Introduction to Genetics- Phenotype Genes Complete
advertisement

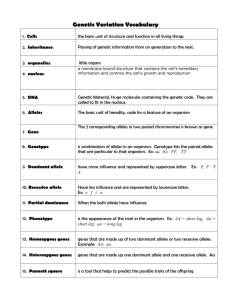
Introduction to Genetics- Phenotype Genes • • Offspring get half of their genes from either parent; inheritance is random Phenotype: traits of an organism (determined by proteins produced) • Phenotype depends on type of inheritance SJCHS Complete Dominance 2 different kinds of alleles • Dominant allele: Determines the phenotype • NOT THE MOST COMMON ALLELE • Wild type: Most common allele • Example • • Thumb extension trait 2 possible alleles- Straight thumb (H), Hitchhiker’s thumb (h) Recessive allele: No affect on phenotype if dominant allele present 1 Example • Example • Everyone has 2 alleles for thumb extension and will have one of the following combinations Example • Hh is heterozygous - phenotype is determined by the dominant allele • Dominant allele is H (straight thumb) • Hh will have a straight thumb HH and hh are homozygous- phenotype is same as genotype • HH - straight thumbs • hh- Hitchhiker’s thumbs Examples • Some genetic disorders caused by dominant alleles, others recessive 2 Incomplete Dominance Incomplete dominance: the combination of two different alleles in a heterozygote • Heterozygote still has 2 alleles, not a new or different allele • Example • Snap dragons 2 alleles for color: red or white • If a flower has one of each allele, phenotype will be pink • Example • • • • Human Hair: 2 alleles 1 allele for curly hair 1 allele for straight hair Heterozygote (1 curly hair allele and 1 straight hair allele) results in wavy hair 3 Multiple Alleles • • • Example • • In rabbits, there are 4 different alleles that control coat color Order of alleles from most dominant to most recessive • Brown, Chinchilla, white with black tips, white Multiple Alleles: Some genes have more than 2 alleles Can have multiple dominant or recessive alleles Codominant: When two dominant alleles are present, both phenotypes are equally expressed Example • Human blood type is determined by carbohydrates on surface of cell • 2 dominant alleles code for A carbohydrate, B carbohydrate • Type AB means person has both carbohydrates (and both dominant alleles) • Type O- no carbohydrates (recessive) 4 Polygenic • Polygenic: A single trait can be influences by more than one gene Example • Bell Pepper color: Controlled by 3 genes Gene 1 controls timing of chlorophyll elimination • Y- early, y normal • Gene 2 controls coloring of pigments • R- red, r-yellow • Gene 3 controls amount of pigments • C- normal, c1, c2 less • Different combinations of alleles result in different colors • 5 X Linked Genes • • X Linked Genes: Genes located on X chromosome X linked genetic disorders are more common in males Example • • • Color Blindness Several X linked genes 20 times more often in males Environment • “Nature versus Nurture”: Does the environment or genetics influence certain traits more? • Studies usually use twins or siblings 6 Behavioral Traits • • Is blood type inherited? YES Behavioral Traits • Is risk taking inherited? Study of unrelated subjects showed that “novelty seeking” is associated with a particular allele • Study of twins found no association between “novelty seeking” and having a particular allele • Behavioral Traits • Is musical skill inherited? “Absolute Pitch”: The ability to name a note after hearing the sound Study showed that absolute pitch occurs in more often in people with certain genetic disorders are more likely to have it • Study showed that those who grew up in East Asia were more likely to have it • Study showed that professional musicians with early musical training were more likely to have absolute pitch as opposed to professional musicians without early musical training • • Behavioral Traits • Is intelligence inherited? Studies show that identical twins not raised by the same family tend to have similar IQs (more so than non-identical siblings raised by the same family) • Studies have shown that children adopted into families that value education will have increased IQ scores as opposed to children adopted into families that do not value education • 7 Environment • Some traits not influenced by environment, others are a mix of environment and genetics Phenotype • Inheritance of most traits are complex (a combination of several types of phenotype inheritance) Example • • • • • Human eye color Iris- colored part of eye Made of cells containing a pigment holding organelle (melanosome) Amount of pigment in melanosomes and number of melanosomes determine eye color Pigments act the same as pigments in plants (light that is reflected is the color we see) 8 Example • • Eye color cannot be explained by simple complete dominance Humans have many eye color genes (polygenic) that produce different pigments • Order of alleles from most dominant to most recessive • Brown, Green, Blue • 2 allele for blue eyes (multiple alleles) • Genes located different chromosomes Example • When considering inheritance of eye color, must consider both genes that control eye color and if parents are heterozygous or homozygous for a trait Example • Unanswered questions Number of genes that control eye color Amount of pigment produced can change over time (eye color can change in a person’s lifetime) • Grey, hazel eye color inheritance cannot be explained • Parents with blue eyes can produce offspring with green or brown eyes • • 9