centrioles.
* Eukaryotic cells synthesis a large amount of the protein tubulin, which microtubules are made of.
More and more tubulin is made and all tubulin is extracted from the cell's cyotoskeleton. At this time up to ten percent of cell's protein may be tubulin.
* Every chromosome replicated in the S phase called daughter chromosomes or sister chromatids stay attached to one another by a structure called a centromere. The centromere circles the two sister chromatids with a ring of protein. Every replicated chromosome has one centromere.
* During replication the chromosomes are extended, uncoiled and not yet visible. In interphase the chromosomes begin the long process of condensation, slowly coiling tightly together.
Prophase
* Individual chromosomes become visible under a light microscope, while the condensation process continues. Main component of a chromosome is chromatin fiber which is made of coiled strings of
DNA. The chromatin fibers are about 25nm thick and contain nearly 400nm of double stranded DNA per helical turn.
* The two centriole pairs move apart, which forms an axis of microtubules between them, called spindle fibers.
* Centrioles continue to move until they reach the opposite poles of the cell. While the spindles are forming, the nuclear envelope breaks down. The spindle fibers can then extend across the entire cell.
The position of the spindle determine the plane in which the cell will divide.
* A second group of microtubules form and grow from each centromere to spindle poles.
* Two of those type microtubules grow out from every chromosome and then connect opposite sides of the centromere to the two poles.
Metaphase
* The microtubules grow and attach themselves on the chromosomes.
* Each chromosome is pushed and pulled by the microtubules so they line up on the equatorial plane or sometimes called the metaphase plate. The chromosomes are then facing opposing spindle fibers.
Anaphase
* Anaphase is the shortest phase of mitosis.
* The chromatid twins are all pulled apart by the spindle fibers, separating as free chromosomes. Each newly separated chromosomes quickly moves to the spindle pole that its microtubule is joined.
* The poles of the cell get moved apart. Sister chromatids are pulled to opposite poles by shortening the microtubules joined to them.
Telophase
* The spindle apparatus created in prophase dissolves completely.
* A new nuclear envelope forms around both sets of daughter chromatids, which are now chromosomes due to the separation in anaphase. The chromosomes then uncoil.
Cytokinesis
* Mitosis is complete at the end of telophase. At opposite sides of the eukaryotic cell, the cell has divided into two nuclei, each containing one set of the replicated genome.
The two nuclei are still enclosed within one cell.
* Cytokinesis is the phase when the physical division of the cell's cytoplasm into two daughter cells.
* In eukaryotic cells, cytokinesis completes through the cleavage of the cell into two nearly equal halves. There are two simple processes for cytokinesis; one for animal and other eukaryotic cells that don't have cell walls and one for plant cells.