Accelerating Two Masses Vernier Without A Force Sensor
advertisement

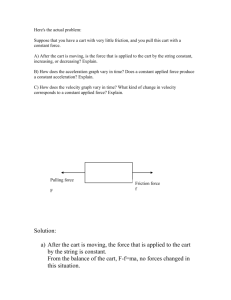
Physics HS/Science Unit: 04 Lesson: 01 Accelerating Two Masses (Vernier without a Force Sensor) Introduction: This lab activity is intended to provide additional experience with Newton’s second law. The basic set up is shown in the figure below, where a frictionless cart is pulled on a horizontal surface by a weight hanging over the edge of the table. The motion of the cart is monitored with a motion detector attached to a computer. This arrangement can be considered as two separate masses moving in two different directions (horizontal and vertical), with one mass pulling the other and joined by a string transferring the force from one to another. However, the analysis can be simplified by considering that both masses move together as a single system, reducing the motion to a single dimension. This motion is that of a single system with mass equal to the total mass being accelerated. In this analysis, the string tension is an internal force and, thus, is not part of the analysis to find the acceleration of the system. If the tension in the string is known, it can be considered as an external force to each of the accelerating masses and Newton’s second law checked for that particular mass (cart or hanging mass). Materials: computer, motion detector, frictionless cart and track, pulley, mass hanger and masses Procedure: 1. Measure the mass of the cart and the mass hanger. Record the information on the Lab Report sheet. 2. Set the cart on a level track, attach a string to the cart and attach the other end of the string to the mass hanger over the pulley as shown. Attach the motion detector to the computer. 3. Load the program “Logger Pro”, and confirm that the program is functioning 4. Place a 200 gram mass on the mass hanger. With the cart approximately 0.5 meters from the motion detector held in place, start the data collection and then release the cart. Stop the experiment when the cart has accelerated for an appropriate distance. 5. Using the “examine” tool” find the acceleration value from the graph while the cart was accelerating. Record these values in the space provided on the data sheet. 6. Fill in the remaining blanks, and answer the questions on the Lab Report. ©2012, TESCCC 08/16/12 page 1 of 2 Physics HS/Science Unit: 04 Lesson: 01 Accelerating Two Masses (Lab Report) Mass of cart ________________ kg Mass of empty “mass hanger” __________________ kg Motion of Total System: Total mass of cart and hanger kg Weight of loaded hanger (external force) N Acceleration of cart and mass hanger m/s2 Total mass times acceleration N Create a free-body diagram of the entire system of two masses with the motion represented in the “x” direction. The sketch of the two-mass system should guide your diagram. Draw the diagram here. Analysis: The net external force on this total system is the weight of the loaded mass hanger, and the mass being accelerated is the mass of the cart and the loaded hanger. This will also be the tension in the string when the cart is in a fixed position. Roughly compare the following quantities, and explain their difference and similarity. Give measurements and estimated error values. Total mass times acceleration ____________________ N Weight of loaded hanger ________________________ N Motion of Cart as a System: Consider the cart as a separate system. Describe how Newton’s second law describes the motion of the cart as a system with the string as an external force. Include a free-body diagram. ©2012, TESCCC 08/16/12 page 2 of 2