pdf, bigger scale
advertisement

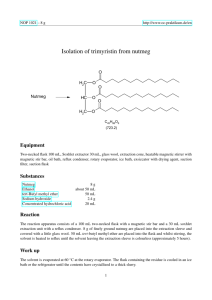
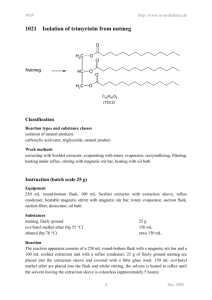
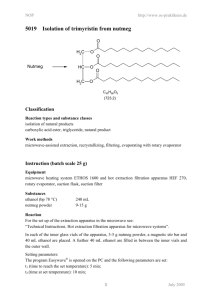
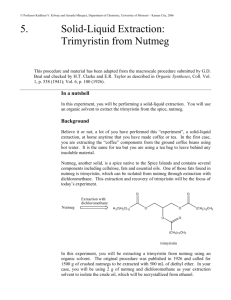
NOP 1021 – 25 g http://www.oc-praktikum.de/en Isolation of trimyristin from nutmeg O Nutmeg H2C O HC O H2C O O O C45H86O6 (723.2) Equipment Two-necked flask 250 mL, Soxhlet extractor 100 mL, glass wool, extraction cone, heatable magnetic stirrer with magnetic stir bar, oil bath, reflux condenser, rotary evaporator, ice bath, exsiccator with drying agent, suction filter, suction flask Substances Nutmeg Ethanol tert-Butyl methyl ether Sodium hydroxide Concentrated hydrochloric acid 25 g about 150 mL 150 mL 2.4 g 20 mL Reaction The reaction apparatus consists of a 250 mL two-necked flask with a magnetic stir bar and a 100 mL soxhlet extraction unit with a reflux condenser. 25 g of finely ground nutmeg are placed into the extraction sleeve and covered with a little glass wool. 150 mL tert-butyl methyl ether are placed into the flask and whilst stirring, the solvent is heated to reflux until the solvent leaving the extraction sleeve is colourless (approximately 5 hours). Kinetics For following the kinetics of the reaction, Eppendorf cups are numbered and their exact weight is noted. After each cycle of the soxhlet extraction, when the maximum amount of solvent is in the flask, the exact time is 1 NOP 1021 – 25 g http://www.oc-praktikum.de/en noted and a 1 mL sample is taken with a plastic transfer pipette and placed into one of the weighted Eppendorf cups located in a heating block at 60 ◦ C. After evaporation of the solvent the dry weight is noted. The weight difference is attributed to the extracted raw product. It is advisable to use a table for collecting the kinetics data according to the following layout: ID time relative time weight empty weight dried weight difference 1 2 ... 09:30 10:04 ... 0 min 34 min ... 0.93 g 0.93 g 0.93 g 1.02 g 0.0 g 0.09 g The weight difference is plotted over time in order to determine the time when approximately 95 % of the product have been extracted. To do this quantitatively, the following extraction kinetics are assumed: m(t) = mmax (1 − e−kt ) (1) Calculate mmax and k by a curve fitting procedure of your choice. Then use the above equation to calculate the time t at which 95 % of mmax have been extracted. Work up The solvent is evaporated at 60 ◦ C at the rotary evaporator. The flask containing the residue is cooled in an ice bath or the refrigerator until the contents have crystallized to a thick slurry. Crude product yield: 12 g The crude product is recrystallized from a small amount of ethanol. Prior to filtering the crystals, the flask is placed into the refrigerator for at least 30 minutes. The crystalline slurry is filtered and the product is dried in an evacuated desiccator over silica gel. Should the crystals not be colourless after the first recrystallization, a second recrystallization is carried out. Yield: 6.5 g; melting point 54-55 ◦ C Hydrolysis of the triglyceride 0.3 g of the product are placed into a 100 mL round-bottom flask. 10 mL of a 6 M sodium hydroxide solution in water are added with the necessary safety precautions. Then, 10 mL ethanol are added and the solution is heated slightly under reflux for one hour. If ethanol is lost, it has to be refilled aproximately to the level at the start of the reaction. The solution is poured into 100 mL water in a large beaker. After addition of 20 mL concentrated hydrochloric acid, a solid white product is formed, which is filtered, washed with 5 mL of water and dried. Analysis of the fatty acids Approximately 10 mg of the product of the hydrolysis are placed in a 100 mL measuring flask. Fill up with 50 mL of methanol and 50 mL of water. Calculate the approximate molarity of the solution, assuming it is pure tetradecanoic acid (synonymous to myristic acid). Calculate the nominal mass of myristic acid and of similar fatty acids that you might expect in your product. What kind of isotope patterns do you expect? 2 NOP 1021 – 25 g http://www.oc-praktikum.de/en A mass spectrum of the dissolved fatty acids in solution is generated with the mass spectrometer with electron spray interface (ESI). Include spectra in positive and negative mode in your report and discuss every peak, even if you are not sure what it is. Duration of the experiment Two days Where can I stop the experiment Before and after the evaporation of the solvent Recycling The evaporated tert-butyl methyl ether and the evaporated ethanol from the mother liquor are collected and redistilled. Suggestions for waste disposal Waste Disposal residue from mother liquor residue from extraction domestic waste domestic waste Pre-lab questions 1. What are the main sources of hazard for health and environment in the experiment? 2. What do you have to keep in mind when setting up the glass apparatus? 3. What are the advantages of a soxhlet extractor in comparison to a simple extraction e.g. in a round-bottom flask? 4. What active substance(s) are in nutmeg? What kind of effects do they have on humans upon ingestion? Where would you expect to find them after the experiment? 5. Please write down the mechanism of the ester hydrolysis. 6. Where does the glycerin go? 7. Answer the questions regarding the MS analysis above. 3