Final Review Outline – US Gov 14-15
advertisement

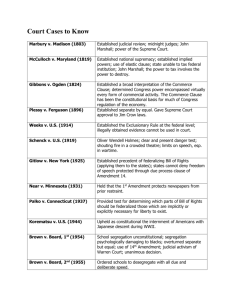
U.S. Government 2014-15 Final Exam Outline Below is an outline of the main topics and subtopics we have covered during the 2nd semester. This IS NOT meant to be an exhaustive list of terms, ideas, or anything of the sort. It is meant simply to help guide your studying. Everything from BOTH the reading and from class is “fair game” for the exam. I encourage everyone to work your way through this outline in light of the reading assignments for each unit/section. Consult the wiki and Edublogs page for the relevant reading assignments! Do not assume that something won’t appear on the final exam simply because it hasn’t appeared on tests thus far. At the same time, there shouldn’t be any surprises, assuming you have completed all the reading and followed class discussions throughout the semester. ** I have also included a list of key ideas from the 1st semester that overlap with 2nd semester topics. You are responsible for these, particularly when they intersect with 2nd semester topics. Topic Outline Key topics/ideas from 1st semester • Separation of Powers/Checks & balances • Federalism - Federal vs. state powers - the 10th Amendment & the Supremacy Clause - Commerce Clause - Obligations between & among states - Full Faith and Credit Clause - Privileges and Immunities Clause - “Cooperative” Federalism - grants in aid, block grants, conditional funding • Constitutional Amendments • Constitutional interpretation: strict vs. loose • Congress - House vs. Senate - purpose, constituency, size & length of terms, structure & control - Legislative process - House vs. Senate: rules, debate, process - • • Influences on decision-making - constituency, interest groups, party, logrolling - Additional congressional powers - advice & consent, impeachment - Pork barrel spending/earmarks The Presidency - Pres. powers: expressed, inherent, delegated - Resources of the president - Vice Presidency, First Lady, Cabinet, White House Staff - Presidential relationships - with Congress: divided vs. unified government - with the public: popular mobilization, rhetoric / persuasion, public appearances / media The Federal Bureaucracy - Roles of agencies - rulemaking & administrative adjudication - Controlling/Reducing the bureaucracy - termination, de-regulation, devolution, privatization • The Federal Judiciary - Court structure and principles - types of courts: trial vs. appellate - types of law: civil vs. criminal - Judicial review - Limitations on courts - “Cases & Controversies” requirement - reliance on other branches of government - Judicial appointments/selection - U.S. Supreme Court - writ of certiorari, “Rule of Four” - oral argument & opinion writing - Judicial philosophy: strict vs. loose interpretation 2nd Semester Topics Civil Liberties • Civil liberties vs. civil rights • Role/force of civil liberties protections - Constitution vs. other laws: judicial review - federal vs. state powers: Supremacy Clause • Application of the Bill of Rights - 14th Amendment & selective incorporation • First Amendment - Establishment Clause - schools vs. elsewhere - separation, accommodation, endorsement - Lemon test - prayer in public schools, holiday displays, 10 Commandments displays - Free Exercise clause - mandatory school attendance, polygamy laws, illegal drug use in religious rituals, health coverage for contraception - Free Speech - • • • • • • political speech & symbolic speech (flag burning, protests at military funerals) - expressive association (Boy Scouts’ case) - exceptions/restrictions: “clear & present danger,” “imminent lawless action,” threats, libel & slander, obscenity - Freedom of the Press - Pentagon Papers, Wikileaks, prior restraint Second Amendment - individual vs. group right - military need vs. personal self-defense Fourth Amendment - searches & seizures, searches in schools - warrants & individualized suspicion (drug tests for welfare, etc.) - reasonable expectation of privacy (thermal imaging case, drug-sniffing dogs, cell phones/technology) - exclusionary rule Fifth Amendment - grand juries, double jeopardy, self-incrimination, Miranda rights - eminent domain/property seizure Sixth Amendment - right to effective assistance of counsel, speedy & public trial - Confrontation Clause Eighth Amendment - cruel, unusual, excessive punishment; evolving standards of decency - death penalty for mentally retarded & juveniles, life imprisonment for non-homicide crimes, “three strikes” laws - Guantanamo Bay prison/cases Right to Privacy - source, interpretation birth control, abortion, same-sex sexual behavior assisted suicide / right to die Civil Rights • Political, economic, legal, social equality • From Plessy v. Ferguson to Brown v. Board - strategy of NAACP, opinion of the Court • Implementing desegregation - de facto vs. de jure segregation - busing and affirmative action - Boston bus riots, Seattle school busing case, college admissions (Grutter & Gratz v. Bollinger) • Civil Rights Legislation - Civil Rights Act of 1964, Voting Rights Act of 1965, Title IX, 24th Amendment • Discrimination/civil rights, beyond race - marriage; gender discrimination - discrimination against homosexuals, ethnic minorities, and aged/disabled - immigrants’ rights Public Opinion & Elections • “Levels” of public opinion - values vs. beliefs - political ideology - liberal vs. conservative - trends of partisanship and ideology in America • Formation of public opinion - Political socialization - family, friends, schools, media, religion - social/demographic groups: race, gender, ethnicity, age - Measuring public opinion • • • • • - scientific polling, sampling - Direction, intensity, and continuity of public opinion The American electorate / suffrage - poll taxes, literacy tests, expansion of the electorate (15th, 19th, 23rd, and 26th Amendments) - voter registration & voter turnout Voter choices & voting systems - methods of voting: plurality/winner-take-all vs. run-off vs. IRV/preference voting vs. proportional representation - The Electoral College - factors: candidate characteristics, party ID, issue voting, prospective & retrospective voting Primary elections/nominations - primary vs. general elections - primaries & caucuses - open vs. closed primaries - frontloading Campaign funding - hard vs. soft money - Federal Election Commission - campaign finance restrictions, and limits on campaign finance restrictions Direct democracy - referenda, initiatives, recall Political Parties & Interest Groups • History and organization of political parties - party systems & realignments • Functions of political parties - recruiting and nominating candidates - facilitating voter choice - funding and supporting candidates • America’s two-party system - • • • • divided vs. unified government plurality/winner-take-all elections (vs. proportional representation) - potential for third parties in American politics Party organization - RNC and DNC / national committees Interest groups and Pluralism - pros and cons of interest groups - interest groups vs. political parties Types of interest groups - economic vs. non-economic groups Organization and tools of interest groups - benefits of joining interest groups - Iron Triangles & issue networks - lobbying, campaign contributions, litigation - Jack Abramoff & lobbying reform Economic, Social, and Foreign Policy • Reasons for government involvement in the economy - property & security, providing public goods - controlling/promoting externalities - solving market failures & promoting competition • Measuring economic success - GDP, GDP growth, GDP per capita - unemployment - debt, deficit, surplus - other measures • Fiscal policy - taxation: progressive vs. regressive vs. flat - redistribution of wealth, promoting policy through taxation (i.e., “sin taxes”) - spending: mandatory vs. discretionary - budget-making process • Monetary policy • • • • • • Federal Reserve System interest rates, open market operations, reserve requirement Social welfare policies - contributory vs. non-contributory - means-tested vs. non-means-tested - pros & cons of welfare policies - threats to Social Security & Medicare Health & Environmental policy - role of the government - pros and cons of universal health care, federal environmental & education regulations - different lobbying and interest group influences Foreign policy goals - security, economic prosperity, humanitarian aid Who shapes foreign policy - Congress vs. president - role of bureaucracy & Cabinet, interest groups Tools of foreign policy - diplomacy - military action & foreign aid - international agencies & the international monetary system Foreign policy approaches - Bush vs. Obama, pre-emptive war - foreign policy and current conflicts (Afghanistan, Iraq, Libya, Syria) - Patriot Act & domestic surveillance