MA1 Examination Blueprint - Certified General Accountants
advertisement

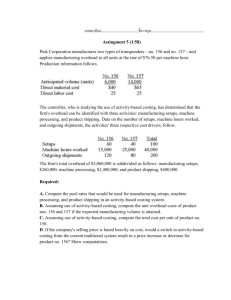
Management Accounting Fundamentals [MA1] Examination Blueprint 2014–2015 Purpose The Management Accounting Fundamentals [MA1] examination has been constructed using an examination blueprint. The blueprint, also referred to as the test specifications, outlines the content areas covered on the examination and the weighting allotted to each content area. This document also lists the topics, the level of competence for each topic, and the related learning objectives. In addition, information is provided on the proportion of each question type presented in the examination (that is, multiple choice, quantitative problems, and so on). Use Students should use the examination blueprint to prepare for the course examination. The blueprint may not include all the topics listed in the course materials. However, students are still responsible for acquiring a broad-based knowledge of all topics not listed in the blueprint since these topics will be tested in assignment and review questions. The topics not listed in the blueprint will also provide students with a greater depth of understanding of the concepts. Examination objectives The objectives of this three-hour, comprehensive examination are to test CGA students on the prerequisite knowledge required for advancement into many courses, and to ensure that students have the broad-based knowledge in management accounting concepts needed to function properly in upperlevel education and certification courses. Examination guidelines for questions i) Question type The following are guidelines on the type of questions and their approximate weightings: Question item Multiple-choice questions Short-answer questions Quantitative problems Qualitative/worksheet-related questions Percent weighting 20% to 30% 10% to 20% 50% to 60% 10% to 20% Several questions will also be decision oriented, where the student is asked to take the role of creditor, investor, manager or auditor and make a recommendation or a decision based on analysis performed. ii) Question content The following table is organized according to content area and provides information on topics, learning objectives, weighting, and levels of competence. Examination sessions: March 2015; June 2015 Page 1 of 11 Management Accounting Fundamentals [MA1] examination blueprint Content area Topics Learning objectives Module 1. Basic concepts of management accounting Weighting (%) 2% to 5% Levels of competence 1.1 The manager’s need for information Describe the role of management accountants in an organization. Level 2 1.2 Comparing financial and managerial accounting Describe the major differences and similarities between financial and managerial accounting. Level 2 1.3 Organizational structure Summarize the purpose of decentralization and line and staff relationships in accomplishing the organization’s objectives.. Level 2 1.4 Ethical standards Summarize the importance of upholding ethical standards. Level 2 1.5 Process management Describe the basic concepts underlying lean production: Six Sigma, enterprise systems, and enterprise risk management. Level 2 1.6 General cost classifications Identify the three basic cost elements involved in the manufacture of a product, and give an example of each. Level 1 1.7 Cost classifications on financial statements Prepare and explain the cost classifications on a manufacturing income statement and a schedule of cost of goods manufactured. Level 1 1.8 Costs for planning, costing, and decision making Compare and contrast types of costs: product and period, variable and fixed, direct and indirect, differential, opportunity, and sunk; and give an example of each. Level 1 Examination sessions: March 2015; June 2015 Page 2 of 11 Content area Topics Learning objectives Module 2. Job-order costing Weighting (%) 3% to 8% Levels of competence 2.1 Job-order costing — Overview Calculate predetermined overhead rates, and explain why estimated overhead costs (rather than actual overhead costs) are used in the costing process. Level 1 2.2 Job-order costing — Flow of costs Prepare journal entries to record the flow of direct materials cost, direct labour cost, and manufacturing overhead cost in a job-order costing system. Level 1 2.3 Application of manufacturing overhead using predetermined overhead rates Apply overhead cost to Work in Process using the predetermined overhead rate. Level 1 2.4 Complications of overhead application Calculate any balance of under- or overapplied overhead cost for a period, and prepare the journal entry needed to close the balance into the appropriate accounts. Level 1 2.5 Job-order costing in service companies Explain the role of job-order costing in service companies. Level 1 2.6 Scrap and rework Prepare journal entries to deal with scrap and rework of unacceptable production. Level 1 2.7 Computer illustration 2.7-1: Cost schedules Prepare worksheet templates to calculate schedules of Cost of Goods Manufactured and Cost of Goods Sold. Level 1 Examination sessions: March 2015; June 2015 Page 3 of 11 Content area Topics Learning objectives Module 3. Process costing Weighting (%) 3% to 8% Levels of competence 3.1 Comparison of job-order and process costing Summarize the major similarities and differences between job-order and process costing. Level 2 3.2 A perspective of process cost flows Prepare journal entries to record the flow of materials, labour, and overhead through a process costing system. Level 1 3.3 Equivalent units of production Explain and calculate the equivalent units of production for both the weighted-average method and the FIFO method. Level 1 3.4 Production report — Weighted-average method Prepare a production report using the weighted-average method. Level 1 3.5 Production report — FIFO method Prepare a production report using the FIFO method, and compare production reports prepared under the weighted-average method and FIFO. Level 1 3.6 Spoilage Calculate the cost of spoilage. Level 1 3.7 Operation costing and flexible manufacturing Describe the conditions under which operation costing is useful to management, and summarize the impact of a flexible manufacturing system on joborder and process costing. Level 2 3.8 Computer illustration 3.8-1: Production report — Weighted-average method and FIFO method Prepare a worksheet that calculates and prepares a production report and cost reconciliation for both weighted-average and FIFO methods, and compare the two methods. Level 1 Examination sessions: March 2015; June 2015 Page 4 of 11 Content area Topics Learning objectives Module 4. Cost behaviour and cost-volume-profit analysis Weighting (%) 15% to 20% Levels of competence 4.1 Variable cost behaviour patterns Identify examples of variable costs, and explain the effect of a change in activity on both total variable costs and per-unit variable costs. Level 1 4.2 Fixed costs Identify examples of fixed costs, and explain the effect of a change in activity on both total fixed costs and fixed costs expressed on a per-unit basis. Level 1 4.3 Analysis of mixed costs Determine the fixed and variable portion of a mixed cost using the high-low method and the regression method. Level 1 4.4 Contribution margin and contribution format income statement Prepare an income statement using the contribution method. Level 1 4.5 Computer illustration 4.5-1: Regression analysis Prepare a worksheet to analyze mixed costs. Level 2 4.6 Basics of cost-volume-profit analysis Explain how changes in activity and changes in variable costs, fixed costs, selling price, and volume affect contribution margin and net income. Level 1 4.7 Break-even analysis Calculate the break-even point by both the equation method and the contribution margin method. Level 1 4.8 CVP considerations in choosing a cost structure Use cost-volume-profit formulas to determine the activity level needed to achieve a desired target net profit figure. Level 1 4.9 Sales mix Calculate the break-even point for a multiple product company, and explain the effects of shifts in the sales mix on contribution margin and the break-even point. Level 1 4.10 Assumptions of CVP analysis Summarize the assumptions made regarding costvolume-profit analysis. Level 2 4.11 Computer illustration 4.11-1: CVP sensitivity analysis Prepare a worksheet to perform a sensitivity analysis on CVP. Level 2 Examination sessions: March 2015; June 2015 Page 5 of 11 Content area Topics Learning objectives Module 5. Activity-based costing and service department costing Weighting (%) 8% to 12% Levels of competence 5.1 Overhead costing methods Explain how activity-based costing differs from traditional costing methods. Level 1 5.2 Design of an activity-based costing system Determine overhead costs and calculate product and customer margins using activity-based costing. Level 1 5.3 Comparison of traditional and ABC costs Describe the benefits and limitations of activity-based costing. Level 2 5.4 Computer illustration 5.4-1: Activity-based costing Prepare a worksheet to compare the effects of allocating manufacturing overhead based on direct labour-hours and activities performed. Level 1 5.5 Guidelines for service department cost allocation Prepare costing schedules to allocate fixed and variable service department costs to other departments using the direct method, the step method, and the reciprocal method. Level 1 5.6 Computer illustration 5.6-1: Step method and direct method of cost allocation Calculate and compare the allocation of costs using the step method and the direct method, and explain the differences between the two methods. Level 1 Examination sessions: March 2015; June 2015 Page 6 of 11 Module 6. Absorption and variable costing and budgeting 14% to 18% 6.1 Absorption and variable costing Explain how absorption costing differs from variable costing, and compute the unit product cost under each method. Level 1 6.2 Absorption and variable costing income statements Prepare income statements using both absorption and variable costing, and reconcile the two net income figures by observing the effect of deferred fixed manufacturing overhead costs. Level 1 6.3 Advantages and disadvantages of absorption and variable costing Explain the advantages and limitations of both the absorption and variable costing methods. Level 1 6.4 Impact of lean production Explain how the use of lean production methods decreases or eliminates the difference in net income reported under the absorption and variable costing methods. Level 1 6.5 Basic framework of budgeting Summarize the purpose and advantages of budgeting, as well as its role in planning and control. Level 2 6.6 Preparing the master budget Prepare the following budgets: sales budget, production budget, direct materials budget, manufacturing overhead budget, selling and administrative expense budget, cash budget, budgeted income statement and balance sheet. Level 1 6.7 Computer illustration 6.7-1: Sales budget and cash collection schedule Prepare a worksheet to conduct a what-if analysis of changes to selling price and sales volume on a sales budget and a schedule of cash collections. Level 1 Flexible budgets Prepare a flexible budget, and explain the advantages of the flexible budget approach over the static budget approach. Level 1 6.8 6.9 Computer illustration 6.9-1: Determining flexible budget and sales volume variances Prepare a worksheet to calculate the flexible budget and sales volume variances. Level 1 Examination sessions: March 2015; June 2015 Page 7 of 11 Module 7. Standard costs for materials, labour, and variable overhead 9% to 12% 7.1 Standard costs — Management by exception Define the term management by exception and describe how it relates to standard costs. Level 2 7.2 Setting standard costs Explain how direct materials standards, direct labour, and variable overhead standards are set. Level 1 7.3 A general model for variance analysis Calculate and interpret the following variances and explain their significance: direct materials price and quantity variance, direct labour-rate and efficiency variances. Level 1 7.4 Variable overhead variances Prepare a variable overhead performance report using the flexible budget to show both spending and efficiency variances. Level 1 7.5 Variance analysis and management by exception Explain how managers would determine whether a variance constitutes an exception that requires their attention. Level 1 7.6 Advantages and disadvantages of standard costs Explain the advantages and disadvantages of using standard costs. Level 1 Examination sessions: March 2015; June 2015 Page 8 of 11 Module 8. Fixed overhead analysis and reporting for control 12% to 16% 8.1 Overhead rates and standard costing Explain the significance of the denominator activity figure in determining the standard cost of a unit of product. Level 1 8.2 Fixed overhead budget and volume variances Calculate and interpret the fixed overhead budget and volume variances. Level 1 8.3 Journal entries to record standard costs and variances Prepare journal entries to record standard costs and variance. Level 2 8.4 Computer illustration 8.4-1: Fixed costs in a flexible budget Prepare a flexible budget to analyze fixed costs and perform a what-if analysis. Level 1 8.5 Full income statement variance analysis Prepare an income statement incorporating variance analysis. Level 1 8.6 Decentralization and segment reporting Prepare a segmented income statement using the contribution format, and explain the difference between traceable fixed costs and common fixed costs. Level 1 8.7 Responsibility centres Summarize the differences between cost centres, profit centres, and investment centres, and explain how performance is measured in each. Level 2 8.8 Return on investment and residual income Calculate and interpret the return on investment and residual income and list the strengths and weaknesses of each method. Level 1 8.9 Balanced Scorecard Explain the use of Balanced Scorecards to assess performance. Level 1 Compute the delivery cycle time, throughput time, manufacturing cycle efficiency, and time spent on non-value-added activities. Level 1 8.10 Other performance measures Examination sessions: March 2015; June 2015 Page 9 of 11 Module 9. Relevant costs for decision making 12% to 16% 9.1 Cost concepts for decision making Identify sunk costs, and explain why they are not relevant in decision making based on a general rule for distinguishing between relevant and irrelevant costs. Level 1 9.2 Adding and dropping product lines or other segments Prepare an analysis showing whether a product line or other organizational segment should be dropped or retained. Level 1 9.3 The make-or-buy decision Explain make-or-buy decisions and prepare a makeor-buy analysis. Level 1 9.4 Computer illustration 9.4-1: Relevant costs Prepare a worksheet to analyze the relevant costs of a decision to retain or close a store. Level 1 9.5 Special orders Prepare an analysis showing whether a special order should be accepted. Level 1 9.6 Joint product costs and the contribution approach Prepare an analysis showing whether joint products should be sold at the split-off point or processed further. Level 1 9.7 Utilization of a constrained resource Determine the most profitable utilization of scarce resources. Level 2 Examination sessions: March 2015; June 2015 Page 10 of 11 Module 10. Pricing and quality in management accounting 2% to 5% 10.1 Cost-plus pricing Calculate the target selling price of a product using cost-plus pricing under the absorption costing and variable costing approaches. Level 1 10.2 Computer illustration 10.2-1: Pricing Prepare a spreadsheet to derive the markup percentage needed to achieve a target return on investment (ROI) and prepare a price quotation under both absorption costing and variable costing approaches. Level 2 10.3 Time and materials pricing Calculate and use billing rates and the material loading charge used in time and material pricing in service organizations. Level 1 10.4 Target costing Explain the rationale of target costing. Level 1 10.5 Costs of quality List the four types of quality costs and describe a quality cost report. Level 2 10.6 Ethical considerations Summarize four standards of ethical conduct to be followed by the management accountant. Level 2 Examination sessions: March 2015; June 2015 Page 11 of 11