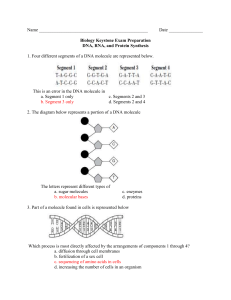
1. The diagram below shows part of a molecule of deoxyribonucleic
advertisement

1. The diagram below shows part of a molecule of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). C D B A (a) Name A, B, C and D. A ................................................................................................................................ B ................................................................................................................................ C ................................................................................................................................ D ................................................................................................................................ (4) (b) Analysis of a molecule of DNA showed that cytosine accounted for 42 per cent of the content of the nitrogenous bases. Calculate the percentage of bases in the molecule which would be thymine. Show your working. Answer............................................... (3) (c) During the process of transcription, one of the DNA strands is used as a template for the formation of a complementary strand of messenger RNA (mRNA). The diagram below shows the sequence of bases in part of a strand of DNA. DNA G C G T C A T G C mRNA 1 (i) Write the letters of the complementary bases in the boxes of the mRNA strand. (2) (ii) How many amino acids are coded for by this part of the strand of mRNA? .......................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 10 marks) 2. Describe the role of messenger RNA (mRNA) in the following processes. (a) Transcription .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (3) (b) Translation .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 6 marks) 2 3. The diagram below represents the structure of a transfer RNA (tRNA) molecule. Transfer RNA has a similar structure to messenger RNA (mRNA), but the single strand of nucleotides is folded back on itself. The folds are held in place by base pairing. B G G A A A Amino acid (a) List the four bases in the region labelled A which pair with those already shown. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) The three shaded bases in region B are responsible for binding to an mRNA molecule during translation. Give the name used to describe this group of three bases on the tRNA. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) 3 (c) Each amino acid is coded for by three bases on the mRNA molecule. Explain why a group of three bases is the smallest number that can be used to code for all of the amino acids found in proteins. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (d) The particular amino acid bound to a tRNA molecule depends on the three bases at position B. Explain why this is important during the translation of mRNA to form a polypeptide. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) 4 (e) In an experiment to investigate the role of tRNA in the synthesis of proteins, cells were exposed for a brief time to radioactively labelled amino acids. Samples of the cells were then removed at intervals over a period of 20 minutes, and the level of radioactivity associated with tRNA and protein was measured as counts per minute (cpm). The graph below shows the results of the experiment. 350 – Protein Level of radioactivity /cpm 300 – 250 – 200 – 150 – 100 – tRNA 50 – – – – (i) – – 0– 0 5 10 15 20 Describe the results shown in the graph. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... 5 (ii) Suggest an explanation for the changes in radioactivity found in protein over the first five minutes. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 12 marks) 4. The diagram below shows a stage in the process of translation during protein synthesis. This process is occurring on a ribosome. Amino acids Ribosome Amino acid 4 tRNA molecule 1 2 3 Anticodon GU A GGU AAA G C C AC G GG U Part of a messenger RNA molecule 6 (a) Describe the structure of a ribosome. ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... (2) (b) The table below shows the anticodons of some tRNA molecules and the specific amino acids that each one carries. tRNA anticodon Amino acid GGU Proline CCA Glycine AAA Phenylalanine CGA Alanine ACC Tryptophan UUU Lysine Using the information in the table, identify amino acids 2 and 3 shown in the diagram on the previous page. Amino acid 2 ......................................................................................................................... Amino acid 3 ......................................................................................................................... (2) 7 (c) During translation, amino acids are linked by a peptide bond. (i) Draw a diagram to show two amino acids linked by a peptide bond. (3) (ii) Name the type of reaction that occurs during the formation of a peptide bond. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 8 marks) 5. Protein synthesis involves transcription and translation. (a) (i) Where does transcription take place in a eukaryotic cell? ……………………………………………………………………………………… (1) (ii) Name the type of chemical reaction that occurs when a strand of messenger RNA is formed from individual nucleotides. ……………………………………………………………………………………… (1) 8 (b) The diagram below shows part of a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule. C (i) G A A C C G C C C G A A U C A C C What is the maximum number of amino acids coded for by this strand of mRNA? ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Complete the diagram below to show the sequence of bases on the strand of DNA that coded for this mRNA. (2) (c) A strand of mRNA was found to have 53 codons but the protein produced from it contained only 51 amino acids. Suggest two reasons for this difference. …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… (2) 9 (d) Describe the process of translation. …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… (5) (Total 12 marks) 10 6. During the process of protein synthesis in cells, the ribosome acts as a kind of ‘workbench’ where protein molecules are constructed. The diagram below shows a protein being formed on a ribosome. (a) Name the following structures shown on the diagram. P .................................................................................................................................. Q .................................................................................................................................. R .................................................................................................................................. S .................................................................................................................................. (4) 11 (b) Complete the following passage describing the process of protein synthesis by writing Leave the appropriate word in each space. blank Genetic information is stored in the nucleus of a cell as molecules of ................................................ . Protein synthesis occurs in the cytoplasm. Genetic information is first copied in the process of ................................................ , then leaves the nucleus in the form of molecules of ................................................ . In the cytoplasm these molecules pass to ribosomes to begin the process of ................................................ . At the ‘workbench’ on the ribosome ................................................ base pairing occurs. Adenine pairs with ................................................ and cytosine pairs with ................................................ . Adjacent amino acids are joined together by ................................................ bonds. (4) (Total 8 marks) 7. The diagram below shows part of a molecule of messenger RNA. G (a) A U C G U G On the diagram, draw a ring around a mononucleotide and label it with the letter M. (1) 12 (b) Messenger RNA is formed during protein synthesis by a process called transcription. Describe the events which occur during transcription. ....................................................................................................................................... ....................................................................................................................................... ....................................................................................................................................... ....................................................................................................................................... ....................................................................................................................................... ....................................................................................................................................... ....................................................................................................................................... ....................................................................................................................................... ....................................................................................................................................... ....................................................................................................................................... (5) (c) During translation, transfer RNA molecules line up against the messenger RNA molecule. The diagram below shows the structure of one transfer RNA molecule. A (i) G C State precisely where in the cell translation takes place. ............................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) On the diagram of the messenger RNA molecule above, draw a ring around the codon that this transfer RNA molecule would bind to. Label it with the letter C. (1) (Total 8 marks) 13 8. The function of a protein depends on its shape. (a) (i) Explain what is meant by the primary structure of a protein. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Explain how the primary structure of a protein is important in determining its shape. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (b) Explain why most enzymes are specific to only one substrate. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) 14 (c) Describe the process that converts a genetic sequence on messenger RNA into the primary sequence of a protein. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (4) (Total 9 marks) 15 9. Proteins have a wide range of functions in living organisms. The function of a protein is related to its precise three dimensional shape, which is determined by its specific sequence of amino acids. The diagram below shows a model of a typical protein molecule. (a) (i) Complete the diagram below to give the structure of the amino acid glycine. H C H (2) 16 (ii) Explain how a specific sequence of amino acids can form the precise three dimensional shape of a protein molecule. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (3) (b) The following DNA base sequence codes for part of a protein molecule. TACGGTATGCCAACCTTC (i) State the number of amino acids coded by this section of DNA. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Name the process involved in converting a base sequence of DNA into a base sequence of messenger RNA (mRNA). ........................................................................................................................... (1) (iii) Give the complementary mRNA sequence to the DNA sequence above. ........................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 9 marks) 17 10. (a) The diagram below shows the structure of a mononucleotide from a DNA molecule. A B Name the parts of the mononucleotide labelled A and B. A .............................................. B .............................................. (1) (b) The table below shows the percentage of different bases present in the DNA from two organisms. Percentage of each base present Organism Yeast Cow (i) Adenine Guanine Thymine Cytosine 31 19 31 19 29 Complete the table to show the percentage of adenine, guanine and cytosine in the DNA of a cow. (1) 18 (ii) Explain how you worked out the percentage of guanine present in the DNA of a cow. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (3) (c) DNA and messenger RNA (mRNA) have different properties. DNA is very stable but mRNA breaks down quickly and most of it will be broken down within a day of it being produced. Suggest why it is important for DNA to be more stable than mRNA. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) 19 (d) Protein synthesis involves transcription and translation. Describe the process of transcription. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (5) (Total 12 marks) 11. The diagram below shows some cell structures involved in protein synthesis in eukaryotic cells. Nucleus Rough endoplasmic reticulum 20 (a) Describe the events that occur inside the nucleus to produce a molecule of messenger RNA (mRNA). ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (4) (b) Describe the role of the ribosomes in protein synthesis. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) 21 (c) The table below gives some of the base triplets on DNA that code for some amino acids and stop signals. Base triplet on DNA Amino acid / stop signal CCC Glycine AAA or AAG Phenylalanine AGA or AGC Serine GCG Arginine TTT Lysine ATT or ATC or ACT Stop signal The diagram below shows the five base triplets of a gene, labelled T1 to T5, and the complementary messenger RNA (mRNA). The sequence of amino acids at the end of the protein produced is also shown. Last part of the DNA strand: T1 T2 T3 T4 CCC GCG AG C TTT T5 Complementary mRNA: Amino acid sequence: (i) Glycine – – – Write in the codons found on the mRNA complementary to the base triplets T1, T2, T3 and T4 on the diagram above. (2) (ii) Using the information in the table, complete the amino acid sequence shown in the diagram above. The first one has been done for you. (2) 22 (iii) Use the information in the table to suggest a base triplet for T5, on the DNA molecule. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 12 marks) 12. Some cells from the small intestine were placed in a solution containing amino acids. The diagram below shows the movement of these amino acids over a 15 minute period. Amino acids move through the cell surface membrane into the cells Amino acids found in the cytoplasm of the cells Amino acids found at ribosomes where they are joined together to form protein (a) (i) Name two mechanisms by which amino acids can move through the cell surface membrane. 1 ........................................................................................................................ 2 ........................................................................................................................ (2) (ii) Name the stage of protein synthesis that occurs at the ribosomes. ........................................................................................................................... (1) 23 (b) (i) If a protein formed at a ribosome is 300 amino acids long, state how many water molecules would be released during its synthesis. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Assuming that the start codon on mRNA is three bases long and the stop codon is also three bases long, calculate the minimum number of bases in the mRNA needed to code for a protein that is 300 amino acids long. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (c) Suggest two molecules, other than amino acids and water, that may be found at the ribosomes and that are involved in protein synthesis. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 7 marks) 13. The diagram below shows part of a DNA molecule. Y Z X Adenine W Cytosine 24 (a) (i) Name the parts of the molecule represented by each of the following letters. W ...................................................................................................................... X ...................................................................................................................... Y ...................................................................................................................... Z ...................................................................................................................... (4) (ii) Name the type of bond that holds the two strands of DNA together. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (b) The table below shows the amino acids coded by mRNA codons. Second base C A G UUU U UUC UUA UUG Phenylalanine Phenylalanine Leucine Leucine UCU UCC UCA UCG Serine Serine Serine Serine UAU UAC UAA UAG Tyrosine Tyrosine Stop Stop UGU UGC UGA UGG Cysteine Cysteine Stop Tryptophan U C A G CUU CUC C CUA CUG Leucine Leucine Leucine Leucine CCU CCC CCA CCG Proline Proline Proline Proline CAU CAC CAA CAG Histidine Histidine Glutamine Glutamine CGU CGC CGA CGG Arginine Arginine Arginine Arginine U C A G AUU A AUC AUA AUG Isoleucine Isoleucine Isoleucine Methionine ACU ACC ACA ACG Threonine Threonine Threonine Threonine AAU AAC AAA AAG Asparagine Asparagine Lysine Lysine AGU AGC AGA AGG Serine Serine Arginine Arginine U C A G GUU GUC G GUA GUG Valine Valine Valine Valine GCU GCC GCA GCG Alanine Alanine Alanine Alanine GAU GAC GAA GAG Aspartic acid Aspartic acid Glutamic acid Glutamic acid GGU GGC GGA GGG Glycine Glycine Glycine Glycine U C A G (i) Third base First base U Name the process by which mRNA is formed in the nucleus. ........................................................................................................................... (1) 25 (ii) Reading from left to right, what is the sequence of amino acids coded by the following length of mRNA? G A U C G U U G U A A G ........................................................................................................................... (1) (iii) A mutation occurred so that the base cytosine was replaced by guanine in this mRNA. Using the information in the table, explain why this mutation could affect the tertiary structure of the protein formed from this mRNA. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 10 marks) 14. (a) The statements in the table below refer to three biological molecules. If a statement is correct place a tick ( ) in the appropriate box and if a statement is incorrect place a cross ( ) in the appropriate box. Four boxes have already been completed for you. Statement Starch Glycogen Monosaccharide Is a polymer Glycosidic bonds are present Is an energy store in animal cells Has high solubility in water (4) 26 (b) The diagram below represents a polypeptide consisting of amino acids. State the minimum number of bases needed to code for this polypeptide along a strand of mRNA. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (c) Describe the key stages involved in protein synthesis, from the genetic code in the nucleus to the sequence of amino acids being assembled at the ribosome. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (5) 27 (d) Explain how the sequence of amino acids determines the shape of a protein. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 12 marks) 15. The diagram below summarises the steps involved in the semi-conservative replication of DNA. Double strand of DNA Step 1 Enzyme A Two strands separated Step 2 Complementary nucleotides line up against each strand Step 3 Enzyme B Nucleotides join to form two new polynucleotide chains Step 4 Two identical DNA molecules formed (a) Describe how Enzyme A separates the two DNA strands in Step 1. ……………………………………………….……………………………………… ……………………………………………….……………………………………… (1) 28 (b) In Step 3 the individual nueleotides are joined up to form a polynucleotide chain by Enzyme B. Name the type of reaction that Enzyme B catalyses. ……………………………………………….……………………………………… (1) (c) Give the phase of the cell cycle during which DNA replication occurs. ……………………………………………….……………………………………… (1) (Total 3 marks) 16. (a) Protein synthesis involves the process of transcription followed by translation. The diagram below shows part of a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule. It shows a sequence of seven bases. G (i) A U C G U G Name the pyrimidine bases shown in this sequence. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Write down the sequence of bases on the strand of DNA that coded for this messenger RNA. ........................................................................................................................... (1) 29 (b) In some prokaryotic cells, the production of mRNA during transcription can occur at a rate of 50 bases per second. Calculate how long it would take to produce a mRNA molecule that coded for a protein containing 200 amino acids. Show your working. Answer .................................... (3) 30 (c) Describe the process of translation. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (5) (d) In prokaryotic cells, a molecule of mRNA can be translated as soon as it is made. Suggest an explanation for this. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 12 marks) 31 17. (a) The diagram below shows a nucleotide with a nitrogenous base found in RNA but not DNA. E OH O OH P O H2C O C H F C H H C C OH OH H H C C C N H C O N O H G (i) Name the molecules labelled E, F and G. E ......................................... F ......................................... G ........................................ (3) (ii) Name the part of the cell where RNA nucleotides are combined to form strands of messenger RNA (mRNA). ........................................................................................................................... (1) 32 (b) The table below shows which amino acids are coded for by different codons on mRNA. First position (i) Second position Third position U C A G U phe phe leu leu ser ser ser ser tyr tyr Stop Stop cys cys Stop trp U C A G C leu leu leu leu pro pro pro pro his his gln gln arg arg arg arg U C A G A ile ile ile met thr thr thr thr asn asn lys lys ser ser arg arg U C A G G val val val val ala ala ala ala asp asp glu glu gly gly gly gly U C A G The letters below represent a section of mRNA coding for the enzyme RNA polymerase. Using the table, give the amino acid sequence coded for by this mRNA sequence. UACGUGGAAAGA ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (ii) Name the process that converts the mRNA sequence into a sequence of amino acids. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 7 marks) 33 18. Lactose is a sugar found in human milk. (a) Lactose is a disaccharide that can be hydrolysed to its two monosaccharides, galactose and glucose. (i) The diagram below shows lactose being hydrolysed. Complete the diagram by drawing the missing components of the monosaccharide galactose in the left-hand box and the monosaccharide glucose in the right-hand box. Lactose CH 2 OH HO CH 2 OH O H H O H H O H OH H H OH CH 2 OH H OH H H OH OH CH 2 OH O Galactose O Glucose (2) (ii) Explain the term hydrolysis. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) 34 (b) Galactosaemia is a rare and potentially serious inherited condition. It is caused by a recessive allele that reduces the ability of the body to break down galactose. A couple is expecting a second child. Neither parent has galactosaemia but their first child does have galactosaemia. (i) Using the symbols G and g, complete the genetic diagram below to show the probability of the couple’s second child not having galactosaemia. Parents’ genotypes .......................................... .......................................... Parents’ gametes Possible genotypes of second child .................. .................. .................. .................. Probability of their second child not having galactosaemia ............................. (3) (ii) The couple wanted confirmation that their second unborn child did not have galactosaemia. To do this, fetal cells were taken, the DNA extracted and the alleles associated with galactosaemia were sequenced. A mutation was found in one of these alleles but the protein produced by this allele was the same as the protein produced by the normal allele. The couple were told this could be explained by the degenerate nature of the genetic code. Explain how the degenerate nature of the genetic code could allow the mutated allele to produce the same protein as a normal allele. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) 35 (iii) Outline the ethical issues related to genetic screening of a fetus for inherited disorders such as galactosaemia. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 12 marks) 19. Amino acids are coded for by one or more DNA triplet codons. The table below shows some amino acids found in human proteins and their corresponding DNA triplet codons. A DNA triplet codon for the stop signal is also shown. Amino acid Triplet codons Threonine TGA TGG TGT Glutamine GTT GTC Glycine CCA CCG CCT CCC Arginine TCT Alanine CGG CGC Stop signal ACT The diagram below shows part of a DNA molecule. This part of the DNA molecule is located near the end of a gene. codon 47 T C T codon 48 C G codon 49 G T G G codon 50 G T codon 51 C C C A 36 (a) Give the sequence of amino acids found in the polypeptide chain that is coded for by this part of the DNA strand. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (b) Give the next triplet codon that you would expect to see on this DNA strand if codon 51 coded for the last amino acid in the polypeptide chain. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (c) Complete the diagram below to show the sequence of bases on a molecule of messenger RNA synthesised from this part of the DNA strand. (2) (d) Mutations can occur during DNA replication. (i) Suggest what would happen to the structure of the protein coded for by this DNA molecule if thymine in codon 49 were replaced by cytosine. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) 37 (ii) Suggest what would happen to the structure of the protein coded for by this DNA molecule if adenine replaced the first thymine in codon 47. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 9 marks) 20. Urease is an enzyme which catalyses the breakdown of urea to ammonia and carbon dioxide. An experiment was carried out into the effect of pH on the activity of urease. 10 cm3 of pH 3 buffer solution was mixed with 1 cm3 of urease solution. This mixture was then added to 10 cm3 of urea solution and the concentration of ammonia in the mixture was measured after 60 minutes. This procedure was repeated using buffer solutions of pH 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 and 9. The results are shown in the graph below. 100 80 60 Concentration of ammonia/ arbitrary units 40 20 0 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 pH 38 (a) What do these results suggest is the optimum pH for urease activity? .................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Suggest how the experiment could be modified to determine the optimum pH more accurately. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (1) (c) Explain why no ammonia was produced at pH 3. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (3) (d) Explain why less ammonia is produced at pH 9 than at pH 8. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (2) (e) Describe how this experiment could be modified to determine the effect of enzyme concentration on the activity of urease. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (4) (Total 11 marks) 39 21. The graph below shows the results of an investigation into the effect of substrate concentration on the initial rate of an enzyme-controlled reaction. 0.20 B C Initial 0.15 rate of reaction / mg of products s –1 0.10 0.05 A 0 0 (a) 10 20 30 40 Substrate concentration / mg cm –3 50 60 Suggest two conditions, apart from temperature, that should be kept constant in this investigation. 1 ................................................................................................................................. 2 ................................................................................................................................. (2) (b) Explain why changes in the substrate concentration cause an increase in the rate of reaction between points A and B on the graph. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (2) 40 (c) Suggest why the curve levels off between points B and C. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (2) (d) On the graph on page 6, sketch a curve to show how the results for the investigation would change if it were repeated at a lower temperature. Explain any differences between the two curves. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 9 marks) 22. Read through the following passage about enzymes, then write on the dotted lines the most appropriate word or words to complete the passage. Enzymes can be described as biological .............................................. as they reduce the .......................................... needed for a metabolic reaction to occur. The ........................................... combines with the enzyme at a specific region of the molecule called the ........................................ . The shape of this region can be altered by a change in pH or ................................................ which will ............................................... the rate of the metabolic reaction. (Total 6 marks) 41 23. The graph below shows the results of an experiment to investigate the effect of amylase Leave concentration on the rate of starch breakdown. 90 80 – Rate of starch breakdown / mg min 1 70 – 60 – 50 – 40 – 30 – 20 – 10 – 0– 0 (a) 100 50 150 200 Concentration of amylase / mg cm 3 250 Outline a procedure that could have been used to produce these results. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (4) 42 (b) Explain the effect of amylase concentration on the rate of starch breakdown. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (c) Suggest reasons why the points on the graph do not lie on a straight line. (3) ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (d) Cellulase is another enzyme that breaks the bonds between glucose molecules in a polymer. Explain why adding this enzyme in addition to amylase would have no effect on the rate of starch breakdown. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 12 marks) 43 24. (a) With reference to enzyme activity, explain the meaning of the following terms: Catalyst ................................................................................................................................ ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... Activation energy …….......................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... (4) 44 (b) An investigation was carried out to study the effect of copper sulphate concentrations on the breakdown of cellulose by the enzyme cellulase. Two concentrations of copper sulphate were used. 0.01 mol dm-3 1.00 mol dm-3 Water was used as a control. The results are shown in the graph below. 5 Water 0.01 mol dm –3 copper sulphate Total quantity of cellulose 4 broken down / arbitrary units 1.00 mol dm –3 copper sulphate 3 2 1 0 (i) 0 1 2 3 Time / days 4 5 6 Name the type of reaction that is catalysed by cellulase. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Name the bond that is broken by cellulase. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) 45 (iii) Using the information shown in the graph, describe the effect of copper sulphate on the rate of breakdown of cellulose. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (iv) Copper ions bind to cellulase and cause disulphide bonds to break. Explain the effect of copper ions on the activity of the cellulase. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 12 marks) 46 25. Sucrose is a disaccharide made up from one molecule of glucose bonded to one molecule of fructose. Sucrose needs to be digested by the enzyme sucrase before it can be absorbed into the blood. (a) The diagram below illustrates how the enzyme sucrase may catalyse the breakdown of sucrose into glucose and fructose. Sucrose R Glucose Fructose Q Sucrase Use the diagram to identify: (i) reactant Q ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) the region labelled R ........................................................................................................................... (1) (iii) the name of the bond between the glucose and fructose molecules that is broken by the reaction shown in the diagram. ........................................................................................................................... (1) 47 (b) (i) Explain why sucrase will digest sucrose and not any other disaccharide. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (3) (ii) Name and describe one way that glucose is absorbed across cell membranes. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 8 marks) 26. Proteins are chains of amino acids and have a wide range of functions in living organisms. (a) (i) The diagram below shows part of the general structure of two different amino acids. Complete the diagram to show how these two amino acids can be joined together. H R N—C— H H R O —C—C H OH (1) (ii) Name the bond that is formed between the two amino acids. ........................................................................................................................... (1) 48 (b) Explain how the specific sequence of amino acids in a protein determines its threedimensional structure. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) Enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions within living organisms. The graph below shows the effect of changing enzyme concentration on the rate of reaction. Rate of reaction X Enzyme concentration (i) Explain why increasing the enzyme concentration above point X on the graph does not increase the rate of the reaction further. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) 49 (ii) Outline the practical procedures that could have been used to obtain the results shown on the graph. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (4) (Total 10 marks) 27. (a) Describe the structure of a plant cell wall. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) 50 An experiment was carried out to determine the effect of two enzymes, enzyme A and enzyme B, on the yield of apple juice. An apple was cut into small pieces and blended in a food processor to produce apple pulp. Four samples of apple pulp of equal mass were mixed with various combinations of enzyme A, enzyme B and water, as detailed in the table below. Both enzyme solutions were at the same concentration. Sample number Mixture 1 Apple pulp + 5 cm3 enzyme A + 5 cm3 water 2 Apple pulp + 5 cm3 enzyme B + 5 cm3 water 3 Apple pulp + 5 cm3 enzyme A + 5 cm3 enzyme B 4 Apple pulp + 10 cm3 water The samples were incubated at 30 °C for 15 minutes. Each sample was then placed in a separate filter funnel and the apple juice collected into a measuring cylinder. The volumes of the apple juice collected from each sample are shown in the bar chart below. 40 Volume of apple juice collected / cm3 (b) 30 20 10 0 1 2 3 Sample number 4 51 (i) Suggest why the apple pulp incubated with water only (sample 4) yielded some apple juice. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Describe the effect that enzymes A and B have on the yield of apple juice in samples 1, 2 and 3. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) 52 (iii) Suggest how these enzymes increase the yield of apple juice. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (4) (Total 10 marks) 28. The diagram below illustrates part of a glycogen molecule. CH2OH C H C HO (a) CH2OH O H H OH H C C H OH H C C C O CH2OH O H H OH H C C H OH H C C C O CH2OH O H H OH H C C H OH H C C C O CH2OH O H H OH H C C H OH H C C C O CH2OH O H H OH H C C H OH H C C C O O H OH H C C H OH H C OH State the role of glycogen in the human body. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) 53 (b) An enzyme is used to break the bonds holding the monomers (glucose molecules) together. (i) In the space below draw one of the monomers that would result from this reaction. (2) (ii) Explain why this enzyme will not break the bonds in a protein molecule. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (3) (c) Explain the advantages, to living organisms, of using enzymes in biological reactions. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 8 marks) 54 29. The enzyme pectinase can be used in the commercial process of peeling oranges. In this process, the waxy (lipid) surface of the oranges is first removed. The oranges are then submerged in a solution of pectinase. This enzyme hydrolyses the polysaccharide pectin that holds the cells in the peel together. After about 12 hours in the solution of pectinase, the orange peel falls off the oranges leaving clean segments. (a) (i) Suggest why the waxy surface of the oranges is removed before they are submerged in pectinase. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (ii) Explain why pectinase does not hydrolyse the cellulose found in the orange peel cell walls. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (b) (i) Suggest why chopping up the oranges could speed up hydrolysis. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) 55 (ii) The pectinase shows a small increase in concentration over the 12 hours of the hydrolysis. Suggest why the concentration of the pectinase increases slightly. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 8 marks) 30. (a) Explain what is meant by each of the following terms. (i) Allele ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (ii) Phenotype ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) 56 (b) Manx cats have no tails and have the genotype Mm. Cats with normal tails have the genotype mm. The genotype MM is an example of a lethal genotype and the embryo with this genotype does not develop. In the space below, draw a genetic diagram to find the probability that a kitten produced by crossing two Manx cats will have a normal tail. (3) 57 (c) Siamese cats have light-coloured fur, but with dark-coloured faces, ears, tails and paws. This is due to a temperature-sensitive mutation. As a result of this mutation, the enzyme responsible for the production of the pigment is easily denatured. A Siamese cat Suggest an explanation for the distribution of dark-coloured fur in a Siamese cat. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 10 marks) 58