Activity Based Costing
advertisement
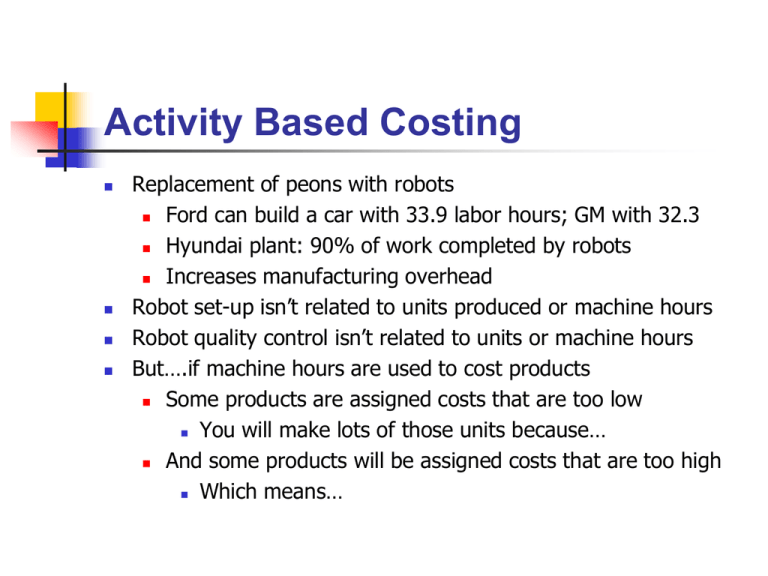
Activity Based Costing Replacement of peons with robots Ford can build a car with 33.9 labor hours; GM with 32.3 Hyundai plant: 90% of work completed by robots Increases manufacturing overhead Robot set-up isn’t related to units produced or machine hours Robot quality control isn’t related to units or machine hours But….if machine hours are used to cost products Some products are assigned costs that are too low You will make lots of those units because… And some products will be assigned costs that are too high Which means… Activity Based Costing Assign overhead costs based on activities (cost drivers) Selecting appropriate cost driver Unit costs: pickles for cheeseburgers Batch costs: cleaning shake machine for vanilla shakes Product costs: ketchup buyer Facility costs: rent and utilities Activity Based Costing Identifying cost drivers What are the activities completed by the enterprise? Possible drivers of costs Product volume Batches Product related: only pizza requires an oven Determine cost of each activity Peons Robots Utilities, rent, etc. Cost of each activity is then used to calculate cost of product based on amount of activities necessary to produce product Activity Based Costing Uses of ABC Customer Costing Whale curve Who is profitable? Who is not? Profit versus potential Banks What customers would McDonalds like to fire? Supplier Costing Price Quality JIT Warranty Liability Service Timeliness Quality Management Prevention costs: prevent poor quality in products or services Reduce failures Engineering and design Training Supplier evaluation Field trials Quality Management Assurance costs: products or services meeting expectations Prevent defective goods from being shipped Inspections Testing Samples Quality Management Internal failure costs: products or services don’t meet expectations Detected before goods are shipped Scrap Rework Shut down production Design changes Quality Management External failure costs: products or services don’t meet expectations After goods are shipped to customers Recalls Lost sales Warranty claims Repairs Lawsuits