CHM 1321A Assignment 1 Answers
advertisement

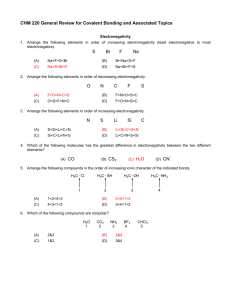
CHM 1321A Assignment 1 Answers 1) Draw Lewis structures, showing all unshared electrons, for the following covalent molecules: (a) CH3NH2 (b) CH2CH2 (c) C2H2 H H C C H H H C C H (d) CH3CH2CHO (e) CH3CH2OH2+ (f) (CH3)3N H H O H C C C H H H H H H C C O H H H H H H H C N C H H C H H H H (g) CH3CN (h) CH3CH(OH)CH3 (i) CH3NCO H H C C N H H H O H H C C C H H H H H H C N C O H (j) CH2CHCH(OH)CH2CO2H (k) NCCH2COCH2CHO (l) CH3CH(CH3)CH2C(CH2CH3)2CHO H H C N H H H H H H H O C C C C C H O H O H H H O H O N C C C C C H H H H H C H H C H H H H O H C C C C C H H C H H H H H C H H C H H (m) (CH3)3C+ (n) CH3CH2O- (o) CH3CHCHCH2CHCHCOOH H H C H H H C C H H C H H H H H C C O H H H H H H H H O H C C C C C C C O H H H (p) HC(O)N(CH3)2 H O C H H C H N C H H H 2) There is a small portion of the periodic table that you must know to do organic chemistry. Construct this from memory including the group numbers, numbers of valence electrons, and electronegativities. Note: Other texts may give slightly different values I H2.1 III IV V VI VIII B2.0 C2.5 N3.0 O3.5 F4.0 Si1.8 P2.1 S2.5 Cl3.0 Br2.8 I2.6 3) Draw structures for (a) Two compounds with the formula C4H10 CH3 H2 C CH3 H3C CH C H2 H3C Butane CH3 2-methylpropane (b) Three compounds with the formula C3H8O2 (There may be other structures, check with your TA if you are not sure) OH H2 C HO OH OH Propane-1,2-diol H2 C HO CH3 C H2 Propane-1,3-diol CH3 CH3 O O Dimethoxymethane 2-Methoxy-ethanol CH3 O Propane-1,1-diol H2 C H3C O C H2 OH CH H3C CH HO C H2 C H2 H2 C H3C OH C H3C CH HO OH CH3 Propane-2,2-diol 1-Methoxyethanol (c) Two compounds with the formula C2H7N H2 C H N NH2 H3C H3C ethylamine CH3 N,N-dimethylamine (d) Five compounds of formula C3H6O O H2 C O C H3C Propanal CH3 Propan-2-one H OH H C H C OH C H2 H2C C H3C OH H3C Prop-2-en-1-ol C H Propen-1-ol H2C O H2C CH2 Propen-2-ol CH3 H2 C O H2C Oxacyclobutane C H2C CH CH3 Methyloxacyclopropane H2C CH OH Cyclopropanol 4) Name all the compounds in Question 3. Answers in Red. 5) Show the direction of the dipole moments of the following bonds. Predict whether the dipole is relatively large or small. δ+ δ δ+ δ δ+ δ+ δδC Cl δ δ (b) C-H (a) C-Cl - C + B C C H δ- δ N H N (c) C-N C O (d) C-O + (e) C-B δ- δ+ δ δ O H C Br + - (f) N-H (g) O-H (h) C-Br 6) Draw the important resonance forms and show the resonance hybrid structures for the following: (a) O C H3C H3C (b) H3C H3C O C O C O C (c) H3C H3C (d) CH3 CH3 H3C O C δ− O CH3 H3C δ+ CH3 CH2 O C CH2 O C O C H3C CH2 insignificant H3C O C δ− O CH2 H3C NH2 NH2 H3C O C NH2 H3C O C δ− O δ C H3C NH2 δ+ + NH2 OH CH3 C H3C C H2 H3C O C δ− CH2 H C H2 CH3 O H CH3 C C H3C H2 δ+ H O H3C C δ+ H 2 CH3 S H2C CH H2C CH2 (e) S H2C CH H2C CH2 (f) H C H2C H2C C H2 H C H2C H2C C CH2 H C H2C H2C (g) H2C H2C (h) C H2 H C C CH2 H C H2C H2C C H2 CH2 C CH2 H2C H2C Hδ- δCH2 C C CH2 C H2 H2C H2C H C C H2 CH2 C CH2 H2C H2C Hδ+ δ+ CH2 C C CH2 C H2 CH3 N H2C CH3 CH3 N H2C CH3 (i) δ+ H2C C H2C CH2 CH2 C CH2 CH2 C H2 H2C C H2C CH2 CH2 C CH2 CH2 C H2 δ+ S S octets full - no resonance possible CH3NO2 H3C O N O +2 N H3C O O H3C O N δ− O δ N O H3C δ− + O insignificant (j) CH3COOH H3C O C O H H3C O C O H H3C O C O H δ− O δ C H O H3C δ+ + 7) For the following resonance forms, label the major and minor resonance forms, and show which ones are of equal energy. Justify your choices. (a) H2 H3C C C N H H3C C C N Minor Major All atoms have a full Octet. In the second structure, the negative charge is located on the more electronegative atom. (b) O C H3C C H H C CH3 H3C Minor O C C H H C H3C CH3 O C H C C H CH3 Major In the Major resonance structure, all atoms have a full octet, and none are charged. In the minor resonance form, one carbon is lacking an octet, and there is a large separation between positive and negative charges. The middle structure has one carbon lacking an octet, and there is a small separation between positive and negative charges.This structure is intermediate between the other two. (c) H3C O C O C H C H2 CH3 H3C O C C H O C C H2 CH3 H3C O C C H Major Minor O C C H2 CH3 Major All atoms in all structures have a full octet. in the Major (2 equivalent) resonance forms, the negative charge resides on the more electronegative oxygen atom. In the Minor resonance form, the negative charge resides on the less electronegative carbon. (d) H2 C H3C NH2 H3C C NH2 Minor H2 C NH2 H3C C NH2 H2 C NH2 C NH2 Major Major In the Major (2 equivalent) resonance forms, all atoms have an octet (this criterion overides having a positive charge on a more electronegative atom). In the minor resonance form, the positively charged carbon atom is lacking an octet. 8) For each pair of ions, determine which is more stable. Justify your answer in each case. a) (a) H3C H C CH3 or H3C H C OCH3 H3C H C OCH3 Delocalization with the lone pairs of the oxygen stabilizes the second compound. b) H H H2C C C CH3 H H2 H2C C C CH2 or H H H2C C C CH3 Delocalization with the electrons in the double bond stabilizes the first compound. In the second compound, the double bond is too far away. The CH2 carbon has no lone pairs to donate to the positively charged carbon. c) H2 C CH3 or H2 C C N H 2C C N Delocalization with the lone pairs of the nitrogen stabilizes the second compound. d) H2 C H2 C CH2 H2C C H2C CH CH2 CH H2C or H2C C H2 CH C H H2 C CH2 C H2C H2C CH C H2 Delocalization with the electrons in the double bond stabilizes the first compound. In the second compound, the double bond is too far away. The CH2 carbon has no lone pairs to donate to the positively charged carbon. e) CH3 H3C CH3 H3C N CH or C C H3C CH3 H3C H3C CH3 CH3 N C H3C CH3 Delocalization with the lone pairs of the nitrogen stabilizes the first compound. f) O C H3C O or CH3CH2O O C H3C O Delocalization with the lone pairs of both oxygens stabilizes the first compound. 9) Draw the shape of s and p orbitals including phasing. Show the resulting shapes following sp, sp2 and sp3 hybridization. p s sp p s s p s p sp2 p p p sp3 10) Draw complete molecular orbital structures for the following molecules using the LCAO method. Label the atomic orbitals used to make bonds. Label the bonds. (b) CH3CO2H (c) CH3CHCHCH2CH3 (d) CH3NO2 (e) CH3CN (a) CH3CH2NH2 (f) CH3OCH3