Ecology & Biome Vocabulary
advertisement

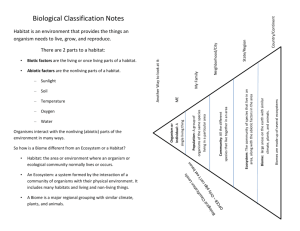
Ecology & Biome Vocabulary Create a table in your lab notebook with these headings. You will use the front and back of a page. There are vocabulary words underlined, the definition column should be the largest. You may choose to draw a picture or list examples. Word Definition Organism Any living thing Abiotic Not living Examples rocks, water, sun Biosphere Ecosystem Community Population Organism Levels of Ecological Organization - way of grouping like things ecologically Biosphere Parts of the Earth needed to support life, top portion of Earth’s crust, all waters on Earth and the surrounding atmosphere Biome Large area of land that has similar weather and organisms: examples include desert, tropical rainforest, freshwater, saltwater and grassland Ecosystem Consists of all the living and nonliving factors of the environment. Abiotic nonliving things in an environment (Never living); soil, water, temperature, wind. Air Biotic living or once living (dead) things in an environment; plants and animals. Community All the populations in an ecosystem (includes different species). Ex. All the seals, sharks, whales, and seaweed by a corral reef Population All organisms in an ecosystem that belong to the same species. (all the same kind of organism in an area) Ex. School of fish or a flock of birds Organism Any living thing. Ex. Plant, animal, fungi, bacteria etc. Producer Organisms (plants) that use the sun to make food (photosynthesis) Consumer Organism that cannot make their own food, eat other organisms. Decomposer: organism that breaks down wastes and dead plants and animals Plants use decomposer waste as fertilizer Fungi (mushrooms), bacteria, worms Habitat Where an organism lives Forest – habitat of a wolf Microhabitat – small habitat within a larger one Decaying tree – habitat for insects Niche How an organisms survives. • Obtains food & shelter • Finds mate & cares for young Adaptation A change developed over many generations that help an organism to survive. Animals depend on these features to help them obtain food, keep safe, build homes, withstand weather, and attract mates. Examples include: gills in fish, hollow bones in birds, xylem in plants, the shape of a bird's beak, color of the fur, the thickness of the fur, the shape of the nose or ears Biological Diversity, AKA Biodiversity Variety of organisms in an area • More Biodiversity = healthy or stable ecosystem, like Tropical Rainforest • Less Biodiversity = unstable or fragile ecosystem, like Tundra Biomes • 6 Major Terrestrial Biomes (land) – – – – – – Tundra Taiga Deciduous Forest Tropical Rain Forest Desert Grasslands • 2 Major Aquatic or Marine Biomes (water) – Salt Water (Ocean, Reef, Shoreline) – Fresh Water (Rivers, Lakes, Ponds, swamps) Make the headers below to fill in as each biome is discussed. Climate, plants, and animals should be the biggest columns. Biome Location Climate: Temperature, Rainfall, soil Plants Animals Tundra Located near North Pole (Alaska) Extremely cold Little precipitation, but limited drainage Soil is frozen, called “Permafrost” Low biotic diversity Simple vegetation (plants) Short season of growth and reproduction Treeless Plants: lichen, moss, grass, small shrubs Animals: insects and migratory birds in summer, hawks, snow owls, mice, arctic hares, reindeer Tundra Taiga (TI guh) Largest Biome South of the Tundra Long cold, snowy winters and Short warm, rainy, humid summers Plants: Coniferous forest (cone bearing) Animals: Moose, lynx, shrews, bears, foxes Deciduous Forest •Eastern U.S., Russia, Japan, New Zealand, Southeastern Australia •4 distinct seasons •Deciduous trees (have leaves that change color that they lose in the Fall) •Lots of decomposition on forest floor: insect diversity •Plants: Oak, maple, and hickory trees •Animals: Bald eagles, coyote, platypus, squirrel, deer Tropical Rain Forest Near the equator Warm temperatures and lots of precipitation Temperature doesn’t vary much night and day Little nutrients in soil because of competition of abundance of plant life Very diverse plants and animals (Coconut trees) Desert Driest Biome Rain quickly evaporates or drains away Animals: Few large animals, kangaroo rat, scorpions (Most nocturnal and burrowing because extreme temperatures Few plants: cacti, joshua tree Sandy soil with little organic matter Grasslands Located in mid and western U.S. Thin soil and a season with little rain Plants: grasses, small shrubs, few trees Animals: kangaroo, zebra, wildebeest, lion Freshwater Rivers, streams, creeks, lakes and ponds algae, moss, plankton, alligators, turtles Salt Water Ocean (Light & Dark zones), coral reef, seashore Starfish, crab, sharks, whales, fish, seaweed, kelp Intertidal zone Biome Collage • Choose a biome to draw and color. Include an example of each vocabulary word in your biome and label each word. – Biosphere – Ecosystem – Abiotic – Biotic – Community – Population – Organism – Producer – Consumer – Decomposer – Niche – Microhabitat – Adaptation Abiotic Biosphere Fresh Water Biome Population