Student name___________ Biochemistry I Homework I Due 9/13/04

Student name___________
Biochemistry I
Homework I
Due 9/13/04
56 points total
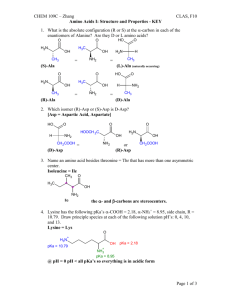
1). 22 points total
T or F (2 points each; if false, briefly state why it is false) .
_ _ __ Biomolecules have directionality, thus they are informational. T
_ _ __ The three-dimensional structures of biomolecules combine the properties of flexibility and stability. T
_ _ __ The low dielectric constant of water makes it unable to screen the interactions between two charged molecules. F- high dielectric; good screener.
_ _ __ Vapor pressure depression is a colligative property of water caused by the presence of solute molecules enhancing liquid water to escape to the vapor phase. F
- caused solute molecules inhibiting water escaping to the vapor phase.
_____ Some amino acid side chains have pKa's in the physiological range, thus helping to regulate biological function. T
_____ Buffers are composed of a weak acid and its conjugate base. T
____ All things being equal, natural processes tend to go from a high entropy to low entropy state. F; from low to high
_____ Concentration has no effect on the net free energy change of biological reactions. F;
∆
G =
∆
G o + RTln [Products]/[Reactants]
_____ The C
α
carbon of all amino acids are chiral. (F; glycine is achiral)
_____ The cyclic nature of proline makes it absorb light in the ultraviolet region, hence making it useful for quantitating proteins. (F; proline is not aromatics).
____ The peptide bond is polar and planar. T
_ _ __ Due to its small side chain, glycine assumes the most restricted space in
Ramachandran plots. (F; most space!)
Student name___________
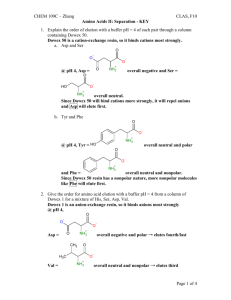
2).
20 points
Given the following polypeptide:
I don't have the figure to insert here.
A). Write down the one letter code for the polypeptide:
CHAMPIE (+7 points)
B). Circle ALL the ionizable groups in the above structure.n-term, c-term, cys, glu, his
(+5 points)
C). Provide the approximate pKa values for the ionizable groups.
(+5 points) ionizable group
C-terminal COOH
COOH of glu
Histidine NH+
Cysteine SH
N-terminal NH
3
+ approximate pKa value
2
4
6
8
9 to 10
D). Calculate the pI of the polypeptide. (+3 points)
C-terminal
COOH pKa ~ 2
Glu R-grp
COOH pKa ~ 4
His R-grp
NH+ pKa ~ 6
Cysteine
Rgrp -SH pKa ~ 8
N-terminal
NH
3
+ pKa ~ 10
Net charge on molecule pH 0 pH 3 pH 5 pH 7 pH 9 pH 11
0
-1
-1
-1
-1
-1
0
0
-1
-1
Net charge on group at a given pH
+1
+1
0
0
+1
0
0
0
-1
-1
0
0
-1
-1
+1
+1
+1
+1
+1
0
+2
+1
0
-1
-2
+3 pI reflects the average of the pKa values that bracket the range where the net charge on the molecule is zero. pI = (4+6)/2 ~ 5
Student name___________
3. 7 points total
The amino acid glycine is often used as the main ingredient of a buffer in biochemical experiments. The amino group of glycine, which has a pKa of 9.3 can exist in either the protonated form (-NH
3
+ ) or the free base (-NH
2
) because of the reversible equilibrium
-NH
3
!" NH
2
+ H + a). In what pH zone can glycine be used as an effective buffer due to its amino group.
8.3 to 9.3; the best buffering is +/- 1 pH unit from the pKa (+2) b). In a 0.1 M solution of glycine at pH 9.0, what fraction of glycine has its amino group in the NH
3
+ form?
Using the Henderson Hasselbach equation, we can calculate the ratio of
[NH2]/[NH3 + ] pH = pKa + log[NH
2
]/[NH
3
+ ] (+1) log[NH
2
]/[NH
3
+ ] = -.3 so [NH
2
]/[NH
3
+ ] = .5 (+1)
__________________________________________________________________
Approach 1:
If we assume the concentration of NH
3
+ = 0.1 M, so we can calculate the concentration of [NH
2
[NH
2
] by
] = .5 x 0.1 M = .05 M (+1)
The fraction of NH
3
is calculated by [NH
3
+ ]/(total concentration of all species) fraction NH
3
+ = [NH
3
+ ]/([NH
3
+ ] + [NH
2
] = .1/.15 = 67% (+2)
__________________________________________________________________
Approach 2:
Alternatively, we know that [NH
2
]/[NH
3
] = 0.5
We can rewrite that as NH2 = 0.5 * [NH
3
]
This means that we have 2 times the moles of NH
3
in solution as we have NH
2
. +1
So if our total moles are 3 moles (i.e., one mole NH
2
plus 2 moles of NH
3
) then fraction NH
3
= 2/3 = 67% +2
Student name___________
4). 7 points total
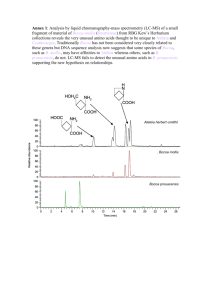
Examine the Ramachandran diagram of the peptide bonds in lysozyme shown in the figure.
The following symbols represent different classes of amino acids: small dots - nonpolar residues; large filled circles - charged polar residues; open circles - neutral polar residues.
For this example, just count the symbols in a given region of the Ramachandran plot.
A). By visual inspection, what is the predominant secondary structure? α -helix (+2)
B). Are there any other identifiable structures? β -sheet (+2)
C). What amino acid is represented by the symbol X. Why? glycine (+1)
It is the smallest amino acid - a simple H - thus there is less conformational hinderance to rotation about the psi-phi angles. It has greater conformational freedom and can exist in the "forbidden" regions of the Ramachandran plot. (+2)