http://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/25_345.html Hazardous Areas
advertisement
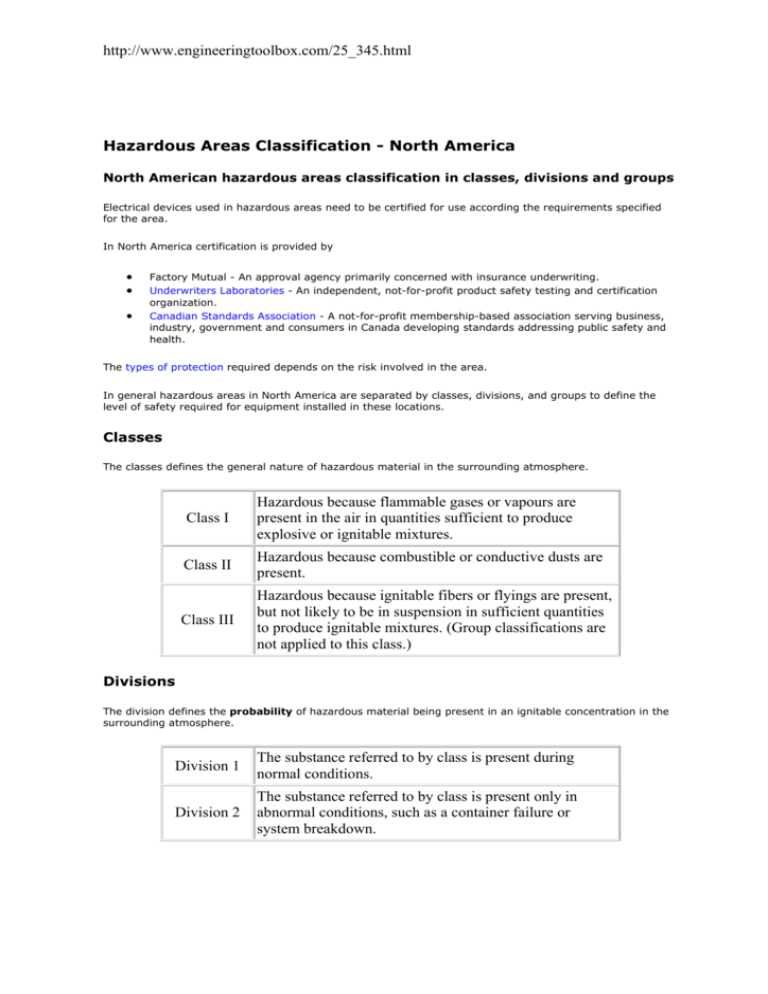
http://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/25_345.html Hazardous Areas Classification - North America North American hazardous areas classification in classes, divisions and groups Electrical devices used in hazardous areas need to be certified for use according the requirements specified for the area. In North America certification is provided by • • • Factory Mutual - An approval agency primarily concerned with insurance underwriting. Underwriters Laboratories - An independent, not-for-profit product safety testing and certification organization. Canadian Standards Association - A not-for-profit membership-based association serving business, industry, government and consumers in Canada developing standards addressing public safety and health. The types of protection required depends on the risk involved in the area. In general hazardous areas in North America are separated by classes, divisions, and groups to define the level of safety required for equipment installed in these locations. Classes The classes defines the general nature of hazardous material in the surrounding atmosphere. Class I Hazardous because flammable gases or vapours are present in the air in quantities sufficient to produce explosive or ignitable mixtures. Class II Hazardous because combustible or conductive dusts are present. Class III Hazardous because ignitable fibers or flyings are present, but not likely to be in suspension in sufficient quantities to produce ignitable mixtures. (Group classifications are not applied to this class.) Divisions The division defines the probability of hazardous material being present in an ignitable concentration in the surrounding atmosphere. Division 1 The substance referred to by class is present during normal conditions. Division 2 The substance referred to by class is present only in abnormal conditions, such as a container failure or system breakdown. http://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/25_345.html Groups The group defines the hazardous material in the surrounding atmosphere. Group A Acetylene Group B Hydrogen, fuel and combustible process gases containing more than 30% hydrogen by volume or gases of equivalent hazard such as butadiene, ethylene, oxide, propylene oxide and acrolein. Group C Ethyl and ethylene or gases of equivalent hazard. Group D Gasoline, acetone, ammonia, benzene, butane, cyclopropane, ethanol, hexane, methanol, methane, natural gas, naphtha, propane or gases of equivalent hazard. Group E Combustible metal dusts, including aluminum, magnesium and their commercial alloys or other combustible dusts whose particle size, abrasiveness and conductivity present similar hazards in connection with electrical equipment. Group F Carbonaceous dusts, coal black, charcoal, coal or coke dusts that have more than 8% total entrapped volatiles or dusts that have been sesitized by other material so they present an explosion hazard. Group G Flour dust, grain, wood, plastic and chemicals. The specific hazardous materials within each group and their automatic ignition temperatures can be found in Article 500 of the National Electrical Code and in NFPA 497. Group A, B, C and D apply to class I locations. Group E, F and G apply to class II locations. Temperature Code A mixture of hazardous gases and air may ignite in contact with a hot surface. The condition for ignition depends on several factors as surface area, temperature and concentration of gas. Equipment approved receives a temperature code indicating the maximum surface temperature of the equipment. http://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/25_345.html Temperature Code Maximum Surface Temperature o F o C T1 842 450 T2 572 300 T2A 536 280 T2B 500 260 T2C 446 230 T2D 419 215 T3 392 200 T3A 356 180 T3B 329 165 T3C 320 160 T4 275 135 T4A 248 120 T5 212 100 T6 185 85 Equipment that not exceed a maximum surface temperature of 212 oF (104 oF ambient temperature) is not required to be marked with a temperature code (NEC). Recommended reading for this topic: • • • • • • • • National Electrical Code, NFPA 70, Chapter 5, Article 500 29 CFR 1910 Subpart S, Electrical 1910.307 NFPA 497, "Classification of Gases, Vapors, and Dusts for Electrical Equipment in Hazardous Classified Locations" NFPA Handbook, "Electrical Installations in Hazardous Locations, " by P. J. Schram and M. W. Earley NFPA 70E, Chapter 5, "Hazardous (Classified) Locations" NFPA 325, "Fire Hazard Properties of Flammable Liquids, Gases, and Volatile Solids" ANSI/UL 913, "Intrinsically Safe Apparatus" NFPA 496, "Purged and Pressurized Enclosure for Electrical Equipment in Hazardous Locations."