The Gas Constant is: R = 8.31 J/mol-K = 8.31x10-3 kJ/mol
advertisement

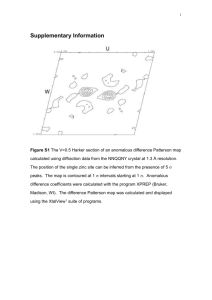
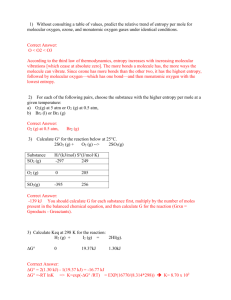
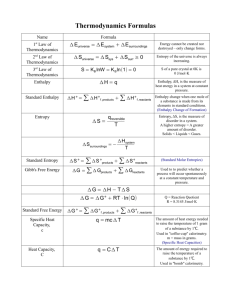
CHEM 1423 - Exam 4 – April 23, 2015 - Version A Name______________________________ The Gas Constant is: R = 8.31 J/mol-K = 8.31x10-3 kJ/mol-K (54) PART I. MULTIPLE CHOICE (Circle the ONE correct answer) 1. Consider the sparingly soluble salt, Magnesium Phosphate, Mg3(PO4)2. In neutral solution, the concentration of Phosphate ions, PO43-, is 8.0x10-6 M. Therefore, the Solubility Product, Ksp is approximately: (A) 1.5x10-24 (B) 1.1x10-25 (C) 1.0x10-27 (D) 6.8x10-22 For #2 - #3: Consider the equilibrium of the sparingly soluble salt, Hg2Br2. The dissociation equilibrium in aqueous solution is: 2 Hg (aq ) 2 Br (aq ) Hg 2 Br2 ( s ) Ksp = 6.4x10-23 2. What is the concentration of bromide ions, [Br-], when Hg2Br2 is dissolved in pure water? (A) 6.3x10-5 M (B) 1.4x10-6 M (C) 4.0x10-6 M (D) 2.8x10-6 M 3. What is the solubility of Hg2Br2 in a solution containing 0.20 M KBr(aq) [a strong electrolyte]? (A) 2.0x10-11 M (B) 8.9x10-12 M (C) 4.0x10-11 M (D) 7.6x10-8 M 4. Which of the following statements is/are correct? (1) (2) (3) (4) The entropy change on condensing a gas is negative The entropy usually increases when a gas is dissolved in a liquid The entropy of CaCO3(s) is higher than the entropy of CO2(g) The entropy generally decreases when a solid dissolves in a liquid (A) 2 & 3 & 4 (B) 1 & 3 (C) 1 & 2 & 3 (D) 1 & 3 & 4 5. Consider the reaction: 2 Mg(s) + O2(g) 2 MgO(s) , Ho < 0. This reaction is: (A) Reactant Favored at all temperatures (B) Product Favored at all temperatures (C) Product Favored at high temperature (D) Product Favored at low temperature Version A For #6 - #8: Consider the reaction: 2 C2H6(g) 2 C2H2(g) + 4 H2(g) For this reaction, So = +466 J/K C2H2(g) C2H6(g) Smo(25 oC) 201 J/mol-K 230 J/mol-K Gfo(25 oC) 209 kJ/mol -33 kJ/mol 6. What is Go for the above reaction [at 25 oC] ? (A) -484 kJ 7. (B) +352 kJ (C) +484 kJ (D) -242 kJ What is the Standard Molar Entropy (Smo) of H2(g) ? (A) +262 J/K (B) +131 J/K (C) -131 J/K (D) 0 J/K 8. What is Ho for the above reaction at 25 oC? (A) +345 kJ (B) -381 kJ (C) -345 kJ (D) +623 kJ 9. For the hypothetical reaction, A F B, Ho = -40. kJ/mol (independent of temperature). The equilibrium constant for the reaction at 300 oC is 1.0x107. What is the entropy change, So for this reaction? (A) +64 J/K (B) +204 J/K (C) -127 J/K (D) -204 J/K CO( g ) 2 H 2 ( g ) , DHo = +91 kJ and 10. For the reaction, CH 3OH ( g ) DSo = +221 J/K. What is the entropy change of the system, DSsys, for the related 2 CH 3OH ( g ) , at 25 oC? reaction, 2 CO( g ) 4 H 2 ( g ) (A) +611 J/K (B) -442 J/K (C) -611 J/K (D) +442 J/K 11. The normal melting point of toluene is -95 oC. The Enthalpy of Fusion of toluene is 6.6 kJ/mol. What is the entropy change of the surroundings when one mole of liquid toluene crystallizes to solid toluene at -95 oC? (A) -37 J/mol-K (B) -48.3 J/mol-K (C) +69 J/mol-K (D) +37 J/mol-K 12. The reaction A B is endergonic at 25 oC and the enthalpy change is -45 kJ. What can be concluded about the entropy change for this reaction? (A) S < -70 J/K (C) S < -150 J/K (B) S > +150 J/K H (C) S T Version A 13. The reaction C D is exergonic at 25 oC and S = -40 J/K. For this reaction, (A) G > 0 & H > 0 (B) G < 0 & H > 0 (C) G > 0 & H < 0 (D) G < 0 & H < 0 14. For the reaction, H2(g) + I2(g) F 2 HI(g), the equilibrium constant is K = 2x10-5. at 300 oC. When the gas pressures are: P(H2) = P(I2) = 3.0 bar, P(HI) = 0.005 bar, the value of DG at 300 oC is approximately: (A) -9.4 kJ (B) -60.9 kJ (C) +112.4 kJ (D) +60.9 kJ 15. The Gibbs Free Energy of Formation of HBr(g) is -53.0 kJ/mol. Therefore, the equilibrium constant, KP, for the reaction, 2 HBr(g) F H2(g) + Br2(g), at 25 oC is approximately: (A) 5.1x10-10 (B) 2.6x10-19 (C) 3.3x10+10 (D) 2.0x10+9 16. In class we discussed the transformation of a protein (e.g. Ribonucleus) between the Native and Random Coil forms with variation in temperature. Consider a hypothetical protein with two native forms, and . For the transition from the to the structure, Ø , the enthalpy and entropy changes are: DHo = -180 kJ/mol and DSo = -490 J/mol-K. For this protein, the ________ form is the more stable one at all temperatures below ______ oC. (A) , 94 oC (B) , 367 oC (C) , 94 oC (D) , 367 oC 17. In class, we discussed how explaining why nonpolar amino acid side groups in a protein are hydrophobic can be modeled by studying the thermodynamics of mixing 2 moles of an alkane such as C4H10(liq) with water; i.e. the process: 2 C4H10(liq) Ø 2 C4H10(aq). We explained that, for this process, (A) DHo < 0 & DSo < 0 (B) DHo > 0 & DSo < 0 (C) DHo < 0 & DSo > 0 (D) DHo > 0 & DSo > 0 18. Regarding the following reaction, which of the statements below is/are NOT Correct? 2 C2H6(g) + 7 O2(g) 4 CO2(g) + 6 H2O(l) (1) O2 is reduced (3) CO2 is oxidized (A) 3 only (2) C2H6 is the reducing agent (4) 28 electrons are transfered (B) 3 & 4 (C) 1 & 2 & 4 (D) 2 & 3 _________________________________________________________________________ PART II. FOUR (4) PROBLEMS : REMEMBER TO SHOW WORK FOR CREDIT The Gas Constant is: R = 8.31 J/mol-K = 8.31x10-3 kJ/mol-K Version A (17) 1. The Enthalpy of Fusion of I2(sol) is DHofus = 7.80 kJ/mol, and its Entropy of Fusion DSofus = 20.2 J/mol-K. (11) (a) Calculate the Entropy change of the universe, DSuniv, for the crystallization (freezing) of three (3) moles of I2 at 90 oC. (6) (b) Calculate the normal melting point of I2, in oC. Note: The normal melting point is the temperature at which solid and liquid are in equilibrium under standard conditions. (12) 2. For the gas phase reaction, 4 NO2(g) + O2(g) F 2 N2O5(g), at 200 oC, when the pressures are: P(NO2) = P(O2) = 0.30 bar and P(N2O5) = 2.0 bar, the Gibbs Free Energy Change is DG = +18.5 kJ. Calculate the equilibrium constant, KP, for this reaction at 200 oC. (6) Write a balanced half reaction in aqueous Basic solution for the reaction of the BiO3-1 ion to form the Bi3+ ion. 3. (11) 4. Balance the following oxidation-reduction reaction in aqueous Acid solution. CrO42- + Cu Cr(OH)3 + Cu(OH)2 CHEM 1423 - Exam 4 – April 23, 2015 - Version B Name______________________________ The Gas Constant is: R = 8.31 J/mol-K = 8.31x10-3 kJ/mol-K (54) PART I. MULTIPLE CHOICE (Circle the ONE correct answer) 1. Consider the reaction: 2 Mg(s) + O2(g) 2 MgO(s) , Ho < 0. This reaction is: (A) Reactant Favored at all temperatures (B) Product Favored at all temperatures (C) Product Favored at low temperature (D) Product Favored at high temperature 2. Which of the following statements is/are correct? (1) (2) (3) (4) The entropy change on condensing a gas is negative The entropy usually increases when a gas is dissolved in a liquid The entropy of CaCO3(s) is higher than the entropy of CO2(g) The entropy generally decreases when a solid dissolves in a liquid (A) 2 & 3 & 4 (B) 1 & 2 & 3 (C) 1 & 3 (D) 1 & 3 & 4 For #3 - #4: Consider the equilibrium of the sparingly soluble salt, Hg2Br2. The dissociation equilibrium in aqueous solution is: 2 Hg (aq ) 2 Br (aq ) Hg 2 Br2 ( s ) Ksp = 6.4x10-23 3. What is the concentration of bromide ions, [Br-], when Hg2Br2 is dissolved in pure water? (A) 6.3x10-5 M (B) 2.8x10-6 M (C) 4.0x10-6 M (D) 1.4x10-6 M 4. What is the solubility of Hg2Br2 in a solution containing 0.20 M KBr(aq) [a strong electrolyte]? (A) 2.0x10-11 M (B) 8.9x10-12 M (C) 4.0x10-11 M (D) 7.6x10-8 M 5. Consider the sparingly soluble salt, Magnesium Phosphate, Mg3(PO4)2. In neutral solution, the concentration of Phosphate ions, PO43-, is 8.0x10-6 M. Therefore, the Solubility Product, Ksp is approximately: (A) 1.5x10-24 (B) 6.8x10-22 (C) 1.0x10-27 (D) 1.1x10-25 Version B 6. For the hypothetical reaction, A F B, Ho = -40. kJ/mol (independent of temperature). The equilibrium constant for the reaction at 300 oC is 1.0x107. What is the entropy change, So for this reaction? (A) +64 J/K (B) +204 J/K (C) -127 J/K (D) -204 J/K For #7 - #9: Consider the reaction: 2 C2H6(g) 2 C2H2(g) + 4 H2(g) For this reaction, So = +466 J/K C2H2(g) C2H6(g) Smo(25 oC) 201 J/mol-K 230 J/mol-K Gfo(25 oC) 209 kJ/mol -33 kJ/mol 7. What is Go for the above reaction [at 25 oC] ? (A) +484 kJ 8. (B) +352 kJ (C) -484 kJ (D) -242 kJ What is the Standard Molar Entropy (Smo) of H2(g) ? (A) -131 J/K (B) +262 J/K (C) +131 J/K (D) 0 J/K 9. What is Ho for the above reaction at 25 oC? (A) -345 kJ (B) +623 kJ (C) -381 kJ (D) +345 kJ CO( g ) 2 H 2 ( g ) , DHo = +91 kJ and 10. For the reaction, CH 3OH ( g ) DSo = +221 J/K. What is the entropy change of the system, DSsys, for the related 2 CH 3OH ( g ) , at 25 oC? reaction, 2 CO( g ) 4 H 2 ( g ) (A) +611 J/K (B) +442 J/K (C) -611 J/K (D) -442 J/K 11. The reaction A B is endergonic at 25 oC and the enthalpy change is -45 kJ. What can be concluded about the entropy change for this reaction? (A) S < -150 J/K (C) S > +150 J/K (B) S > -70 J/K H (C) S T 12. The reaction C D is exergonic at 25 oC and S = -40 J/K. For this reaction, (A) G > 0 & H > 0 (B) G < 0 & H > 0 (C) G > 0 & H < 0 (D) G < 0 & H < 0 Version B 13. The normal melting point of toluene is -95 oC. The Enthalpy of Fusion of toluene is 6.6 kJ/mol. What is the entropy change of the surroundings when one mole of liquid toluene crystallizes to solid toluene at -95 oC? (A) +37 J/mol-K (B) -48.3 J/mol-K (C) +69 J/mol-K (D) -37 J/mol-K 14. The Gibbs Free Energy of Formation of HBr(g) is -53.0 kJ/mol. Therefore, the equilibrium constant, KP, for the reaction, 2 HBr(g) F H2(g) + Br2(g), at 25 oC is approximately: (A) 5.1x10-10 (B) 3.3x10+10 (C) 2.6x10-19 (D) 2.0x10+9 15. For the reaction, H2(g) + I2(g) F 2 HI(g), the equilibrium constant is K = 2x10-5. at 300 oC. When the gas pressures are: P(H2) = P(I2) = 3.0 bar, P(HI) = 0.005 bar, the value of DG at 300 oC is approximately: (A) -60.9 kJ (B) -9.4 kJ (C) +112.4 kJ (D) +60.9 kJ 16. In class, we discussed how explaining why nonpolar amino acid side groups in a protein are hydrophobic can be modeled by studying the thermodynamics of mixing 2 moles of an alkane such as C4H10(liq) with water; i.e. the process: 2 C4H10(liq) Ø 2 C4H10(aq). We explained that, for this process, (A) DHo > 0 & DSo > 0 (B) DHo > 0 & DSo < 0 (C) DHo < 0 & DSo > 0 (D) DHo < 0 & DSo < 0 17. In class we discussed the transformation of a protein (e.g. Ribonucleus) between the Native and Random Coil forms with variation in temperature. Consider a hypothetical protein with two native forms, and . For the transition from the to the structure, Ø , the enthalpy and entropy changes are: DHo = -180 kJ/mol and DSo = -490 J/mol-K. For this protein, the ________ form is the more stable one at all temperatures below ______ oC. (A) , 94 oC (B) , 367 oC (C) , 94 oC (D) , 367 oC 18. Regarding the following reaction, which of the statements below is/are NOT Correct? 2 C2H6(g) + 7 O2(g) 4 CO2(g) + 6 H2O(l) (1) O2 is reduced (3) CO2 is oxidized (A) 1 & 2 & 4 (2) C2H6 is the reducing agent (4) 28 electrons are transfered (B) 3 & 4 (C) 3 only (D) 2 & 3 _________________________________________________________________________ PART II. FOUR (4) PROBLEMS : REMEMBER TO SHOW WORK FOR CREDIT The Gas Constant is: R = 8.31 J/mol-K = 8.31x10-3 kJ/mol-K Version B (17) 1. The Enthalpy of Fusion of I2(sol) is DHofus = 7.80 kJ/mol, and its Entropy of Fusion DSofus = 20.2 J/mol-K. (11) (a) Calculate the Entropy change of the universe, DSuniv, for the crystallization (freezing) of three (3) moles of I2 at 90 oC. (6) (b) Calculate the normal melting point of I2, in oC. Note: The normal melting point is the temperature at which solid and liquid are in equilibrium under standard conditions. (12) 2. For the gas phase reaction, 4 NO2(g) + O2(g) F 2 N2O5(g), at 200 oC, when the pressures are: P(NO2) = P(O2) = 0.30 bar and P(N2O5) = 2.0 bar, the Gibbs Free Energy Change is DG = +18.5 kJ. Calculate the equilibrium constant, KP, for this reaction at 200 oC. (6) Write a balanced half reaction in aqueous Basic solution for the reaction of the BiO3-1 ion to form the Bi3+ ion. 3. (11) 4. Balance the following oxidation-reduction reaction in aqueous Acid solution. CrO42- + Cu Cr(OH)3 + Cu(OH)2