Stress and Strain - Academic Home Page
advertisement

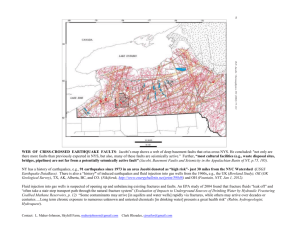
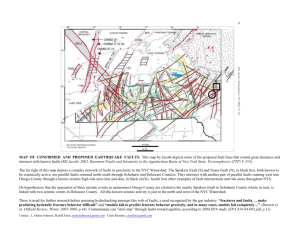
Faults BASIC DEFINITIONS ► FAULT: A surface or narrow zone along which one side has moved relative to the other. A fault may form through either brittle (fractures) or ductile (shear) deformation. Faults are classified based upon the orientation of the displacement vector along the fault surface. DIP-SLIP FAULTS: Faults along which the movement is approximately parallel to the dip STRIKE-SLIP FAULTS: Faults along which the movement is approximately parallel to the strike OBLIQUE-SLIP FAULTS: Faults along which the movement is inclined to both the strike and dip of the fault surface. It may be described as the sum of a strike-slip and a dip-slip vector HANGING WALL vs FOOTWALL ► ► A fault divides rock into two fault blocks For any inclined fault, the block above the fault is the hanging wall block, and the block below the fault is the footwall block www.data.scec.org/Module/footnt02.html CLASSIFICATION of DIP-SLIP FAULTS ► NORMAL FAULTS: Dip-slip faults on which the hanging wall moves down relative to the footwall Place younger rocks on older rocks May result in omission of strata Form in regions of lateral extension www.data.scec.org/ Module/footnt02.html EXAMPLES OF NORMAL FAULTS Outcrop scale normal faults Conjugate Normal Faults, Canyonlands National Park darkwing.uoregon.edu/~millerm/conjN1.html Normal Fault Scarps, Turkey www.msnucleus.org/.../pt/hazards/4/pth4_1a.html EXAMPLES OF NORMAL FAULTS FW FW HW FW HW Outcrop scale normal faults HW FW HW HW FW Conjugate Normal Faults, Canyonlands National Park darkwing.uoregon.edu/~millerm/conjN1.html Normal Fault Scarps, Turkey www.msnucleus.org/.../pt/hazards/4/pth4_1a.html CLASSIFICATION of DIP-SLIP FAULTS ► THRUST or REVERSE FAULTS: Dip-slip faults on which the hanging wall moves up relative to the footwall Place older rocks on younger rocks May result in repetition of strata Form in regions of lateral compression www.data.scec.org/ Module/footnt02.html EXAMPLES OF THRUST FAULTS Outcrop scale thrust faults www.pitt.edu/.../7Structures/ReverseFaults.html Thrust Fault in Concrete from 1964 Quake, Anchorage, Alaska www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/.../alaska/0709log.html Thrust Fault in Sediments www001.upp.so-net.ne.jp/fl-fg/05-01.htm EXAMPLES OF THRUST FAULTS Outcrop scale thrust faults www.pitt.edu/.../7Structures/ReverseFaults.html HW FW HW FW HW Thrust Fault in Concrete from 1964 Quake, Anchorage, Alaska www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/.../alaska/0709log.html FW Thrust Fault in Sediments www001.upp.so-net.ne.jp/fl-fg/05-01.htm CLASSIFICATION of STRIKE-SLIP FAULTS ► RIGHT-LATERAL (DEXTRAL) FAULTS: Strike-slip faults across which the block moves to the right ► LEFT-LATERAL (SINISTRAL) FAULTS: Strike-slip faults across which the block moves to the right EXAMPLES OF STRIKE-SLIP FAULTS Right Lateral Fault in Asphalt www.uwsp.edu/.../fault_transform_photo.html San Andreas Fault, CA http://education.usgs.gov/california/ pp1515/chapter2/fig2-21.jpg Right Lateral Slip, Izmit, Turkey, 1999 Quake http://www.geo.uib.no/jordskjelv/ index.php?topic=earthquakes&lang=en EXAMPLES OF STRIKE-SLIP FAULTS Right Lateral Fault in Asphalt www.uwsp.edu/.../fault_transform_photo.html San Andreas Fault, CA http://education.usgs.gov/california/ pp1515/chapter2/fig2-21.jpg Right Lateral Slip, Izmit, Turkey, 1999 Quake http://www.geo.uib.no/jordskjelv/ index.php?topic=earthquakes&lang=en STRATIGRAPHIC INDICATORS OF FAULTS ► Truncation of Units Unconformity? Intrusion? ► Omission of units Unconformity? ► Repetition Folding? of Units PHYSIOGRAPHIC INDICATORS OF FAULTS ► Scarps Terraces? River Valley? ► Linear Valleys Erodable Strata? ► Pull-Apart Basins or Push-Up Ridges http://www.bedford.k12.ny.us/flhs/ science/images/sanandreas1.jpg MESOSCOPIC STRUCTURAL INDICATORS OF FAULTS ► Slickensides ► Drag Folds ► Vein Sets Horizontal Slickensides http://wso.williams.edu/~cgarvin/photos/ slickensides.jpg Drag Fold Associated with Thrust Fault web.umr.edu/.../205-mile_landslides.htm MESOSCOPIC STRUCTURAL INDICATORS OF FAULTS ► Slickensides ► Drag Folds ► Vein Sets Horizontal Slickensides http://wso.williams.edu/~cgarvin/photos/ slickensides.jpg Drag Fold Associated with Thrust Fault web.umr.edu/.../205-mile_landslides.htm Why do certain types of faults have predictable dips? FRACTURE EXPERIMENTS ► To understand the mechanics of fracturing, geologists perform controlled experiments on rock cores ► Rock is wrapped in a metal jacket Provides confining pressure σ2 and σ3 are perpendicular to core length ► Piston presses along the length of the core σ1 is parallel to core length FRACTURE EXPERIMENTS ► Core fractures with a consistent pattern FRACTURE EXPERIMENTS ► Core fractures with a consistent pattern ► Two sets of fractures with an acute angle of approximately 60º between them Conjugate fractures FRACTURE EXPERIMENTS σ1 ► Core fractures with a consistent pattern ► Two sets of fractures with an acute angle of approximately 60º between them Conjugate fractures ► σ1 bisects the acute σ1 angle between the conjugate fractures FRACTURE EXPERIMENTS σ1 ► σ1 bisects the acute angle between the conjugate set ► σ3 bisects the obtuse angle between the conjugate set σ3 ► σ2 runs σ1 parallel to the intersection of the conjugate set ANDERSON’S THEORY OF FAULTING ► The surface of Earth is a “free surface”, that is, it is a surface that cannot support shear stress Shear stress = 0 ► Shear stress = 0 along principal stress planes Principal stress directions must be parallel or perpendicular to a principal stress plane ► The surface of Earth is a principal stress plane At the surface of Earth, the principal stress directions must be parallel or perpendicular to a principal stress plane COMBINING FRACTURE EXPERIMENTS WITH ANDERSON’S THEORY ► σ1 must be either parallel or perpendicular to Earth’s surface ► Fractures form in conjugate sets around σ1 ► The orientation of fractures (faults) will vary with the orientation of σ1 and the other principal stresses ► There are only 3 possible orientations of the principal stresses relative to the Earth’s surface σ1 Vertical… ► Produces fractures/faults that dip at 60º ► Motion is along dip with hanging-wall down ► NORMAL FAULTS σ1 Horizontal, σ3 Vertical… ► Produces fractures/faults that dip at 30º ► Motion is along dip with hanging-wall up ► THRUST FAULTS σ1 Horizontal, σ2 Vertical… ► Produces fractures/faults that dip at 90º ► Motion is along strike ► STRIKE-SLIP FAULTS