Pre Algebra Units and Topics
advertisement

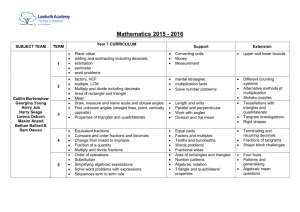
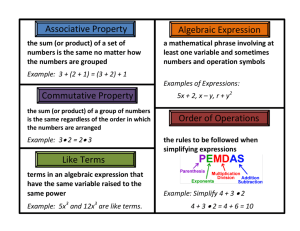
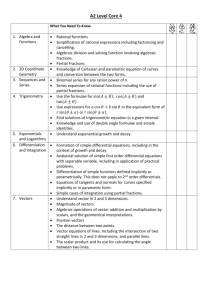
Pre Algebra Units and Topics Number Theory Unit 1. Divisibility Divisibility Laws for numbers from1 to 10 Factors and multiples of algebraic terms (review numeric terms) Prime numbers, prime factors, relatively prime numbers Prime factorisation of algebraic terms (review numeric terms) GCF, LCM of numeric and algebraic terms using prime factorisation Application of LCM and HCF eg word problems using HCF and LCM) 2. Square and Square Roots Review squares of numbers from -20 to 20 and 25, perfect squares, use of the radical sign, squares and square roots of multiples of ten, decimal fractions Estimating the square root of any number Generalising and using the rules for squaring or finding the square root of a product or a fraction Solving equations with squares and square roots Representing and using numbers in rational forms (surds) Cubes of numbers from1 to5. 3. Exponents Review operation rules for numbers and algebraic terms with exponents Write numbers and algebraic terms as positive and negative powers Multiply and divide algebraic terms with positive and negative exponents Problem Solving using exponents 4. Scientific Notation Review writing large numbers and decimals in scientific notation form Multiplying, dividing, adding and subtracting numbers and algebraic terms written in scientific notation 5. Rational and irrational numbers Defining and recognising different sets of numbers Recognising and differentiating between rational and irrational numbers Proofing that a number is rational or irrational number. Algebra Simplification of expressions Adding and subtracting like terms with powers e.g. 9xy2 + 2x2y – 12xy2 + x2y Using the distributive property e.g. 2a2b – 4a(ab + 3ab2) – 4(ab)2+ 1/a(4a3b +a2b2) Multiplying and dividing algebraic terms e.g. 7ab x 2a3b2 Simplifying algebraic fractions Multiplying algebraic fractions e.g. 2x3b . 15a5b 5a 2x2b3 Adding and subtracting algebraic fractions e.g.2ab + 9b x a Dividing fractions e.g. 2x3b 12x5b 5a 25a2 Factorization Solving Equations and Inequalities Solving simple two step equations e.g. 4x + 19 = -7 Solving equations with simplification first sometimes using the distributive property e.g. 1 – 2(x + 6) – 9x = 24 Solving equations with the unknown on both sides e.g. x – 6 = -4x + 13 Solving inequalities including with the unknown on both sides of the inequality e.g. 7x – 2(x +12) > -4x +8 Solving inequalities with negative coefficient of the variable -4x + 7 < 34 Representing the solution of an inequality on a number line and on a graph Solving word problems for equations and inequalities. Solving for a variable (subject of the formula) e.g. T = r2l (l) Solving for a variable in word problems Solving simultaneous equations By elimination By substitution Substitution In expressions In formulae In word problems Relations and Functions Introduction to relations and functions Representing relations and functions as ordered pairs, on mapping diagram, graphs domain and range Function notation Coordinate Geometry Graphing on the coordinate plane Linear function Symmetry and reflection The Square Function Geometry Definition of one, two and three dimensions Review of units Angles relationship with algebra variables including between parallel lines Constructing and bisecting angles Naming polygons Types of polygons – regular, irregular, convex, concave Sum of the interior and exterior angles of a convex polygon Properties of different types of triangles and quadrilaterals Types of triangles Unknown angles in a triangle Pythagorean Theorem Congruent and Similar Triangles Constructing Triangles Angle- Side relationship in Triangles Relationship between the sides of a triangle Angle relationships in various quadrilaterals Parts of a circle Perimeter of compound shapes Using perimeter to solve problems with unknown lengths and arcs Area of triangles Using area of triangles to find unknown lengths and quantities Area of quadrilaterals Using area of quadrilaterals to find unknown lengths and quantities Using area of a circle to find unknown lengths and arc length Area of compound shapes Properties of polyhedrons (right and oblique), cylinders, cones and spheres Angles Polygons Circles Perimeter Area Solids Surface area of solids Determine the surface area of prisms, pyramids, cylinder, cones and spheres (face or net) Using surface area to find unknown lengths and arcs Volume of solids Determine the volume of prisms, pyramids, cylinder, cones and spheres Using volume to find unknown lengths and arcs Statistics Organizing data - frequency, tables, line plot, stem and leaf Representing data in graphical form- Bar Graphs, Histograms, Pie Chart, Scatter Plots, Line Graphs, Box and Whiskers Interpreting data – Central tendencies, quartiles, percentiles, interpreting information from different graphs, appropriate use of different types of graph, misrepresentation of graphs, predicting trends from graphs, making decisions based on an statistical data